![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Disease is any change in normal state of health or homeostasis.
|
______ is any change in normal state of health or ______.
|
|
|
Etiology is the study of cause of disease.
|
______ is the study of cause of disease.
|
|
|
Pathogens are disease causing organisms.
Primary pathogens can cause disease in healthy individuals. Opportunistic pathogens require an opportunity to cause disease. |
______ are disease causing organisms.
______ an cause disease in healthy individuals. ______ require an opportunity to cause disease. |
|
|
Virulence is the measure of the severity of a disease.
|
______ is the measure of the severity of a disease.
|
|
|
Contamination is the presence of microbes.
|
______ is the presence of microbes.
|
|
|
The term infection is used when talking about microbes and infestation when talking about larger parasites.
|
The term ______ is used when talking about microbes and ______ when talking about larger parasites.
|
|
|
Pathogenesis is the study of how a disease develops.
|
______ is the study of how a disease develops.
|
|
|
Pathology is the study of causes of diseases, how it develops, and the effect of disease on the host.
|
______ is the study of causes of diseases, how it ______, and the ______ of disease on the ______.
|
|
|
Symptoms are completely subjective, unmeasurable, and unapparent.
|
______ are completely subjective, unmeasurable, and unapparent.
|
|
|
Signs of a disease are objective, measurable, and observable changes.
|
______ of a disease are objective, measurable, and observable changes.
|
|
|
Syndrome is the same set of signs and symptoms that happen together.
|
______ is the same set of ______ and ______ that happen together.
|
|
|
Sequelae are the after effects of a disease or when it persists.
|
______ are the after effects of a disease or when it persists.
|
|
|
Skin and mucous membranes are physical barriers to infection and they may supply foundation for microbial ecosystems.
|
______ and ______ are physical barriers to ______ and they may supply ______ for microbial ecosystems.
|
|
|
Humans are usually sterile in utero but soon after birth, microbe populations begin to establish.
Normal microbiota are resident flora which are established organisms and transient flora are microbes that come and go. |
Humans are usually ______ in utero but soon after birth, microbe populations begin to establish.
Normal microbiota are ______ flora which are established organisms and ______ flora are microbes that come and go. |
|
|
Colonies are usually isolated in specific body regions.
Dominant types of organisms may change with age and situations. Factors that influence distribution are: Nutrient availability salinity oxygen availability host defenses mechanical factors |
______ are usually isolated in specific body regions.
Dominant types of organisms may change with ______ and ______. Factors that influence distribution are: ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
Normal flora plays a role in defense by protecting against colonization of pathogens and using microbial antagonisms such as competitive exclusion and inhibiting the growth of other microbes with bacteriocins.
|
Normal flora plays a role in ______ by protecting against ______ of pathogens and using microbial antagonisms such as ______ and inhibiting the growth of other microbes with ______.
|
|
|
Microbes form symbiotic relationships with the hosts but may change depending on the state of the host and attributes of the microbes.
|
Microbes form ______ with the hosts but may change depending on the ______ of the host and ______ of the microbes.
|
|
|
Mutualism is when the host and microbe both benefit.
Intestinal bacteria Probiotics |
______ is when the host and microbe both benefit.
______ ______ |
|
|
Commensalism is when the microbe benefits and has a neutral effect on the host.
Flora on skin Conjunctiva |
______ is when the microbe benefits and has a neutral effect on the host.
______ ______ |
|
|
Parasitism is when the microbe benefits and has a negative effect on the host.
Pathogens |
______ is when the microbe benefits and has a negative effect on the host.
______ |
|
|
Pathogenicity is the ability to cause disease.
The extent of infection is usually determined by the state of the host resistance. |
______ is the ability to cause disease.
The extent of ______ is usually determined by the state of the host ______. |
|
|
Primary infection is caused by primary pathogens and is the initial state of disease.
Secondary infection are typically opportunistic. Sub-clinical infections are inapparent, they have a pathogen but don't have signs or symptoms of a disease. |
______ is caused by primary pathogens and is the ______ state of disease.
______ are typically opportunistic. ______ are inapparent, they have a pathogen but don't have ______ or ______ of a disease. |
|
|
Local infections only colonize at the point of infection.
Systemic infections are body wide inflammatory response to pathogens and their toxins and result in septicemia. Bacteremia is bacteria in the blood. Toxemia are toxins in the blood. Viremia are viruses in the blood. |
______ only colonize at the point of infection.
______ are body wide inflammatory response to pathogens and their ______ and result in ______. ______ is bacteria in the blood. ______ are toxins in the blood. ______ are viruses in the blood. |
|
|
People that don't have signs or symptoms but have a pathogen are carriers.
|
People that don't have ______ or ______ but have a pathogen are ______.
|
|
|
Predisposing factors:
gender genetic background climate and weather inadequate nutrition age habits and lifestyle chemotherapy emotional disturbances |
Predisposing factors:
gender genetic background climate and weather inadequate nutrition age habits and lifestyle chemotherapy emotional disturbances |
|
|
Communicable pathogens can transmit from one host to another. Contagious pathogens transmit easily between hosts but not all communicable diseases are contagious. ID50 is the infection dose required for 50% of test populations to contract a disease.
Non-communicable disease don't spread between hosts. |
______ can transmit from one host to another. ______ transmit easily between hosts but not all ______ diseases are ______. ______ is the infection dose required for ______ of test populations to contract a disease.
Non-communicable disease don't spread between hosts. |
|
|
Robert Koch demonstrated that specific microbes caused specific diseases. He experimented with grazing animals infected with anthrax.
|
______ demonstrated that specific microbes caused specific diseases. He experimented with grazing animals infected with ______.
|
|
|
Koch's postulates
Same pathogen must be present in each case of disease Pathogen is isolated from diseased host and grown in pure culture Pure culture must cause disease when inoculated into healthy animal Pathogen must be re-isolated from inoculated animal |
Koch's postulates:
1. Same ______ must be present in each case of disease 2. Pathogen is ______ from diseased host and ______ in ______ 3. ______ must cause disease when ______ into healthy animal 4. Pathogen must be ______ from inoculated animal |
|
|
Exceptions to Koch's postulates
some bacteria have unique culture requirements some diseases are caused by multiple pathogens ethical considerations |
Exceptions to Koch's postulates:
some bacteria have ______ requirements some diseases are caused by ______ ______ considerations |
|
|
Stages of an infectious diseases
Incubation period - no signs or symptoms Prodromal period - vague, general symptoms Illness - most severe signs and symptoms Decline - declining signs and symptoms Convalescence - no signs or symptoms |
Stages of an infectious diseases
______ period - no signs or symptoms ______ period - vague, general symptoms ______ - most severe signs and symptoms ______ - declining signs and symptoms ______ - no signs or symptoms |
|
|
acute diseases - signs and symptoms come quick but are short lived
chronic diseases - signs and symptoms are long, slow, progressive build up which could take years latent diseases - illness then nothing followed by another illness |
______ diseases - signs and symptoms come quick but are short lived
______ diseases - signs and symptoms are long, slow, progressive build up which could take years ______ diseases - illness then nothing followed by another illness |
|
|
In order to cause disease pathogen must follow a series of steps:
gain entrance to host adherence (critical step) colonization avoid host defenses cause host damage |
In order to cause disease pathogen must follow a series of steps:
______ ______ ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
Most microbes have a preferred portal of entry. Streptococci, when inhaled may cause pneumonia; when ingested they do not.
A few microbes cause illness no matter how they enter. They may cause different illness based on portal of entry. Plague has 2 forms: bubonic and pneumonic Anthrax has 3 forms |
Most microbes have a preferred ______.
______, when inhaled may cause pneumonia; when ______ they do not. A few microbes cause illness no matter how they ______. They may cause different illness based on ______. Plague has 2 forms: ______ and ______ Anthrax has ______ forms |
|
|
Adherence is the critical step and the binding of adhesins to host receptors is highly specific.
|
______ is the critical step and the binding of ______ to host receptors is highly specific.
|
|
|
Virulence factors:
capsules incomplete phagocytosis fimbriae components of cell wall |
Virulence factors:
______ ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
Exoenzymes
Coagulases & kinases - form or dissolve blood clots Hyaluronidase & collagenase - dissolve hyaluronic acid and collagen fibers IgA proteases & leukocidins - destroy antibodies or WBCs |
Exoenzymes
______ & ______ - form or dissolve blood clots ______ & ______ - dissolve hyaluronic acid and collagen fibers ______ & ______ - destroy antibodies or WBCs |
|
|
Damage often facilitates dispersal of pathogens through things like diarrhea or coughing.
Main sources of damage: steal nutrients binding to and invading host cells induce hypersensitivity reactions (allergies) production of toxins (toxigenicity) |
______ often facilitates dispersal of pathogens through things like ______ or ______.
Main sources of damage: steal ______ ______ to and ______ host cells induce ______ (______) production of ______ (______) |
|
|
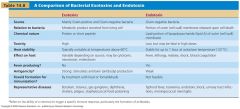
Gram positive bacteria exotoxins
produced as part of their metabolism secreted externally or following cell lysis among most lethal substances |
Gram positive bacteria exotoxins
produced as part of their ______ secreted ______ or following ______ among most ______ |
|
|
Protein exotoxins
enzymatic nature highly soluble heat liable |
Protein exotoxins
______ nature highly ______ heat ______ |
|
|
Toxoids toxins
inactivated exotoxins induce antitoxins that provide immunity passive immunity in form of antitoxin can be given as treatment |
Toxoids toxins
______ exotoxins induce ______ that provide ______ passive ______ in form of antitoxin can be given as ______ |
|
|
Toxin functional categories
neurotoxins enterotoxins cytotoxins |
Toxin functional categories
______ ______ ______ |
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus toxins:
enterotoxin exfoliation toxin toxic shock syndrome toxin Vibrio cholera toxin cholera enterotoxin Clostridium species toxins botulinum neurotoxin tetanus neurotoxin gangrene toxin |
Staphylococcus aureus toxins:
______ ______ ______ Vibrio cholera toxin ______ Clostridium species toxins ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
Gram negative bacteria endotoxins are released when cells die and their cell walls lyse.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) outer membrane - the lipid portion (lipid A) is toxin. Heat stable and not suitable for use as toxoids, do not cause formation of antitoxins. |
Gram negative bacteria endotoxins are released when cells ______ and their cell walls ______.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) outer membrane - the ______ portion (______) is toxin. Heat ______ and not suitable for use as ______, do not cause formation of ______. |
|
|
All endotoxins produce the same symptoms:
Chills, fever, weakness, aches May activate blood clotting proteins - Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) May cause septic shock that can be fatal |
All endotoxins produce the same symptoms:
______, ______, ______, ______ May activate ______ - ______ (______) May cause ______ that can be fatal |
|
|
Endotoxins produced by:
Salmonella Proteus Klebsiella Neisseria |
Endotoxins produced by:
______ ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
Portals of entry
Mucus membranes Respiratory tract Gastrointestinal tract Genitourinary tract Placenta Skin Hair follicles Sweat glands damaged skin Parenteral route Bite puncture Injection wounds |
Portals of entry
Mucus membranes ______ ______ ______ ______ Skin ______ ______ ______ Parenteral route ______ ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
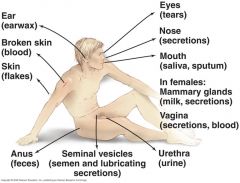
Portals of exit usually mirrors the way a pathogen came in.
Mucus membranes Respiratory and Gastrointestinal are most common. Skin/wounds Biting insects Contaminated needles and syringes |
______ usually mirrors the way a pathogen came in.
______ - ______ and ______ are most common. ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
Epidemiology involves:
determining etiology of infectious disease reservoirs of disease disease transmission identifying patterns associated with outbreaks outlining diagnostic tools and treatment options |
Epidemiology involves:
______ ______ ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
Incidence is the percentage of individuals of a population who develop a disease within a specific time frame.
Prevalence is the percentage of people that have a disease at a given time. Endemic is when a disease in continuously present in a population. Epidemic is when a higher than normal number of cases in a shorter than expected period of time. Pandemic is when a disease is epidemic on more than one continent at the same time. |
______ is the percentage of individuals of a ______ who develop a disease within a ______.
______ is the percentage of people that have a disease at a ______. ______ is when a disease in continuously present in a population. ______ is when a higher than normal number of cases in a shorter than expected period of time. ______ is when a disease is epidemic on more than one ______ at the ______. |
|
|
In order for disease to spread, pathogens must have a reservoir and must be transmitted to a susceptible host.
|
In order for disease to spread, pathogens must have a ______ and must be transmitted to a ______.
|
|
|
Reservoirs are a place for a pathogen to persist and maintain its ability to cause disease.
Reservoirs of infectious disease: Humans non-human animals environment (non-living) Recognizing reservoirs can help protect populations from disease. |
______ are a place for a pathogen to persist and maintain its ______ to cause disease.
Reservoirs of infectious disease: ______ ______ ______ Recognizing ______ can help protect populations from disease. |
|
|
Infected humans and are the most significant human reservoirs. If humans are the only reservoir than a disease is easier to control.
Symptomatic and Asymptomatic carriers. |
______ and are the most significant human reservoirs. If humans are the only reservoir than a disease is ______.
______ and ______ carriers. |
|
|
Non-human animal reservoirs
Zoonotic transmission (zoonoses) Diseases typically more severe in humans Often accidental and may be dead end for pathogens. |
Non-human animal reservoirs
______ transmission (______) Diseases typically more severe in ______ Often ______ and may be ______ for pathogens. |
|
|
Two most important environmental reservoirs are water and soil.
|
Two most important environmental reservoirs are ______ and ______.
|
|
|
Successful pathogens must be passed from reservoir to next susceptible host.
Transmission through: contact vehicle vector |
______ pathogens must be passed from reservoir to next ______ host.
Transmission through: ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
Direct contact transmission occurs when one person physically touches another, with hands being the main source.
|
______ transmission occurs when one person physically ______ another, with ______ being the main source.
|
|
|
Indirect contact transmission via inanimate objects or fomites, such as clothing, tissues, doorknobs, and drinking glasses.
|
______ transmission via inanimate objects or ______, such as ______, ______, ______, and ______.
|
|
|
Droplet transmission occurs through respiratory droplets within three feet of release.
|
______ occurs through respiratory droplets within ______ of release.
|
|
|
Vehicle transmission through food, water, and air.
Food contamination may originate with animal or occur during food preparation. Waterborne disease can involve large numbers of people; prevention involves proper sanitation. Respiratory droplets dry and create droplet nuclei that may remain suspended or become re-suspended. |
Vehicle transmission through ______, ______, and ______.
Food contamination may originate with ______ or occur during ______. ______ can involve large numbers of people; prevention involves ______. ______ droplets dry and create droplet ______ that may remain ______ or become ______. |
|
|
Vectors are any living organism that can carry a pathogen, most common are arthropods.
Mechanical are pathogens on the surface of the body. Biological are pathogens that carry out parts of their life cycles in a host. Control of vector-borne disease directed at controlling arthropod population. |
______ are any living organism that can carry a pathogen, most common are ______.
______ are pathogens on the surface of the body. ______ are pathogens that carry out parts of their ______ in a host. Control of vector-borne disease directed at controlling ______ population. |
|
|
Many diseases occur in cycles that may be annual or occur over decades, such as the flu and plague.
Herd immunity is the percentage of individuals in a population immune to a particular disease and is an important factor in cycles. Low levels could lead to re-emergence of disease, such as smallpox. |
Many diseases occur in cycles that may be ______ or occur over ______, such as the ______ and ______.
______ is the percentage of individuals in a population immune to a particular disease and is an important factor in ______. Low levels could lead to ______ of disease, such as ______. |
|
|
There as been some success in the reduction and eradication of disease.
Efforts directed at: Improving sanitation Reservoir and vector control Vaccination Chemotherapy Reasons all infectious diseases aren't eradicated: Wild animal reservoirs Microbial evolution - jumping species Can't force people to vaccinate or don't have access to vaccines |
There as been some success in the reduction and eradication of disease.
Efforts directed at: ______ ______ ______ ______ Reasons all infectious diseases aren't eradicated: ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
Four mechanisms public health agencies use to control disease transmission:
Isolation - separation of sick people from population Quarantine - separation of people you think have been exposed. Immunization Vector control |
Four mechanisms public health agencies use to control disease transmission:
______ - ______ ______ - ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
National disease surveillance network are a network of agencies across the country and monitor disease development.
Agencies include: Public health departments Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) World Health Organization (WHO) |
National disease surveillance network are a network of agencies across the country and ______ disease development.
Agencies include: ______ ______ ______ |
|
|
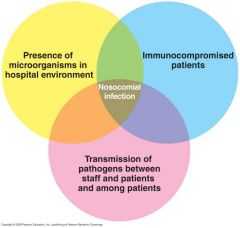
Nosocomial infections are hospital acquired infections that range from mild to fatal and have increased 36% in the last 20 years.
They are the leading cause of death in the US causing 100,000 deaths per year. |
______ are hospital acquired infections that range from mild to fatal and have increased ______ in the last 20 years.
They are the leading cause of death in the US causing ______ deaths per year. |
|
|
Reservoirs of nosocomial pathogens:
Exogenous Other patients Hospital environment Health care workers Endogenous Patient's own normal flora |
Reservoirs of nosocomial pathogens:
Exogenous ______ ______ ______ Endogenous ______ |
|
|
bacteria
|
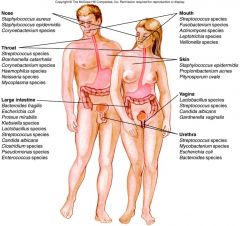
|
|
|
Koch's postulate
|
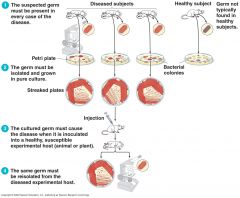
|
|
|
Stages of infectious disease
|
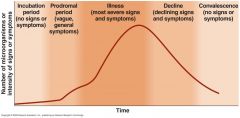
|
|
|
portals of entry
|
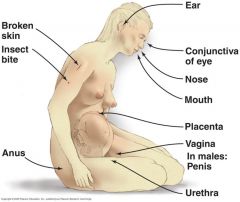
|
|
|
adherence
|
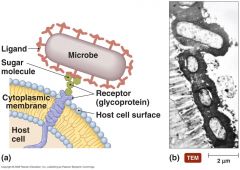
|
|
|
phagocytosis
|
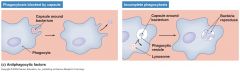
|
|
|
exoenzymes
|
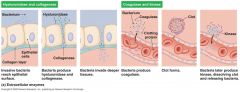
|
|
|
toxins
|
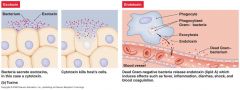
|
|
|
toxins
|
|
|
|
Portals of exit
|
|
|
|
reservoirs of nosocomial infections
|
|

