![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the general function of the limbic system?
|
Anatomical substrate for drive-related and emotional behavior.
|
|
|
Give three examples of drive-related behavior associated with the limbic system.
|
eat, drink, reproduce
|
|
|
What are the five functional components of the limbic system?
|
Cingulated gyrus
Hippocampus Parahippocampal gyrus Amygdala Septal nuclei |
|
|
What is the purpose of the cingulated gyrus?
|
Brings together motivation with physical action. It activates the limbic system.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the hippocampus?
|
Involved in the formulation of long-term memory
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the parahippocampal gyrus?
|
Plays a part in memory and navigation.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the amygdala?
It's considered a substrate for what? |
Involved in fear and anger - both generation and recognition in others.
Empathy |
|
|
What is the purpose for the septal nuclei?
|
One area associated with pleasure.
|
|
|
What sort of abnormalities are associated with injury to the amygdala?
|
Loss of fear. "Emotional blunting - the creature may act rather placid.
|
|
|
What sort of abnormaliteis are associated with injury to the hippocampus?
|
Loss of declarative memory for new events.
Hyperactivity |
|
|
Draw out the papez circuit
|
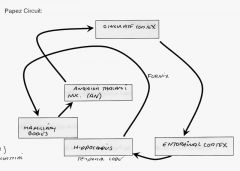
See the drawing.
|
|
|
What does the septum feed?
|
hypothalamus and frontal association cortex.
|
|
|
What is damaged in the kluver-bucy syndrome?
What is a two word discription of the result of this damage? |
Amygdala, anterior hippocampus, portions of temporal lobe.
Behavior disorder |
|
|
List the six signs and symptoms of a rhesus monkey showing the Kluver-Bucy syndrome.
|
1) Loss of fear
2) Placidity 3) Visual agnosia (can't recognize familiar objects) 4) Tendency to examine all objects orally 5) Hypersexuality (indiscriminate) 6) Loss of emotional valence (loss of value) |
|
|
What is damaged in Korsakoff's Psychosis? What causes it?
|
Mammillary bodies.
Alcoholism |
|
|
What is the result of Korsakoff's Psychosis?
|
1) Anterograde amnesia
2) May show disorientation and confusion 3) Confabulation |
|
|
The limbic system is the ____ between ____ and ____.
Give the basic flow between the named elements. |
coordinator
Neocortex and hypothalamus/ANS Neocortex <--> Limbic System <--> Hypothalamus |
|
|
Name the four limbic system efferents plus one interlimbic connection of the amygdala to ___?
|
hippocampus -> hypothalamus
amygdala-> hypothalamus amygdala -> Septum (Basal fore brain) Basal Forebrain (septum) -> Prefrontal Cx Basal Forebrain (septum) -> hypothalamus |
|
|
What are the four neocortex inputs to the limbic system?
|
Frontal Association Cx -> Cingulate Gyrus
Parieto-occipital Cx -> Cingulate Gyrus Temporal Association -> Amygdala Temporal Association -> hippocampus |
|
|
What is one major function of the temporal association cortex?
|
Recognition of people and objects.
|

