![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What surgical procedure is used to provide support for a weakened cornea?
|
Conjunctival flap
|
|
|
What are the layers of the cornea/sclera from outside to in?
|
Tear film (oily, aqueous, mucinous)
Epithelium Stroma (super thick & collagen) Descemet's Membrane Endothelium |
|
|
Name the corneal lesion associated with...
...Boxers ...superficial and slow-healing ...exposes Descemet's Membrane ...eye is ready to rupture ...assoc w/FHV in cat |
Indolent Ulcer...Boxers
Indolent Ulcer...superficial and slow-healing Descemetocele...exposes Descemet's Membrane Descemetocele...eye is ready to rupture Indolent Ulcer...assoc w/FHV in cat |
|
|
What are 2 surgical procedures used to treat corneal ulcers? Which one can be done under topical anesthesia?
|
Conjunctival flap
Keratotomy (punctate or grid); can be done under topical |
|
|
Which of the following are associated with feline herpes keratitis?
a) Symblepharon b) Dendritic neovascularization c) Oral NSAIDs (metacam) d) History of recurrent URI e) Acetylcystiene treatment |
a) Symblepharon
c) Oral NSAIDs (metacam) d) History of recurrent URI (Note - will see DENDRITIC ULCERATIONS; use metacam with CARE in cats; maybe lysine or azithromycin treatment) |
|
|
What is the "signature stamp" of feline herpes keratitis?
|
Symblepharon
|
|
|
What is a stinky treatment for melting corneal ulcers?
|
Acetylcysteine eyedrops
|
|
|
You see a horse in Alabama with a white plaque on the cornea and neovascularization. What are you thinking is the cause and the treatment?
|
Cause - fungal keratitis (older injury)
Tx - Cytology, subpalpebral lavage, antifungal |
|
|
You see a puppy with a history of ocular trauma (cat) and a fluorescein-negative corneal opacity. What is it? How do you treat it?
|
Corneal stromal abscess!
Tx - superficial keratectomy + pedicle conjunctival graft |
|
|
On an ocular exam of an old pony, you notice some portions of the iris adhered to the cornea. What is this and what is the most likely cause?
|
Anterior synechia
d/t old corneal perforation |
|
|
What are some differentials for cornal opacity?
|
Edema
WBC infiltrate Dystrophy/degeneration Fibrosis Superficial punctate keratitis Keratic precipitates |
|
|
How can you determine the depth of involvement in a corneal opacity?
|
Slit-lamp biomicroscopy
|
|
|
You see an old dog with a greyish-white corneal opacity that is primarily over the iris. What are 2 primary differentials that should come to mind?
|
Corneal edema
Corneal endothelial degeneration (maybe Calcium deposits - these cause painful ulcers though) |
|
|
You see a fat-ass dog with a white central corneal opacity. What might be your top differential and how can you diagnose it?
|
Lipid infiltrate
Dx - CBC triglycerides/cholesterol |
|
|
You see crystalline/spicular white deposits on an old dog cornea. What is probably going on and how is it treated?
|
Calcium deposits (senile corneal degeneration);
Tx - 1% EDTA |
|
|
Where are keratic precipitates commonly found?
|
In the BOTTOM region of the cornea in the anterior chamber
|
|
|
Which diseases cause superficial black corneal pigmentation?
a) KCS b) Pannus c) Lagophthalmos d) Entropion e) Corneal sequestration |
a) KCS
c) Lagophthalmos (incomplete eyelid closure) d) Entropion e) Corneal sequestration (Note - pannus is between epithelium and stroma) |
|
|
Which of the following are true regarding corneal pannus?
a) causes white lesions b) #1 breed is GSD c) usually starts at the temporal cornea d) a superficial hyperpigmentation e) usually bilateral |
b) #1 breed is GSD
c) usually starts at the temporal cornea e) usually bilateral (Note - BLACK lesions, between epithelium and stroma) |
|
|
T or F:
Iris prolapse is usually due to trauma. |
True!
|
|
|
Which of the following are NOT true regarding corneal sequestration?
a) mostly in persians and siamese cats b) starts out looking like a tea stain on the cornea c) associated with FHV d) treatment may involve keratectomy or conjunctival flap e) early debridement is key for rapid healing |
a) mostly in persians and siamese cats (NO; persians and himalayans)
e) early debridement is key for rapid healing (NO; don't pick the scab!) |
|
|
You see a funny pink plaque on a cat cornea. What might be going on?
|
SCC
Healing indolent ulcer Eosinophilic Keratitis |
|
|
How is eosinophilic keratitis treated?
|
Usually just controlled, not cured. Maybe try steroids but watch out for concurrent FHV infection
Dr. Maxwell doesn't like Oviban (diabetes risk) |
|
|
How can phthisis bulbi be prevented following corneal laceration repair?
|
Re-inflate w/air or balanced salt sol'n
|
|
|
What are fancy words for the following?
...inflammation of the globe ...inflammation of globe and all surrounding tissues |
Endophthalmitis...inflammation of the globe
Panophthalmitis...inflammation of globe and all surrounding tissues |
|
|
Define the following:
- squishy tissue around the sclera - junction between the cornea and sclera |
Episclera - squishy tissue around the sclera
Limbus - junction between the cornea and sclera |
|
|
What are definitions for the following?
Episclera Limbus |
- squishy tissue around the sclera
- junction between the cornea and sclera |
|
|
You see a collie with lesions on the limbus that show granulomatous inflammation when biopsied. What gives and how do you treat it?
|
Nodular Granulomatous Episclerokeratitis
Tx - cryosurgery or immunosuppression |
|
|
What is an aggressive, superficial tumor of the limbus? How is it treated?
|
Limbal (epibulbar) melanoma
Tx - excision but eventual enucleation |
|
|
What do you call eyes of different colors (in the same animal)?
|
Heterochromia iridis
|
|
|
What is Waardenburg's Syndrome?
|
White cat w/heterochromia iridis and is deaf
|
|
|
What are common ocular issues with homozygous merle dogs?
|
Micropthalmia
Iris coloboma Corectopia Dark pupil Cataracts |
|
|
What word describes the following:
- keyhole pupil - eyes of different color (or different colors in the same eye) - displacement of pupil from center |
Iris coloboma - keyhole pupil
Heterochromia iridis - eyes of different color (or different colors in the same eye) Corectopia - displacement of pupil from center |
|
|
Define the following:
Iris coloboma Heterochromia iridia Corectopia |
Iris coloboma - keyhole pupil
Heterochromia iridis - eyes of different color (or different colors in the same eye) Corectopia - displacement of pupil from center |
|
|
Which of the following are associated with senile iris atrophy?
a) poodle b) trauma from cat scratch c) anterior synechia d) Basenji e) reduced PLR |
a) poodle (and min pin and Chihuahua)
e) reduced PLR (looks like a mouse has nibbled the iris or a cat has shredded it) |
|
|
Choose persistent pupillary membrane or anterior synechia:
a) often a sequel to trauma b) Basenji c) runs from iris to cornea d) arises from iris margin e) arises from iris collarette |
(AS) often a sequel to trauma
(PPM) Basenji (always AS and some PPM can) runs from iris to cornea (AS) arises from iris margin (PPM) arises from iris collarette |
|
|
What are the 3 forms of persistent pupillary membrane? Which is the least concerning?
|
iris to iris (least concerning)
iris to cornea iris to lens |
|
|
You see a dark bleb of tissue at the ventral aspect of the anterior chamber in a golden retriever. What do you suspect and how can you confirm this suspicion?
|
Iris cyst!
Roll the animal around and see if it moves |
|
|
Which of the following are not signs of uveitis?
a) corneal edema b) conjunctival hyperemia c) elevated 3rd eyelid d) hypopyon e) increased intraocular pressure |
e) increased intraocular pressure (often DECREASED)
|
|
|
You use the slit beam to look in the anterior chamber of a dog and see "dust particles" floating around. What is this called and what is it often indicative of?
|
Aqueous flare (indicative of uveitis)
|
|
|
Which of the following are common signs of uveitis?
a) mydriasis b) miosis c) anterior synechia d) posterior synechia e) lens luxation |
b) miosis
d) posterior synechia e) lens luxation |
|
|
What is a major infectious cause of uveitis in cats?
|
Toxo!
Also FeLV, FHV & FIV |
|
|
T or F:
Primary uveal neoplasia has a good prognosis for restoration of visual function. |
False!
Bad prognosis for vision but good prognosis for patient survival! |
|
|
What are some sequellae to hyphema?
|
glaucoma
synechiae pupillary occlusion cataract phthisis bulbi corneal opacity retinal detachment |
|
|
What are some causes of hyphema?
|
Bleeding disorders
Hypertension Trauma Neoplasia Uveitis Systemic dz Neovascularization Congenital issues |
|
|
You see an old cat with hyphema. What should you do?
|
Look @ retinal vessels!
Check blood pressure! |
|
|
What do you call inflammation at the back of the eye?
|
Chorioretinitis or retinochoroiditis
|
|
|
You see a husky with progressive loss of facial pigmentation and severe bilateral uveitis. What is probably going on?
|
Uveodermatological syndrome
|
|
|
You see a golden with progressive increase of iris pigment. What may be going on?
|
Pigmentary uveitis
|
|
|
How is uveitis treated?
|
Treat underlying condition!
Anti-inflammatories (steroids/NSAIDs) Immunosuppression Maybe atropine |
|
|
How does atropine work when treating uveitis? What are possible side-effects?
|
Atropine stops ciliary body spasm and makes animal more comfortable
It may increase intraocular pressure and lead to glaucoma |
|
|
You see little pigment spots in an iris of a cat. What is it and how is it managed?
|
Iris freckle or diffuse iris melanoma
Monitor size and intraocular pressures; eventually progresses to glaucoma |
|
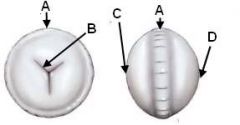
ID these parts of the canine lens:
|
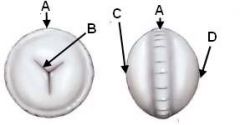
A - Equator
B - Suture lines C - Anterior pole D - Posterior pole |
|
|
What is the outside of the lens called? The middle part? The stuff between?
|
Outside (capsule)
Middle (Nucleus) Stuff between (Cortex) |
|
|
What holds the lens in place?
|
Zonular fibers
|
|
|
Choose nuclear sclerosis or cataracts:
- normal aging change - can't see the retinal reflection - due to lens getting denser - due to proteins in lens changing shape - can be used to age dogs |
NS - normal aging change
Cat - can't see the retinal reflection NS - due to lens getting denser Cat - due to proteins in lens changing shape NS - can be used to age dogs |
|
|
T or F:
Cataracts can not be cleared, only surgerized! |
True!
|
|
|
What is the best way to differentiate nuclear sclerosis from cataracts?
|
Can't see through a cataract...
|
|
|
Who gets congenital cataracts?
|
Malamutes and other siberian breeds
|
|
|
What features are found in cataracts due to diabetes? Which species are prone to these?
|
Equatorial vacuoles
Rats and Dogs |
|
|
What is a chief cause of nutritional cataracts in dogs? How will these present?
|
Milk replacements early in life
Will see PPMs! |
|
|
What ophtho exam finding might lead you to determine the following?
- lens is slipped forwards - lens is slipped up or down - lens is slipped back |
anterior chamber is shallow - lens is slipped forwards
aphakic crescent - lens is slipped up or down anterior chamber is deeper - lens is slipped back |
|
|
Who likes to luxate their lenses?
|
TERRIERS!
(jack russels, bull terriers, rat terriers) |
|
|
Lens luxation secondary to glaucoma and buphthalmos is common in which breed?
|
American cocker spaniel
|
|
|
Choose posterior or anterior lens luxation:
- jiggly lens (iridokinesis) - shallow anterior chamber - posterior synechia - deep anterior chamber |
posterior - jiggly lens (iridokinesis)
anterior - shallow anterior chamber posterior - posterior synechia posterior - deep anterior chamber |
|
|
Choose cat or dog for the following:
- cataracts d/t diabetes - uveitis then lens luxation - lens luxation secondary to glaucoma - lens luxation d/t genetics - trauma-induced lens epithelial tumor |
Dog - cataracts d/t diabetes
Cat - uveitis then lens luxation Dog - lens luxation secondary to glaucoma Dog - lens luxation d/t genetics Cat - trauma-induced lens epithelial tumor |
|
|
How can cat + puppy = uveitis?
|
Lens-induced uveitis!
Cat punctures lens, lens proteins leak-out setting-up immune mediated uveitis! |
|
|
What are the 3 types of cataract surgery?
|
Phacoemulsification (remove lens material and put in implant)
Intracapsular Lens Extraction Discission (remove lens material and leave capsule in place) |
|
|
Which ocular muscles are innervated by the following:
Oculomotor n. Trochlear n. Abducens n. |
Oculomotor n. (medial/dorsal/ventral rectus; inferior oblique)
Trochlear n. (superior oblique) Abducens n. (lateral rectus & retractor bulbi) |
|

What do you call the eye position here? Which nerve is affected?
|

Strabismus (Esotropia)
CNVI paralysis |
|

What do you call the eye position here? Which nerve is affected?
|

Strabismus (Exotropia)
CNIII paralysis |
|

Which nerve is affected here?
|

CNIV (trochlear) paralysis
|
|
|
Define the following:
Anisocoria Miosis Mydriasis Lagophthalmos |
Anisocoria - unequal pupil size
Miosis - small pupils Mydriasis - dilated pupils Lagophthalmos - reduced ability to blink |
|
|
What is the term for the following?
- unequal pupil size - small pupils - dilated pupils - reduced ability to blink |
Anisocoria - unequal pupil size
Miosis - small pupils Mydriasis - dilated pupils Lagophthalmos - reduced ability to blink |
|
|
What are major rule-outs for anisocoria? How does each present?
|
Uveitis or pain (miosis)
Glaucoma (mydriasis) Other stuff (drugs, iris atrophy, retina/optic n. dz, autonomic dz, FeLV, brain trauma) |
|
|
T or F:
Nystagmus is always abnormal. |
False!
Normal vestibular nystagmus can be induced by slowly moving the head. |
|
|
Which of the following statements are not true regarding nystagmus?
a) peripheral nystagmus has the rapid phase away from the lesion b) there is no rapid phase in normal vestibular nystagmus c) central dz is only vertical nystagmus d) nystagmus direction doesn't change in peripheral disease e) Boston Terriers may have congenitally spontaneous nystagmus |
c) central dz is only vertical nystagmus (can also be horizontal or rotary)
e) Boston Terriers may have congenitally spontaneous nystagmus (no, Siamese Cats!) |
|
|
Damage to which cranial nerves results in strabismus?
|
CN III, IV, or VI
|
|
|
Which type of strabismus is associated with hydrocephalus? Which nerve is often affected?
|
Exotropia; CN III lesions
|
|
|
Which breeds may have reduced palpebral reflex genetically?
|
Pug breeds have lagophthalmos (CNV issues)
|
|
|
You see a cat with a D-shaped pupil. What is this called and what is going on?
|
Internal ophthalmoplegia
Partial paralysis of CNIII within the globe |
|
|
What are the clinical signs of Horner's Syndrome? How can you tell preganglionic from postganglionic lesions?
|
Enopthalmos, Ptosis, Miosis, 3rd eyelid elevation
(postganglionic lesions are hypersensitive to phenylephrine while preganglionic take a long time to respond) |
|
|
Which of the following are true regarding Addie's Tonic Pupil?
a) there is no direct PLR in the affected eye b) the affected eye exhibits miosis c) the lesions are caused by impaired parasympathetic tone d) there is no indirect PLR in the affected eye e) the affected eye is hypersensitive to pilocarpine |
a) there is no direct PLR in the affected eye
c) the lesions are caused by impaired parasympathetic tone e) the affected eye is hypersensitive to pilocarpine (there is a consensual PLR in the affected eye; affected eye is dilated) |
|
|
Which nerves are affected in orbital fissure syndrome? What is the cause? Diagnosis? Prognosis?
|
CN III, IV, V, VI
Neoplasia Dx (MRI or CT) Prognosis is poor |

