![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which of the following are NOT functions of the cardiovascular system?
a) Transport of hormones b) Transport of oxygen c) Transport of carbon dioxide d) Blood pressure maintenance e) Thermoregulation |
ALL ARE FUNCTIONS OF THE CV SYSTEM! The 3 principal functions are (1) transport (2) waste removal (3) homeostasis
|
|
|
Which of the following describes systemic circulation? Pulmonary circulation?
a) high pressure/high volume b) high pressure/low volume c) low pressure/low volume d) low pressure/high volume |
a) high pressure/high volume
(systemic circulation) c) low pressure/low volume (pulmonary circulation) |
|
|
Which of the following are NOT true regarding the circulatory system?
a) Arterioles have the most smooth muscle b) Velocity flow into the systemic and pulmonic systems is equal. c) The majority of blood is located in the systemic veins d) Volume flow into the systemic and pulmonic systems is equal. |
b) Velocity flow into the systemic and pulmonic systems is equal.
FALSE! Volume flow is equal though... |
|
|
What is the major determinant of systemic vascular resistance?
a) arteries b) veins c) preload d) afterload |
a) arteries
(note: afterload is influenced by SVR) |
|
|
Where is the SA node located?
|
Where cranial vena cava enters right atrium
|
|
|
Which ion is primarily responsible for depolarization (phase 0) of SA nodal cells?
|
Calcium, yo!
|
|
|
Which of the following are responsible for action potential conduction?
a) sarcolemma b) T-tubules c) sarcoplasmic reticulum d) Z-disc |
a) sarcolemma
b) T-tubules (just invaginations of the sarcolemma) |
|
|
Which of the following is involved in calcium storage?
a) sarcolemma b) T-tubules c) sarcoplasmic reticulum d) Actin filaments e) Myosin filaments |
c) sarcoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
Describe the normal max/min pressures in the:
Right Atrium Right Ventricle Pulmonary trunk |
Right Atrium (0-3)
Right Ventricle (3-25) Pulmonary trunk (12-25) |
|
|
Describe the normal max/min pressures in the:
Left Atrium Left Ventricle Aorta |
Left Atrium (0-5)
Left Ventricle (5-120) Aorta (80-120) |
|
|
Which is the following are NOT true regarding myocyte contraction?
a) the myocyte is the basic contractile unit of the heart b) the sarcomere is bounded by Z-disks c) Ca released from the sarcolemma binds troponin C ultimately exposing actin. d) Myocardial contractility is the maximum velocity of myosin head cycling. |
a) the SARCOMERE is the basic contractile unit of the heart
c) Ca released from the SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM binds troponin C ultimately exposing actin. |
|
|
Which occurs during phase 0 of a ventricular AP?
a) K influx b) K efflux c) Na influx d) Na efflux e) Ca influx |
c) Na influx
|
|
|
Which occurs during phase 0 of a SA or AV node AP?
a) K influx b) K efflux c) Na influx d) Na efflux e) Ca influx |
c) Na influx
e) Ca influx both through slow Ca channels |
|
|
Which occurs during phase 1 of a ventricular AP?
a) K influx b) K efflux c) Na influx d) Na efflux e) Ca influx |
b) K efflux
|
|
|
Which occurs during phase 2 of a ventricular AP?
a) K influx b) K efflux c) Na influx d) Na efflux e) Ca influx |
b) K efflux (VERY LITTLE THOUGH)
c) Na influx e) Ca influx (Na/Ca through slow Ca channels) |
|
|
Which occurs during phase 3 of a ventricular AP?
a) K influx b) K efflux c) Na influx d) Na efflux e) Ca influx |
b) K efflux
|
|
|
Which occurs during phase 4 of a ventricular AP?
a) K influx b) K efflux c) Na influx d) Na efflux e) Ca influx |
a) K influx (pumped in by Na/K ATPase)
b) K efflux (leaking out) c) Na influx (leaking in) d) Na efflux (pumped out by Na/K ATPase) |
|
|
Which of the following determine the automaticity of a pacemaker cell?
a) resting membrane potential b) threshold potential c) systemic Na concentrations d) phase 4 slope |
a) resting membrane potential
b) threshold potential d) phase 4 slope |
|
|
"Funny channels" are important in which of the following?
a) AV node b) Purkinje cells c) Bundle of His d) SA node |
a) AV node
d) SA node |
|
|
Which channels are involved in phase 4 of the AV node AP?
a) "funny" current channels b) Potassium channels c) T-type Ca channels d) L-type Ca channels e) Sodium channels |
a) "funny" current channels
c) T-type Ca channels d) L-type Ca channels |
|
|
What are the 5 main determinants of cardiac output?
|
Heart rate
Afterload Preload Contractility Ventricular synchrony |
|
|
What are the factors contributing to ventricular systolic function?
|
Afterload
Preload Contractility |
|
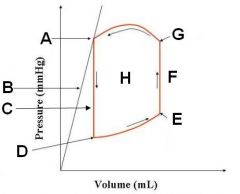
Which point corresponds to...
Opening of the mitral valve? Opening of the aortic valve? Closing of the mitral valve? Closing of the aortic valve? |
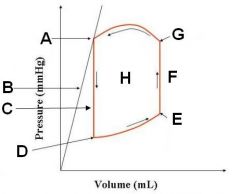
Mitral valve opens at D and closes at E.
Aortic valve opens at G and closes at A. |
|
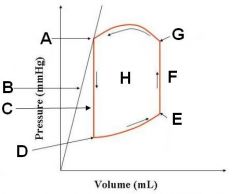
Which segments indicate systole? Diastole? Isovolumetric contraction/relaxation?
|
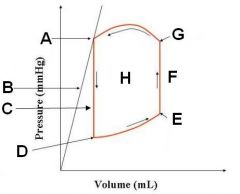
systole (G to A)
Diastole (D to E) Isovolumetric contraction (F) Isovolumetric relaxation (C) |
|
|
Which of the following conditions would cause jugular venous distention and/or jugular pulses?
a) Right heart failure b) hypovolemia c) pericardial disease d) pulmonary obstruction |
a) Right heart failure
c) pericardial disease Also caval obstruction and hypervolemia |
|
|
S1 is caused by the closing of the ____________ valves while S2 is caused by the closing of the __________ valves.
|
S1 (mitral/tricuspid valves)
S2 (aortic/pulmonic valves) |
|
|
What are some causes of a split S1?
|
Bundle branch block
Ectopic beats Ectopic pacemakers Valvular stenosis |
|
|
What are some causes of a split S2?
|
pulmonary hypertension (COPD, High altitude dz, heartworm dz)
|
|
|
Systolic clicks are associated with which of the following?
a) mitral regurg b) tricuspid regurg c) aortic stenosis d) pulmonic stenosis |
a) mitral regurg
b) tricuspid regurg |
|
|
What causes S3? When on the ECG does it occur?
|
Rapid ventricular filling.
Occurs after the T wave but before the next P wave. |
|
|
What causes S4? When on the ECG does it occur?
|
Acceleration of blood during atrial systole.
Occurs after the P wave but before the QRS complex. |
|
|
When on the ECG do S1 and S2 occur?
|
S1 occurs mid-QRS.
S2 occurs at the tail end of the T wave. |
|
|
What is the likely pathology of a continuous murmur?
|
PDA
|
|
|
What is the likely pathology of a plateau-shaped systolic murmur?
a) Ventricular septal defect b) Atrial septal defect c) Semilunar insufficiency d) AV valve insufficiency e) AV valve stenosis |
a) Ventricular septal defect (can also be diamond shaped)
d) AV valve insufficiency |
|
|
What is the likely pathology of a diamond-shaped systolic murmur?
a) Ventricular septal defect b) Atrial septal defect c) Semilunar insufficiency d) AV valve insufficiency e) AV valve stenosis |
a) Ventricular septal defect
b) Atrial septal defect (also aortic/pulmonic stenosis) |
|
|
What are causes of diastolic murmurs?
a) AV valve insufficiency b) Semilunar insufficiency c) Semilunar stenosis d) AV valve stenosis e) VSD |
b) Semilunar insufficiency
d) AV valve stenosis |
|
|
How are regurgitant murmurs different from ejection murmurs?
|
Regurgitant are band-shaped and involve valvular insufficiencies while ejection are diamond-shaped and involve outflow obstructions. BOTH are during systole, though!
|
|
|
If you hear a loud murmur on the right side of the thorax. What are your top 2 differentials?
|
VSD
Tricuspid regurg |
|
|
T or F:
Organic murmurs are due to structural defects while pathologic murmurs can be due to most anything. |
False!
Organic = pathologic murmur! |
|
|
What are some possible causes for physiologic murmurs?
|
Anemia
Hyperthyroid Fever |
|
|
Which of the following would result in BOUNDING pulses?
a) pericardial effusion b) left ventricular failure c) PDA d) aortic insufficiency e) aortic stenosis |
c) PDA
d) aortic insufficiency (also peripheral AV fistula) |
|
|
Which of the following would result in WEAK pulses?
a) pericardial effusion b) left ventricular failure c) PDA d) aortic insufficiency e) aortic stenosis |
a) pericardial effusion (during inspiration - pulsus paradoxus)
b) left ventricular failure e) aortic stenosis |
|
|
Pulsus paradoxus is associated with...
|
...pericardial effusion
|
|
|
Pulsus alternans is associated with...
a) pericardial effusion b) tachyarrthymias c) heart failure d) aortic insufficiency |
b) tachyarrthymias
c) heart failure (note ELECTRICAL ALTERNANS is d/t pericardial effusion) |
|
|
Bigeminal pulses are associated with...
|
...premature beats
|
|
|
When viewing a lateral thoracic radiograph, what structures are located in the 8 o'clock to 11 o'clock region?
|
Right atrium
Pulmonary arteries Aortic arch |
|
|
When viewing a lateral thoracic radiograph, what structures are located in the 6 o'clock to 8 o'clock region?
|
Right ventricle
|
|
|
When viewing a lateral thoracic radiograph, what structures are located in the 3 o'clock to 6 o'clock region?
|
Left ventricle
|
|
|
When viewing a lateral thoracic radiograph, what structures are located in the 12 o'clock to 3 o'clock region?
|
Left atrium
|
|
|
When viewing a DV thoracic radiograph, what structures are located in the 11 o'clock to 1 o'clock region?
|
Aortic arch
|
|
|
When viewing a DV thoracic radiograph, what structures are located in the 1 o'clock to 2 o'clock region?
|
Pulmonary arteries
|
|
|
When viewing a DV thoracic radiograph, what structures are located in the 2 o'clock to 3 o'clock region?
|
Left atrium
|
|
|
When viewing a DV thoracic radiograph, what structures are located in the 3 o'clock to 6 o'clock region?
|
Left Ventricle
|
|
|
When viewing a DV thoracic radiograph, what structures are located in the 6 o'clock to 9 o'clock region?
|
Right Ventricle
|
|
|
When viewing a DV thoracic radiograph, what structures are located in the 9 o'clock to 11 o'clock region?
|
Right Atrium
|
|
|
What is the normal heart size in most dogs and cats?
|
Lateral (2.5 - 3.5 ICS wide, 2/3 height)
DV (1/2 to 2/3 width) VHS <8 for cats, <10.5 for dogs |
|
|
The vertebral heart score starts at which vertebra? What are normal values for dogs/cats?
|
T4
Dogs (8.5 - 10.5) Cats (6.9 - 8.1) |
|
|
What are some differentials for a big round heart on radiography?
|
Pericardial effusion
Biventricular enlargement PPDH Obesity Neoplastic effusion Hemorrage/rupture Pericardial cysts |
|
|
T or F:
Veins are ventral and central. |
True!!!
|
|
|
Which of the following are NOT congruent with left heart failure?
a) Enlarged abdominal viscera b) perihilar pattern c) pulmonary venous enlargement d) left atrial/ventricular enlargement |
a) Enlarged abdominal viscera
(this is a RIGHT HEART issue) |
|
|
Which of the following are NOT congruent with right heart failure?
a) Enlarged abdominal viscera b) Indistinct abdominal cavity c) pulmonary venous enlargement d) enlarged vena cava e) patchy/multifocal pulmonary edema |
c) pulmonary venous enlargement
e) patchy/multifocal pulmonary edema (these are LEFT HEART issues) |
|
|
Choose pleural effusion or pulmonary edema...
...obscured cardiac silhouette |
EFFUSION
|
|
|
Choose pleural effusion or pulmonary edema...
...obscured vasculature. |
EDEMA
|
|
|
Choose pleural effusion or pulmonary edema...
...separation of lungs from body wall. |
EFFUSION
|
|
|
Choose pleural effusion or pulmonary edema...
...loss of detail in the lungs. |
EDEMA
|
|
|
Choose pleural effusion or pulmonary edema...
...air bronchograms. |
SEVERE EDEMA
|
|
|
How does the pulmonary vasculature change in a L to R shunt? What are examples of this shunt?
|
Pulmonary arteries are enlarged
(ASD, VSD, pulmonic valve insufficiency) |
|
|
Describe the pulmonary vasculature in a R to L shunt? What are examples of this shunt?
|
Small pulmonary vasculature
(PDA, ASD, Tetralogy of Fallot) |
|
|
What are some causes of microcardia?
|
Hypovolemia (blood loss/dehydration)
Addison's |
|
|
How can pulmonary vasculature be assessed?
|
Look at 9th rib on DV rad, if vein should be same width as rib height.
|
|
|
What are the 3 major pulmonary patterns?
|
Bronchial
Interstitial Alveolar |
|
|
Enlarged pulmonary arteries in dogs is commonly due to...
|
...heartworm disease
|

