![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 3 parts of the ear?
|
External, Middle, and Innder
|
|
|
What are the parts of the external ear?
|
Pinna (auricle)
Acoustic meatus (external auditory canal) |
|
|
What is the waxy lining of the acoustic meatus called?
|
Cerumen
|
|
|
What are the parts of the middle ear? Which bone houses the middle ear?
|
Tympanic membrane
Tympanic cavity Auditory ossicles Located in Tympanic bulla of temporal bone |
|
|
What are the epithelia of the tympanum and what are their embryological orgins?
|
Outer epithelium - ectoderm
Middle layer - mesoderm Inner epithelium - endoderm |
|
|
What connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx? What is the function of this structure?
|
Auditory tube (internal auditory canal)
For pressure equalization |
|
|
What are the membrane covered voids in the tympanic cavity?
|
Cochlear (round) window
Vestibular (oval) window |
|
|
T or F:
The middle ear is filled with air |
And so is your head! True!
|
|
|
What are the bony ossicles?
What is each attached to? |
Malleus - attached to tympanum
Stapes - attached to vestibular window Incus - articulates malleus and stapes |
|
|
T or F:
The Tensor tympani muscle attaches to the stapes. |
False. It attaches to the malleus. The Stapedius muscle attaches to the stapes.
|
|
|
What is the smallest muscle in the body, what does it attach to and what is its function?
|
Stapedius m. pulls stapes away from inner ear.
|
|
|
What are the parts of the membranous labrynth? Which is not part of the vestibular apparatus?
|
Saccule
Utricle Semicircular ducts Cochlear duct - not vestibular |
|
|
What separates the membranous labrynth from the osseous labrynth? What is contained within the membranous labrynth? How do these fluids differ?
|
Perilymph surrounds the labrynth - pretty much CSF
Endolymph is within the labrynth - high in K low in Na |
|
|
What does the saccule detect? The utricle?
|
Saccule - linear vertical acceleration
Utricle - linear horizontal acceleration |
|

Which number depicts the external face of the tympanum? What does #10 depict?
|
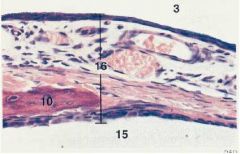
3 is external
10 is the malleus |
|

ID these structures/regions of this cross section of a utricle.
|
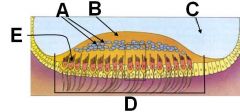
A - otoliths
B - Otolithic membrane C - Endolymph D - Macula E - Neuroepithelial hair cell |
|
|
What are the sensory cells of a macula? What sensory specializations do they have? How are they innervated?
|
Neuroepithelial hair cells have a cluster of stereocilia and one kinocilium.
Vestibulocochlear n. (VIII) |
|
|
T or F:
Both stereocilia and kinocilia are modified non-motile microvilli |
False *******!
This is true for stereocilia but kinocilia are nonmotile cilia |
|
|
Moving the stereocilia towards the kinocilium has what effect on impulse frequency?
|
Increased impulse frequency.
|
|
|
Moving the stereocilia away from the kinocilium has what effect on impulse frequency?
|
Decreased impulse frequency
|
|
|
T or F:
The maculae of the saccules and utricles are identical with one another. |
False! They are actually mirror images!
|
|
|
What is the function of the semicircular ducts?
|
Linear and angular acceleration.
|
|
|
T or F:
Semicircular ducts use maculae as their receptors. |
False!
They use cristae ampullarae |
|
|
What are the 3 vestibular reflexes?
|
Vestibulo-ocular
Vestibulocollic Vestibulospinal |
|
|
What is the receptor organ of the semicircular ducts? What is the region overlying the hair cells in this case?
|
Cristae ampullares
Embedded in the cupula |
|
|
Where are the kinocilia in the cristae ampullares located with respect to the utricle?
|
Lined-up toward utricle.
|
|
|
If the kinocilia in cristae ampullares bend towards the utricle, what does this do to impulse frequency?
|
Increased frequency
|
|
|
If the kinocilia in cristae ampullares bend away from the utricle, what does this do to impulse frequency?
|
Decreased frequency
|
|
|
What does the cochlea spiral around (bony part)? How many spirals does it usually make?
|
Modiolus
2.5 to 4.5 turns |
|
|
What innervates the cochlea?
|
Cochlear part of vestibulocochlear n. (CN VIII)
|
|
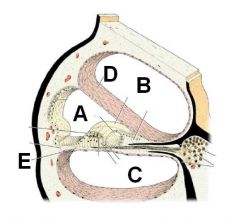
ID these regions (B and C are spaces, D and E are membranes). What fluid is in each space?
|
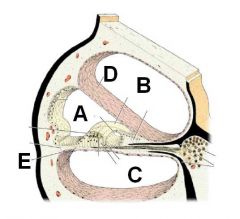
A - Scala Media (cochlear duct) - endolymph
B - Scala vestibuli (perilymph) C - Scala tympani (perilymph) D - vestibular membrane E - basilar membrane |
|
|
What is the apex of the cochlea known as?
|
Helicotrema
|
|
|
What cochlear organ is used for hearing?
|
Organ of Corti (spiral organ)
|
|
|
Which way are the kinocilia oriented in the organ of Corti?
|
*******! No kinocilia in this sucka!!
|
|
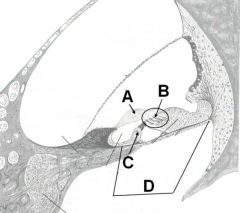
How many hairs at B and C? ID the rest, yo!
|

A - Tectorial membrane
B - 3 hairs C - 1 hair D - Spiral organ (organ of Corti) |
|
|
What are the hairs of the organ of Corti embedded in? Where do these cells synapse?
|
Tectorial membrane
Synapse on spiral ganglion of cochlear n. |

