![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three layers associated with the bilaminar embryo and what does each become in the trilaminar embryo?
|
Epiblast > ectoderm
Hypoblast > endoderm Trophoblast > extraembryonic ectoderm |
|
|
T or F:
The trophoblast is considered extraembryonic ectoderm. |
True!
|
|
|
Where does the mesoderm for the extraembryonic membrane derive from?
|
Lateral plate mesoderm
|
|
|
What are the four extraembryonic membranes? How many lamina is each comprised of?
|
Yolk sac
Chorion Amnion Allantois All are comprised of 2 lamina |
|
|
What two layers comprise the yolk sac? What vessels supply early nutrition from the yolk sac?
|
endoderm and splanchnic mesoderm
vitelline vessels |
|
|
What layers comprise the chorion? The amnion?
|
Both are extraembryonic ectoderm (trophoblast) and somatic mesoderm
|
|
|
What layers comprise the allantois?
|
ectoderm and splanchnic mesoderm
|
|
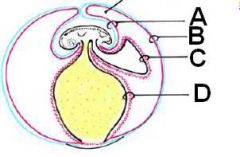
ID these extraembryonic layers in a developing embryo.
|
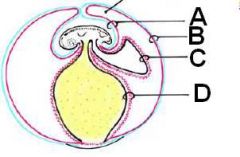
A - Amnion
B - Chorion C - Allantois D - Yolk sac |
|
|
What is the function of the chorion?
|
Where exchange occurs (nutrition, waste, gas, water) Part of the fetal placenta
|
|
|
What is the function of the amnion?
|
contain secretions from primitive kidneys and gut
|
|
|
What is the embryonic orign of the allantois? What developing organ is the allantois in connection with? What is this connection called?
|
Endoderm and splanchnic mesoderm; diverticulum of embryonic hindgut; remains connected with urinary bladder via the urachus
|
|
|
What are the fetal placental layers?
|
Chorioallantoic membrane (endothelium - allantoic vessels, chorioallantoic CT, chorionic epithelium)
|
|
|
What are the maternal placental layers?
|
Endometrium (uterine epithelium, uterine connective tissue, endothelium)
|
|
|
What are the two main layers of the placenta?
|
Chorioallantoic membrane (fetal placental)
Endometrium (maternal placental layers) |
|
|
T or F:
Most large domesticated species practice invasive apposition and implantation. |
False!
These are non-invasive. Carnivores, primates, and rodents are invasive. |
|
|
What is the greatest number of placental layers between fetal and maternal blood?
|
6 layers
|
|
|
What are the histological divisions (by number of contact layers) of placenta types?
|
Epitheliochorial
Syndesmochorial Endotheliochorial Hemochorial |
|
|
What are the placental divisions by the sloughing or separation of endometrium at parturition?
|
Adeciduate (non-deciduate)
Deciduate |
|
|
T or F:
Fetal membranes of the placenta are always 3 layered. |
True!
|
|
|
How many layers total in the epitheliochorial?
|
6 layers
|
|
|
What type of layered placenta is found in carnivores? In primates?
|
Endotheliochorial
Hemochorial |
|
|
How can the placenta be defined by shape? What are representative species of each?
|
Diffuse (horse, pig)
Cotyledonary (Ruminants) Zonary (cat, dog) Discoid (primates, rodents) |
|
|
T or F:
The only thing passed in a deciduate placenta is the fetal layers. |
False! Some uterine lining sloughs with deciduate.
|
|
|
What are cotyledons in touch with in a cotyledonary placenta?
|
Uterine caruncles
|
|
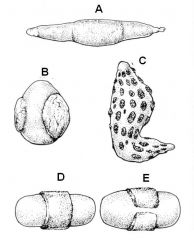
ID these placenta types.
|
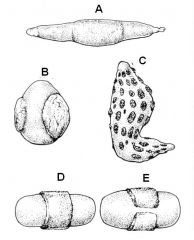
A - Diffuse
B - Cotyledonary C - Discoid D - Zonary (single) E - Zonary (double) |
|
|
How long does the yolk sac remain in the pig? The horse?
|
12 days - pig
1/4 gestation - horse |
|
|
Which type of placenta has all 6 layers intact?
|
Epitheliochrorial (diffuse)
|
|
|
T or F:
Piglets are born with their amniotic sac intact. |
False!
|
|
|
Describe the horse placenta.
|
Diffuse with microcotyledons;
Epitheliochorial (6 layers); adeciduate |
|
|
T or F:
Horses are born with the amniotic sac intact. |
True!
|
|
|
Describe the ruminant placenta.
|
Cotyledonary, epithelialchorial (6 layers), semi-deciduate
|
|
|
T or F:
Cows are born with the amniotic sac intact. |
False!
|
|
|
What is the placental cotyledon + the uterine caruncle called?
|
Placentome!!
|
|
|
Describe the carnivore placenta.
|
Zonary, endothelialchorial, deciduate
|
|
|
T or F:
Pups are born with the amniotic sac intact. |
True!
|
|
|
In what circumstance are freemartins a possibility? What hormone is responsible?
|
Twin male and female ruminants sharing placental blood. Antimullerian hormone is responsible.
|
|
|
What are two abnormalities of placentation? Which results in more fluid?
|
Amnion hydrops (hydramnios)
Allantois hydrops (hydrallantois) - more fluid! |

