![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the parts of the male reproductive system?
|
Testes
Excretory genital ducts Accessory glands Penis |
|
|
What are the functions of the male reproductive system?
|
Produce and transport spermatozoa
Secretion of fluids Placement of semen into female reproductive tract |
|
|
What do spermatozooa and accessory sex gland fluids comprise?
|
Semen
|
|
|
T or F:
The testes perform both endocrine and exocrine functions. |
True!
Exocrine - spermatozooa Endocrine - testosterone and estrogen |
|
|
What are the endocrine secretions of the testes and what cell type excretes which secretion?
|
Testosterone - interstitial (Leydig) cells
Estrogen - sustentacular (Sertoli) cells |
|
|
What are the coverings of the testes?
|
Tunica albugenia
Tunica serosa (visceral vaginal tunic) |
|
|
Which cells provide the exocrine function of the testes and where are they located?
|
Lining cells of the seminiferous tubules and their ducts
|
|
|
ID these structures
|
A - Ductus deferens
B - Epididymus C - Septum D - Testicular lobules E - Semineferous tubules F - Tunica albugenia |
|
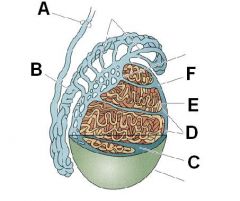
ID these structures
|
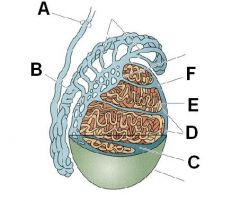
A - Ductus deferens
B - Epididymus C - Septum D - Testicular lobules E - Semineferous tubules F - Tunica albugenia |
|
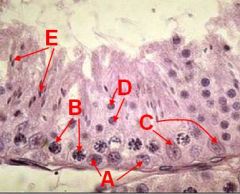
What is this a section through?
ID A - E |
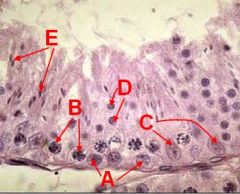
Seminiferous tubule xs
A - Spermatogonia B - Primary Spermatocytes C - Sustentacular Cells D - Early spermatids E - Late spermatids |
|
|
What is the function of Sertoli cells?
|
Support for developing sperm
Establish blood/testis barrier Synthesize estrogen |
|
|
How do sustentacular cells maintain the blood/testis barrier? What are the compartments of this barrier?
|
Tight junctions (zonules occludens)
Basal and adluminal compartments. |
|
|
T or F:
Sertoli cell tumors are common in dogs unless they are cryptorchid. |
False! Sertoli cell tumors are common in dogs but more common in cryptorchid dogs.
|
|
|
T or F:
Sertoli cell tumors may cause development of female secondary sex characteristics. |
True! Overproduce estrogen in this case.
|
|
|
Where are Leydig cells found? What is their histology?
|
septal connective tissue
Large round nuclei, distinct nucleolus, foamy appearance |
|
|
What would be a characteristic of a Leydig cell tumor?
|
Overproduction of testosterone - more aggression!
|
|
|
T or F:
Spermatocytogenesis involves the process of spermatagonia into secondary spermocytes. |
False!
Spermatocytogenesis is the mitotic stage of spermatogenesis where spermatogonia (2n) divide into primary spermatocytes (2n). |
|
|
T or F:
Primary spermatocytes (2n) undergo mitosis to directly form spermatids (1n). |
False!
Primary spermatocytes (2n) do undergo meiosis but they first form secondary spermatocytes (1n) and then finish meiosis to form spermatids (1n). |
|
|
What is the transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa called? Where does this occur?
|
Spermiogenesis
Seminiferous tubule and epididymus. |
|
|
What is the mitotic phase of spermiogenesis called? Where does it occur?
|
Spermatocytogenesis occurs in the seminiferous tubules
|
|
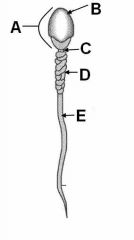
ID these regions of a spermatozoan.
|
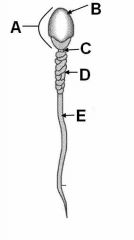
A - Head
B - Acrosomal cap C - Neck D - Middle Piece of tail E - Principal piece of tail |
|
|
What ducts does a spermatozoan must pass through to reach the vas deferens IN ORDER.
|
Seminiferous tubule
Tubulus rectus Rete testis Ductus efferens Ductus epididymidis Ductus deferens |
|
|
T or F:
The epididymis and ductus deferens lack cilia but may have microvilli or stereocilia. |
True!
|
|
|
What is the primary maturation site of sperm cells? What is the epithelium here?
|
Epididymis
Pseudostratefied stereociliated columnar epithelium |
|
|
What is the epithelium of the ductus deferens? At its distal end?
|
Pseudostratefied stereociliated columnar epithelium. Simple columnar distally.
|
|
|
How can you tell the ductus deferens from the epididymis histologically?
|
Ductus deferens should be singular and will have a thicker tunica muscularis.
|
|
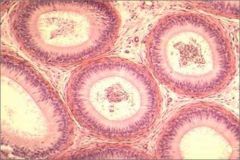
What is this an image of? How do you know?
|
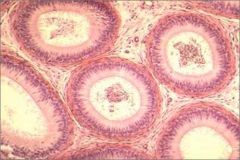
Epididymis
Pseudostratified stereociliated columnar epithelium. No thick tunica muscularis. Many passages indicate coils. |
|
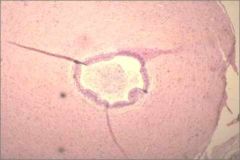
Which genital duct is this a cross section of?
|
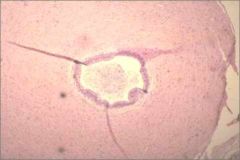
Ductus deferens
|
|
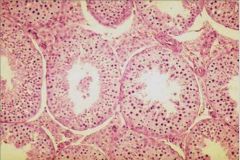
Which region is this a cross section of?
|
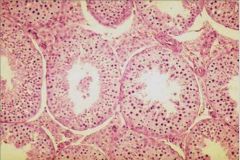
Seminiferous tubule
Note developing spermatids and atypical "stratefied" epithelium |
|
|
List the possible mammalian accessory sex glands.
|
Prostate
Vesicular Ampullary Bulbourethral |
|
|
Which accessory sex gland is absent in carnivores?
Which is present in all domestic species except dogs? |
Vesicular gland
Bulbourethral gland |
|
|
What are the two types of prostate and what species are associated with each?
|
Compact - dogs, cats, horses
Disseminate - bulls, boars, small ruminants |
|
|
What are some functions of accessory sex glands?
|
Plug vagina
Sperm vehicle Nourish sperm pH modification and cleansing of urethral tract |
|
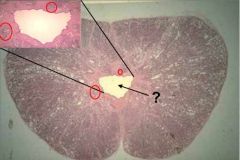
What is this? Sri Lanka? The Big Island of Hawaii? What tissue surrounds this structure? What type of tissue is in the red circles?
|
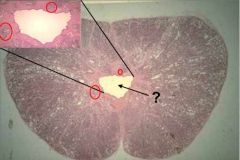
Urethra
Prostate body Prostatic urethra surrounds urethra |
|
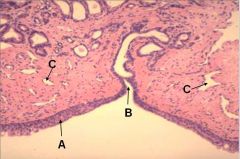
What type of epithelium does A have?
What is B? What is the function of C? |
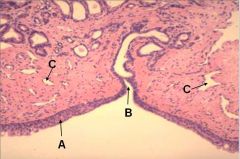
A - transitional epithelium
B - duct of prostate gland C - venous sinus for erectile tissue |
|
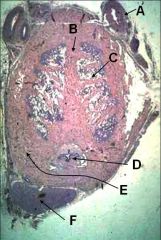
ID these structures in this cross-section through the body of the penis.
|
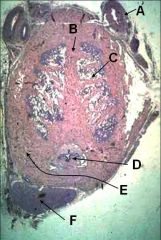
A - Dorsal artery of the penis
B - Septum penis C - Corpus cavernosum penis D - Corpus spongiosum penis (enclosing urethra) E - Tunica albugenia F - Retractor penis m. |
|
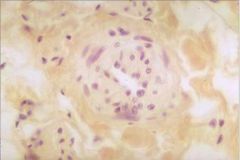
What structure is this (hint - it's in the corpus cavernosum)?
|
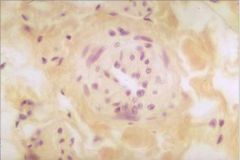
Helicine artery
Relaxation of smooth muscle results in dilation and increased blood flow for erection. |
|
|
T or F:
The distal end of the urethra becomes stratefied squameous epithelium before it joins the skin of the glans penis. |
True!
|

