![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two main divisions of the integument?
|
Skin and skin derivatives
|
|
|
Name some skin derivatives:
|
Glands (sweat, sebaceous, mammary)
Hair Horns Hooves Claws Feathers Horns Antlers Combs Wattles |
|
|
What is the largest organ and what is its weight percentage?
|
Integument! 16% w/w
|
|
|
Name some integument functions:
|
Barrier – 2 way
Temperature regulation Secretion Calcium homeostasis Protection against UV radiation Provides for motion and external form Used in locomotion Behavior displays - sexual & defense Mechanical & immune protection Sensory |
|
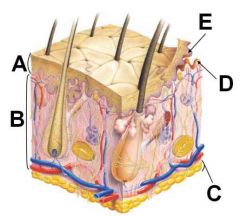
ID these regions of the integument
|
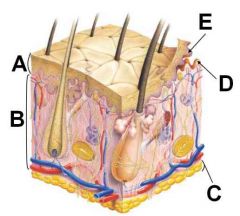
A - Epidermis
B - Dermis C - Hypodermis D - Dermal papillae E - Epidermal pegs |
|
|
What does skin use to make Vitamin D?
|
Dehydrocholecalciferol + uv = Vitamin D
|
|
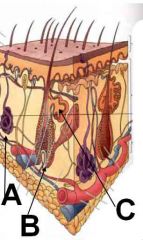
ID these dermal structures
|
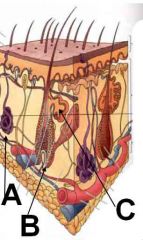
A - Sweat gland
B - Hair follicle C - Sebaceous gland |
|
|
What is skin contiguous with?
|
Body holes (mucous membranes)!!
Eyes, ears, urogenital system, respiratory system, both ends of digestive system |
|
|
What cell type makes up most of the epidermis?
|
Keratinocytes
|
|
|
What are the layers of the epidermis (from superficial to deep)?
|
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum (maybe) Stratum Granulosum Stratum Spinosum Stratum Basale |
|
|
Which layer contains germinal cells for the epidermis? Which epidermal layer is characterized by actively dividing cells?
|
Stratum basale for both!
Basal layer of stratum spinosum can also be actively dividing. |
|
|
What makes the stratum spinosum spiny?
|
Processing artifact - desmosomes and cell shrinkage
|
|
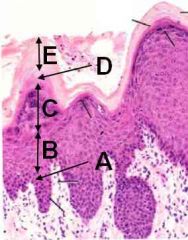
Identifizzle these layas:
|
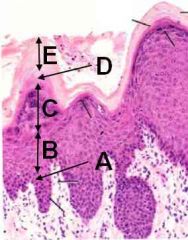
A - Stratum basale
B - Stratum spinosum C - Stratum granulosum D - Stratum lucidum E - Stratum corneum |
|
|
What do keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum contain?
|
Keratinohyaline granules
Profilagrin |
|
|
T or F:
Stratum lucidum is only present in thick skin. |
True!
|
|
|
Whats is the fancy-ass term for skin flaking?
|
Desquamate
|
|
|
What are the two types of keratin and give examples of each.
|
Hard keratin (hooves, horns, feathers, some hair)
Soft keratin (most epidermis and some mucous membranes) |
|
|
What are the non-keratinocyte component of the epidermis?
|
Melanocytes
Merkel cells Dendritic (langerhans) cells Macrophages Lymphocytes |
|
|
What is the embryonic origin of melanocytes? Where are they located?
|
Neural crest cells BITCHES!
Located in the Stratum Basale YOU KNOW!!! |
|
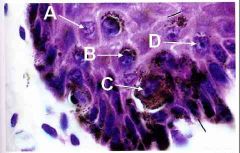
Ok now its time to play WHERE'S THAT MELANOCYTE!!!
|
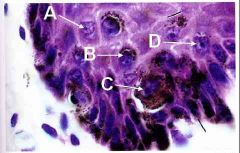
Awww, you lose! It was C
|
|
|
Which cells do melanocytes strive to protect?
|
Stem cells of stratum basale
|
|
|
Where are most dendritic cells located? Where are most Langerhans cells located?
|
Different names for the same thing - Dendritic (Langerhans) cells make up 2-4% of epidermal cell population and are located in the stratum spinosum
|
|
|
What are the precursors of Langerhans cells? What is the function of dendritic cells?
|
From bone marrow precursors. Antigen presenting cells of skin and phagocytic function
|
|

What is the possible function of Merkel cells? Where are they abundant?
|

Possibly mechanoreceptors and may release neuroendocrine substance. Prevalent in stratum basale of oral mucosa and base of hair follicle
|
|
|
What is the region where the epidermis and dermis interdigitate called?
|
Rete apparatus
|
|
|
What is another name for the dermis? What is its histological morphology?
|
Corium is dense, irregular CT
|
|
|
What are the two layers of the dermis? What is the tissue composition of each?
|
Papillary layer (loose to dense irr CT)
Reticular layer (dense irr CT) |
|
|
T or F
The basement membrane between the dermis and epidermis is sparsely vascularized |
False!
|
|
|
T or F:
Both reticular and papillary layers of the dermis contain hair and glands. |
False! Only the reticular layer does, yo!
|
|
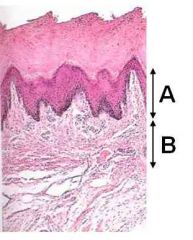
ID these dermal layers
|
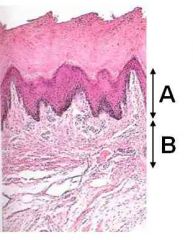
A - Papillary
B - Reticular |
|
|
T or F:
There are tons-o-immune cells in the papillary layer. |
True!
|
|
|
Which of the following are covered by thick skin?
Foot pads Tongue Eyelid Nasal plenum Teat |
Nasal plenum
Teat Foot pads |
|
|
Which sweat glands are present in thick skin? Which types of hair?
|
Merocrine sweat glands.
NO HAIR FOLLICLES!!! |
|
|
What smooth muscle is attached to hair?
|
Arrector Pili muscles
|
|
|
Which sweat glands are present in thin skin?
|
Apocrine sweat glands in all mammals (merocrine in primates)
|
|

Steve Urkel knows what kind of skin this is. How do YOU know?
|

It's thick skin! No hair follicles and presence of stratum lucidum. The stratum corneum is also really really thick.
|
|

Hey Kid
What up, Play? What kinda skin we be in? |

Thin Skin!
Check out all the glands and the hair follicle right by Play! |
|
|
What is the embryologic origin of a hair follicle?
|
Epidermis! Invades the dermis.
|
|
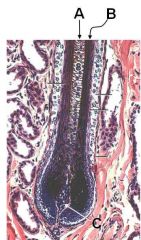
ID these regions of the hair follicle
|
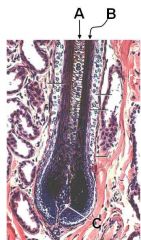
A - Medulla
B - Cortex C - Dermal papilla |
|
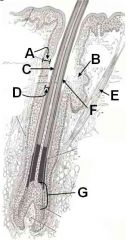
ID this mess-o-hair parts
Which contains melanocytes? |
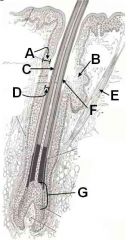
A - External root sheath
B - Sebaceous gland C - Outermost cuticle D - Internal hair sheath E - Arrector Pili m. F - Outermost cuticle (sorry put it in twice) G - Matrix (contains melanocytes) |
|
|
What is the extent of the root of the hair follicle?
|
From surface to the bulb
|
|
|
What are the three main layers to a hair shaft?
|
Outermost cuticle
Cortex Medulla |
|
|
What does the hair cortex produce?
|
Tricohyaline granules and keratin
|
|
|
What are the types of hair follicles (by size and associated structures)?
|
Primary
Secondary |
|
|
What are the types of hair follicles by # of follicles exiting from one opening?
|
Simple
Compound |
|
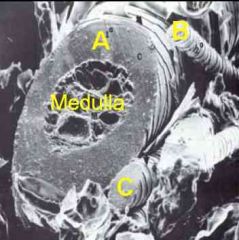
ID these hair follicles by size/associated structures.
|
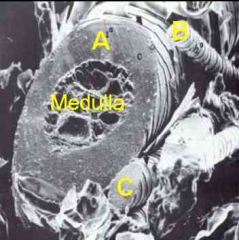
A - Primary
B - Secondary C - Secondary |
|
|
T or F:
All hairs have a cortex and medulla |
False! Not all have medullae.
|
|
|
Contrast primary and secondary hair follicle.
|
Secondary is smaller, nearer the surface and has no:
medulla sweat glands arrector pili muscles |
|
|
What type of hair usually has numerous nerve bundles and skeletal muscle associated with it?
|
Vibrissae (tactile hairs)
|
|
|
What are the main two types of skin glands?
|
Sebaceous and sweat glands
|
|
|
Describe the secretory mechanism of skin glands.
|
Sebaceous (holocrine)
Sweat (merorine or eccrine) Sweat (apocrine) |
|
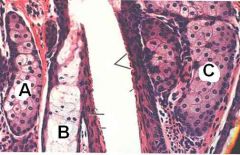
ID these glands of the skin.
What does each release? |
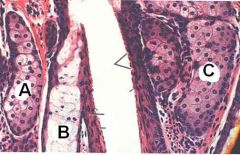
All are sebaceous glands releasing sebum.
|
|
|
Where are eccrine sweat glands mainly found?
|
Weird places (thick skin)
Foot pads – dogs and cats Frog of ungulates Planum nasolabiale in ox |
|
|
T or F:
You should see no blebbing on merocrine sweat glands. |
True!
|
|
|
T or F:
You should see blebbing on eccrine sweat glands. |
False! They are the same as merocrine sweat glands!!!
|
|
|
What is sebum composed of?
|
IGA
FAs Cholesterol Vitamin D precursors |
|
|
T or F:
You should see blebbing on apocrine sweat glands. |
True!
|
|
|
T or F:
You should see apocrine sweat glands on hairy skin. |
True!
|
|
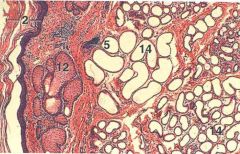
ID 12 and 14
|
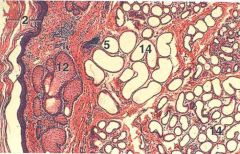
12 - sebaceous sweat gland
14 - Apocrine sweat gland |
|
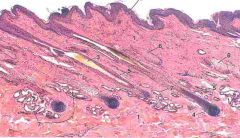
ID 6 and 7
|
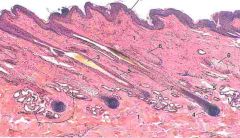
6 - Sebaceous sweat gland
7 - Apocrine sweat gland |
|
|
What is the gland morphology of the mammary gland?
|
Compound tubuloalveolar
|
|
|
Name the (3) types of glands of the anal region.
|
Circumanal glands
Anal glands Glands of the anal sac |
|
|
Where do anal glands open?
|
Open into anus
|
|
|
T or F:
A good veterinarian can express individual anal glands. |
False! I don't care how good you are, you're still expressing anal SACS!
|
|
|
What is the anal gland morphology? What does it secrete in dogs? In cats? In pigs?
|
Modified tubuloalveolar sweat glands.
Cats/Dogs - lipid Pig - mucus |
|
|
What is the secretory mechanism of anal glands? Of glands of the anal sac?
|
Anal glands are merocrine
Anal sac glands are apocrine to holocrine (sebaceous) |
|
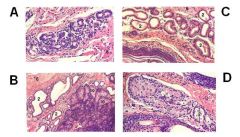
ID the following as:
Anal glands Circumanal glands Glands of the anal sac |
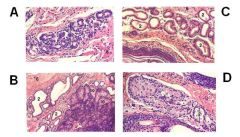
A - Anal gland
B - Glands of the anal sac C - Glands of the anal sac D - Circumanal gland |

