![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Give concise definitions of the following terms:
Autocrine Paracrine Endocrine Exocrine |
Autocrine - self-signaling
Paracrine - nearby signaling Endocrine - ductless gland, deliver via blood, target far away from signal cell Exocrine - ducted gland; directly excrete product to target |
|
|
T or F:
Hydrophilic hormones have a shorter half life than do hydrophobic hormones |
True!
|
|
|
Where are a cell's receptors for a hydrophilic hormone? How 'bout a hydrophobic hormone?
|
External
Internal |
|
|
In which type of secretion mechanism is the product stored before release? What is the opposite of this type of secretion?
|
Regulated secretion
Constitutive secretion |
|
|
What are the two types of endocrine gland cellular morphology?
|
Cord-type
Follicular |
|
|
Name some common endocrine glands:
|
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Adrenal Pineal Pancreas (endocrine portion) Thyroid Parathyroid |
|
|
From what embryological tissue does the pituitary arise?
|
Ectoderm
|
|
|
What is the anterior pituitary called? The posterior? From what tissue does each arise?
|
Adenohypophysis - oral ectoderm
Neurohypophysis - diencephalon |
|
|
What are the three parts of the anterior pituitary?
|
Pars distalis, tuberalis, and intermedia
|
|
|
What are the parts of the posterior pituitary?
|
Pars nervosa and infundibulum
|
|
|
What are the two groups of cell types found in the pars distalis?
|
Chromophobes and chromophils
|
|
|
How can chromophils be further subdivided?
|
Acidophils (somatotropes and mammotropes) and Basophils (thyrotropes, gonadotropes, and POMC cells)
|
|
|
What are the two types of acidophils and what do they produce?
|
Somatotropes > somatotropin
Mammotropes > prolactin |
|
|
What are the types of basophils and what do they produce?
|
thyrotropes > TSH
gonadotropes > LH and FSH POMC cells > POMC, ACTH, & other **** |
|
|
What modifies the production of POMC cells?
|
Pars intermedia modifies ACTH to produse alpha MSH and gamma LPH
|
|
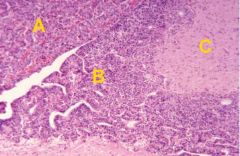
Identify the regions of the pituitary
|
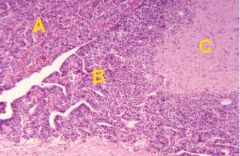
A - Pars distalis (adenohyp.)
B - Pars Tuberalis (adenohyp.) C - Neurohypophysis |
|
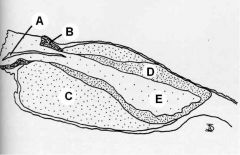
Identify these regions of the pituitary. Which make up the adenohypophysis? The neurohypophysis?
|
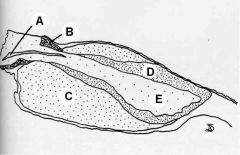
A - 3rd ventricle and infundibulum
B - Pars Tuberalis C - Pars Distalis D - Pars Intermedia E - Pars Nervosa A + E = neurohypophysis B+C+D = adenohypophysis |
|
|
Which axons terminate at the pars nervosa? What cells support these axons?
|
Hypothalamohypophyseal tract axons
Supported by pituicytes |
|
|
What do nerve terminals in the pars nervosa secrete?
|
ADH (vasopressin)
Oxytocin Neurophysins (carriers of ADY and Oxytocin) |
|
|
What are accumulations of neurosecretory granules along an axon called?
|
Herring bodies
|
|
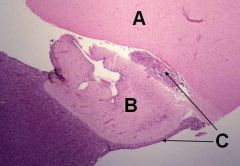
ID these hypophyseal structures
|
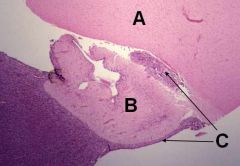
A - Hypothalamus
B - Infundibulum C - Pars Tuberalis |
|
|
What is the primary function of the hypothalamus and pituitary? Which is the master controller of the two?
|
control of homeostasis
hypothalamus controls pituitary |
|
|
What are the two main functions of hypothalamic hormones?
|
Releasing hormones
Inhibitory hormones |
|
|
T or F:
A long axon from the hypothalamus releases hormones at a primary capillary bed in the neurohypophysis which travel to a secondary capillary bed in the adenohypophysis where they excite/inhibit the secretions there. |
True!
|
|
|
T or F:
A short axon from the hypothalamus releases hormones at a primary capillary bed in the infundibulum which travel to a secondary capillary bed in the adenohypophysis where they excite/inhibit the secretions there. |
True!
|
|
|
T or F:
A long axon from the hypothalamus releases hormones at a primary capillary bed in the infundibulum which travel to a secondary capillary bed in the adenohypophysis where they excite/inhibit the secretions there. |
False! The long axons go to the neurohypophysis!
(I think that this is true...Leslie) |
|
|
What is the embryologic origin of the adrenals?
|
Neural crest and mesoderm
|
|
|
What are the 3 vascular systems of the adrenal system?
|
Subcapsular system
Cortical plexus Arterioles from cortex to medulla |
|
|
What is the capsule of the adrenal?
|
Dense, irr CT and loose CT in the outer parts
|
|
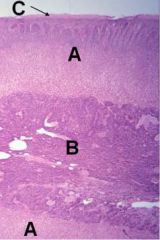
ID these regions of the adrenal
|
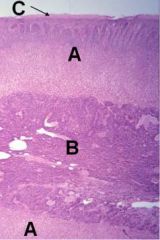
A - Cortex
B - Medulla C - Capsule |
|
|
T or F:
Most mammals have a demarcation between the medullary adrenal and cortex while birds are intermixed. |
True!
|
|
|
What are the three zones of the adrenal cortex?
|
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata Zona reticularis |
|
|
What is made in the three zones of the adrenal cortex?
|
Glomerulosa > aldosterone
Fasciculata > Cortisol Reticularis > sex hormones (DHEA, DHT, androstenedione) |
|
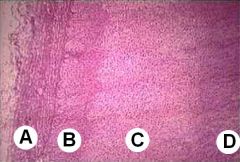
ID these layers of the adrenal
|
A - Capsule
B - Zona Glomerulosa C - Zona Fasciculatis D - Zona reticularis |
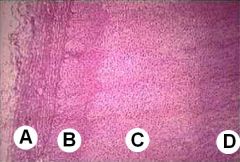
|
OK tough guy - no ID this!
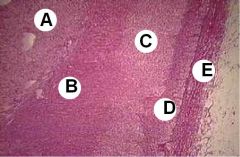
|
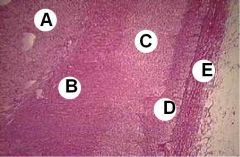
A - Adrenal medulla
B - Zona reticularis C - Zona faciculata D -Zona glomerulosa E - Capsule |
|
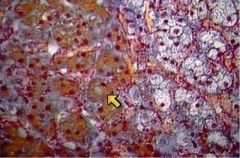
What cell type is indicated here?
What does it secrete? |
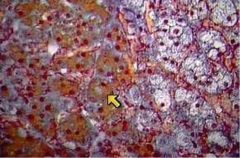
Chromaffin cell
Secretes NE and Epi |
|
|
What is the dorsal evagination of the roof of the diencephalon better known as? What is its function?
|
Pineal gland
Circadian rhythm maintenance |
|
|
What does the Pineal gland secrete and where/when is each substance secreted?
|
Serotonin - daytime - at pre-synaptic axon terminals
Melatonin - nightime - directly into capillaries (also an antioxidant) |
|
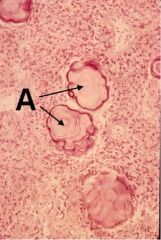
What are these dudes and what is their function?
|
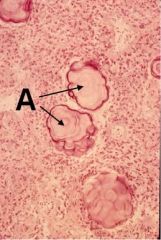
Brain Sand OR corpora aranacea OR psammona bodies
Function unknown!! |
|
|
What pancreatic structure provides endocrine function? Where are these features concentrated?
|
Pancreatic islets concentrated in the pancreatic tail
|
|
|
What are the 5 types of cells in the Islets of Langerhans?
|
Alpha - glucagon
Beta - insulin Delta - somatostatin F-cells - Pancreatic Polypeptides Gamma (C and E cells) |
|
|
Which two cell types are the most prevalent in the pancreatic islets? What do they produce? What stain acts on these cells?
|
Alpha - glucagon
Beta - insulin Gormori's aldehyde fuchsin |
|
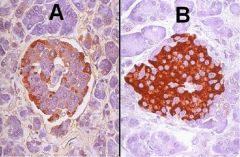
What cells are stained with antibody on slide A? Which cells on slide B?
|
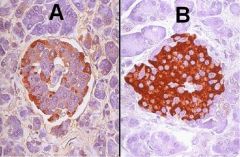
A - alpha cells
B - beta cells |
|
|
How do alpha and beta cells stain with Gomori's Aldehyde Fuchsin stain?
|
Alpha - pink (alcohol insoluble grains)
Beta - purple (alcohol soluble grains) |
|
|
Which pancreatic cells does Zollinger Ellison Syndrome effect? What effect does this have?
|
Gamma cells
Causes excess gastrin leading to duodonal ulcers and underproduction of intrinsic factor (pernicious anemia) |
|
|
What do delta cells produce?
|
Somatostatin
|
|
|
What are the main cell types in the thyroid? What does each type secrete?
|
Follicular cells - T3 and T4 (thyroxin and triiodothyronine)
Parafollicular cells (C-cells) - calcitonin |
|
|
T or F:
Follicular diameter and Folicular cell size are proportional to follicle activity. |
False!
Cell size is proportional while follicle diameter is inversely proportional. |
|
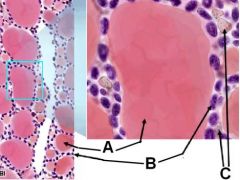
ID these regions of the thyroid
|
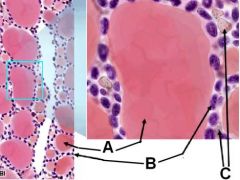
A - Follicle
B - Follicular Lining Cell C - C -Cells (parafollicular cells) |
|
|
What complexes the thyroid hormones?
|
Thyroglobulin
|
|
|
T or F:
Release of T4 is dependent upon the reabsorption of thyroglobulin while T3 is independent. |
False!
Both T3 and T4 are complexed with thyroglobulin, which must move back into the cell prior to T3/T4 release. |
|
|
T or F:
Hyperthyroidism is more prevalent in cats while hypothyroidism is common in dogs. |
True!
|
|
|
What is the embryologic (developmental) origin of the parathyroid?
|
3rd pharyngeal pouch - external parathyroid
4th pharyngeal pouch - internal parathyroid |
|
|
What are the main types of cells in the parathyroid?
|
Principal cells
Oxyphil cells |
|
|
What are the types of principal cells and what does each designation indicate about the production status of the cell?
|
Dark - active
Clear - inactive Water-clear - exhausted! |
|
|
What do principal cells secrete? What is the function of this secretion?
|
PTH (parathyroid hormone)
Ca and P regulation |

