![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of muscle is found in the tunica muscularis of the alimentary canal? What regulates these muscles?
|
Skeletal AND smooth muscle
Myenteric plexus (Auerbach's plexus) |
|
|
What are the tunics of the alimentary canal?
|
Tunica mucosa
Tunica submucosa Tunica muscularis Tunica adventitia |
|
|
What are the sublayers of the tunica mucosa?
|
Epithelium
Lamina propria Muscularis mucosa |
|
|
Which nerves provide sympathetic innervation to much of the alimentary canal? How 'bout parasympathetic innervation?
|
Sympathetic - Splanchnic nn.
Parasympathetic - Vagus and Sacral nn. |
|
|
What innervates the Tunica submucosa? What nervous system is this a part of?
|
Submucosal plexus (Meissner's plexus) is part of the enteric nervous system (along with the myenteric plexi)
|
|
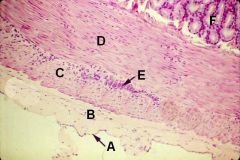
ID these layers and structures of a cross section of the alimentary canal
|
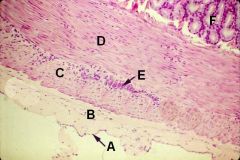
A - Mesothelium
B - Serosa C - Outer longitudinal muscle D - Inner circular muscle E - Myenteric (Auerbach's) Plexus F - Tunica submucosa |
|
|
What is the cranial and caudal extent of the oropharynx? Where is it located with respect to the soft palate?
|
Buccal cavity to esophagus
Ventral to the soft palate |
|

WHAT THE HELL IS THIS!?!?
|
calm down, dude...it's just the Larynx.
|
|
|
What kind of glands can be found in the submucosa of the esophagus? Where are these found in the ruminant? The dog?
|
Tubuloalveolar mucus secreting glands. Found in the cervical region of ruminants but throughout the canine esophagus.
|
|
|
T or F:
Pigs can't vomit. |
True (or I think it's true) - like horses and cats, pigs only have striated muscle in the cervical region. I think this is a good thing because I imagine that pig vomit is pretty f'n nasty.
|
|
|
T or F:
Tunica muscularis is not involved in gastric folds. |
True!
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is found in the stomach?
|
simple columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What are the glandular regions of the stomach? Which one(s) secrete gastric juices?
|
Cardiac
Fundic - secretes gastric juice Pyloric |
|
|
What do glands in the cardiac region secrete?
|
Mucus
Hormones (gastrin and cholecytokinin among others; not secreted into the ducts) |
|
|
What is the cell morphology in the cardiac glands?
|
Neck and upper portion - cuboidal
Remainder - columnar |
|
|
What cells secrete hormones in the cardiac region? How can they be stained?
|
Enteroendocrine (argentaffin) cells
Can stain w/ silver stain |
|
|
What cells are found in a fundic gland? What is the function of each cell type?
|
Mucous neck cells - secretes mucus
Chief cells - secretes gastric enzymes (pepsin, rennin, gastric lipase) Parietal cells - secretes HCl |
|
|
What is a good way to tell chief cells from parietal cells?
|
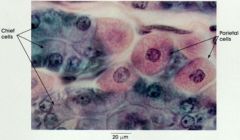
Chief cells are basophilic while parietal cells are acidophilic.
|
|
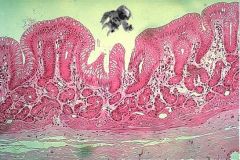
Oh no! Microman fell into the stomach! Which region is he in (and how can he tell)?
|
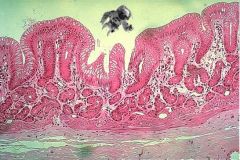
Whew. He's just in the cardiac region. Check out the mucus-producing glands and the shallow pit depth.
|
|
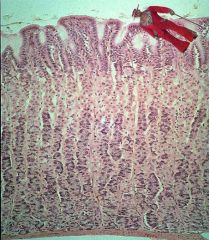
Oh no! Micropimp is in the stomach! Which region is he in and how does he know?
|
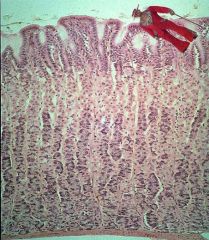
Awwww snap!
He's in the fundic gland region! He can see all the purple basophilic chief cells and the deep pits. Watch out, micropimp! |
|
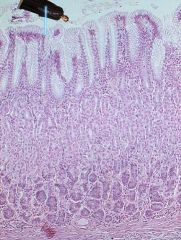
Silly Anakin Skywalker cut himself into a big stomach again. Where did he end up and how does he know?
|
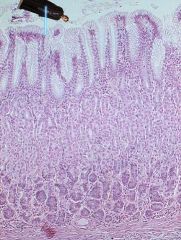
By the lack of basophilic cells, plethora of mucus producing cells, and deep gastric pits he's in the pyloric region! Watch out for that sphincter!
|
|
|
What layer forms the pylorus?
|
Tunica muscularis forms the pyloric sphincter.
|
|
|
What are the three forestomachs (that sounds funny) of ruminants?
|
Rumen, Reticulum, Omasum
|
|
|
Which forestomach is the "fermentation vat"?
|
Rumen
|
|
|
Which forestomach has the longest papillae?
|
Rumen
|
|
|
Which forestomach is the "honeycomb"?
|
Reticulum
|
|
|
T or F:
Papillae in the rumen have no muscularis mucosa. |
True!
|
|
|
T or F:
Papillae in the omasum have no muscularis mucosa. |
False! They have tons-o-muscle!
|
|
|
Which forestomach is "the book"?
|
Omasum
|
|
|
Which regions of the forestomach have muscularis mucosa in their papillae?
|
Omasum and reticulum
|
|
|
T or F:
Papillae of the reticulum and omasum contain both tunica muscularis and lamina muscularis. |
False! Only the omasum is like this.
|
|
|
What are the surface modifications of the small intestine lumenal surface?
|
Plicae circulares
Villi Microvilli |
|
|
What is found at the base of an intestinal vilus?
|
Crypts (not crips)
|
|
|
What are the regions of the small intestine?
|
Duodenum
Jejunum Ileum |
|
|
What are the glands that secrete alkaline secretions in the duodenum called?
|
Intestinal submucosal (Brunner's) glands
|
|
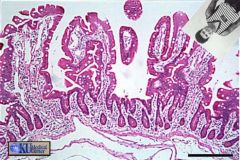
Crazy Zakk got AC Slater stuck in someone's intestine again! Where is he and how does he know?
|
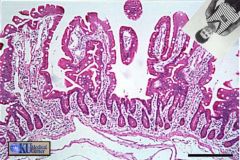
He's in the jejunum! The jejunum has fewer and thinner villi and it does have lymph nodules.
|
|
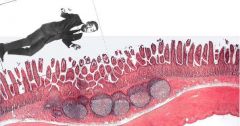
Sammy Davis Jr. lost his glass eye again and he thinks that it's those big nodules below the villi. Tell him where he really is and what those nodules are.
|
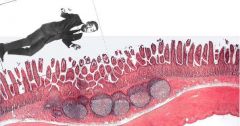
Sammy is in the Ileum. Looks like jejunum but has the Peyer's Patches of aggregated lymph nodules.
|
|
|
What are components of intestinal juice?
|
water, electrolytes, mucins, sIgA, & enzymes
|
|
|
What is a lymph vessel within a villus called and why is it milky?
|
Lacteal.
Milky due to the fats it contains. |
|
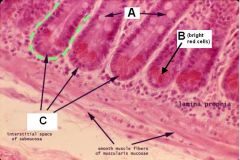
Identify A, B, and C.
What is the function of B? |
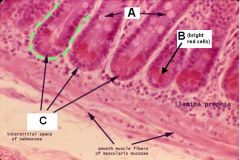
A - Goblet cells
B - Paneth cells (secrete bacteriocidal lysosyme) C - Crypts |
|
|
T or F:
The large intestine has no villi. |
True, dammit!
|
|
|
T or F:
The large intestine has rugae instead of villi. |
True, dammit!
|
|
|
Which species have a prominent cecum?
|
Horse, rabbit, guinea pig
|
|
|
What are the thickened, flat, longitudinally oriented bands of smooth muscle in the cecum and colon called?
|
Taeniae (ceci and coli)
|
|
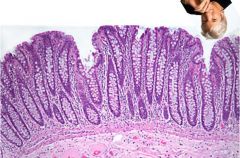
What is Richard Gere doing here? Where is he, anyway?
|
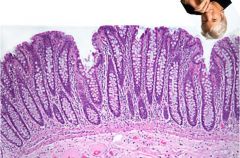
He's somewhere in the colon. Check out the lack of villi and the abundant mucous producing cells.
|
|
|
What distinguishes the recto-anal junction?
|
Marked by a transition from simple columnar epithelium with large numbers of goblet cells to stratified squamous epithelium.
|

