![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the borders of the orbit?
|
Medial - Frontal, presphenoid, lacrymal bones
Ventral - Zygomatic salivary gland and pterygoid mm. Dorsal/Lateral - Temporalis m. |
|
|
|
Which structure surrounds the muscles, nerves, and vessels of the eye?
|
Periorbita
|
|
|
|
T or F:
The periorbita is continuous with the periostium intracranially. |
False! It's continuous with Dura Mater cranially but with the periostium of the medial aspect of the orbit.
|
|
|
|
What are the three glands around the eye and what is their location?
|
Lacrimal gland - dorsolateral
Superficial gland of 3rd eyelid - ventromedial Zygomatic salivary gland - ventrolateral |
|
|
|
Which salivary gland is present in the cat but not in the dog?
|
Ventral buccal (or molar or buccal) salivary gland
|
|
|
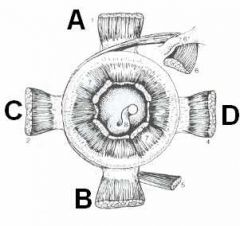
ID these muscles of the eye (caudal view; left eye)
|
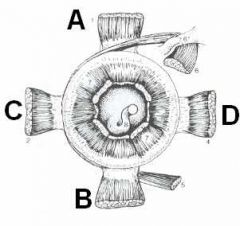
A - Dorsal rectus m.
B - Ventral rectus m. C - Lateral rectus m. D - Medial rectus m. |
|
|
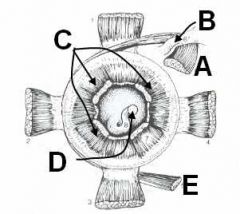
ID these structures of the eye (caudal view; left eye)
|
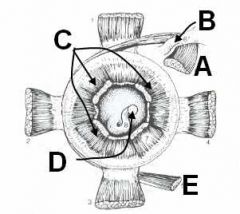
A - Dorsal oblique m.
B - Trochlea C - Retractor bulbi mm. D - Optic nerve (CNII) E - Ventral oblique m. |
|
|
|
Which muscle that is found within the periorbita does not move the eyeball?
|
Levator palpebrae superioris m.
|
|
|
|
What is the origin (not embryologic) for nearly all ocular muscles? Which is the outlier?
|
Origin - apex of orbit
Ventral oblique m. originates on the rostral palatine bone |
|
|
|
Which nerve innervates most ocular muscles? What are the outliers?
|
CNIII (Oculomotor) innervates most
CNIV (Trochlear) innervates dorsal oblique m. CNVI (Abducent) innervates Lateral rectus and retractor bulbi mm. |
|
|
|
T or F:
The retractor muscles insert caudal to the recti muscles. |
True!
|
|
|
|
What do the recti muscles control?
|
Pitch and yaw
|
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the dorsal oblique m.?
|
Trochlear n. (CNIV)
|
Remember that it goes through the TROCHLEA!!
|
|
|
What do the oblique mm. of the eye control?
|
Roll
|
My wife likes to do this with her eyes to me when I say something stupid...
|
|
|
What are the three tunics of the eye and what anatomical structures are they comprised of?
|
Fibrous (cornea and sclera)
Vascular (choroid, ciliary body, iris) Nervous (retina) |
|
|
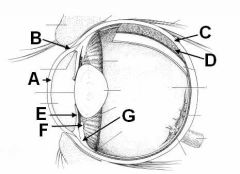
ID these structures of the eye
|
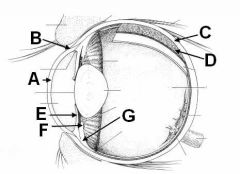
A - Cornea
B - Limbus C - Sclera D - Choroid E - Iris F - Ciliary process G - Ciliary body |
|
|
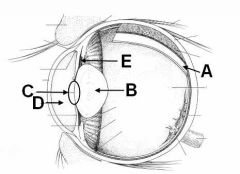
ID these structures
|
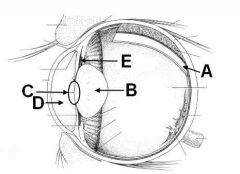
A - Retina
B - Lens C - Pupil D - Anterior chamber E - Posterior chamber |
|
|
|
What are the components of the vitreous body?
|
99% Water
Hyaluronic acid Electrolytes and collagen fibers |
|
|
|
What is the reflective layer of the cornea called? Name two species that this is found in?
|
Tapetum lucidum
Dog and cat |
|
|
|
Which structure of the eye produces the aqueous humor?
|
Ciliary processes and bodies
|
|
|
|
What muscle constricts the iris? What muscle dilates the iris? How are muscle fibers arranged in each?
|
Sphincter pupillae m. - circular
Dilator pupillae m. - radial |
|
|
|
T or F:
Sympathetic fibers innervate both the sphincter pupillae and the dilator pupillae mm. |
False! Sphincter pupillae mm. are innervated by parasympathetic fibers.
|
|
|
|
How many layers in the visual retina? What is the name for this part of the retina? How many layers in the non-visual retina and what are the names for these layers? What is the junction between the visual and non visual parts called?
|
10 - Pars optica retinae
2 - Pars ciliaris retinae et pars iridica retinae Ora serrata |
|
|
|
T or F:
The lens is a flexible, fluid-filled sac composed of epithelial cells and their secretions. |
False!
It's not fluid filled but it is flexible and it is composed of epithelial cells and their secretions. |
|
|
|
Describe the flow of aqueous humor.
|
Produced by ciliary body/processes in the posterior chamber of the anterior compartment, flows through the pupillary aperture into the anterior chamber, exits at the iridocorneal angle, through a trabecular meshwork near the limbus, to the venous scleral sinus to venous system.
|
|
|
|
T or F:
The posterior compartment contains vitreous body. While the posterior chamber contains aqueous humor. |
True! Aqueous humor flows from the posterior chamber into the anterior chamber while the posterior compartment is filled with vitreous body.
|
|

