![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are functions of the kidneys?
|
Filtration - remove toxins via urine
Conservation - salts, glucose, protein and water Regulate blood pressure through renin Hemodynamics via erythropoietin Acid base regulation |
|
|
How much blood perfused in the kidneys through large dogs daily?
How much fluid is filtered? How much urine is discharged? |
1000 to 2000 L
200 to 300 L 1 to 2 L |
|
|
Explain why kidneys are called retroperitoneal?
|
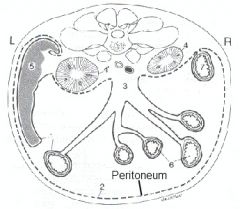
Only the ventral surface is covered with peritoneum.
|
|
|
What are the radiological landmarks for the kidneys?
How large are the kidneys? |
Right kidney - T10 - T13
Left kidney - T13 - L2 Dog - 2.5 to 3.5 x L2 length Cat - 2-3x L2 length |
|
|
In which quadrant(s) are the kidneys located?
|
Right - R cranial/caudal
Left - L cranial/caudal |
|
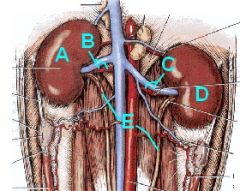
Identify this!!!
|
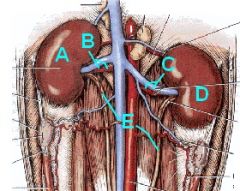
A - Right Kidney
B - Right Renal a. and v. C - Left Renal a. and v. D - Left Kidney E - R. and L. Ureters |
|
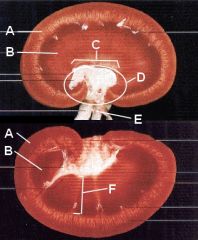
Identify all this crap.
|
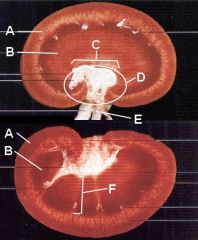
A - Cortex
B - Medulla C - Renal pelvis D - Renal sinus E - Hilus (renal v., a., ureter, lymphatics) F - Renal pyramid |
|
|
What covers the kidneys?
What is special about this structure in the cat? |
Fibrous capsule
Felines have subcapsular veins |
|
|
Contrast canine and feline kidneys
|
Feline kidneys are more easily palpated
Feline have subcapsular veins Felines have cone-shaped renal crest, dogs have longitudinal crest |
|
|
What is the function of the adrenal cortex? The adrenal medulla?
|
Cortex - production of mineralcorticoids, corticosteroids, sex hormones
Medulla - produce epi and norepi |
|
|
Mmmmm...an adrenal sandwich! What is my bread?
|
Phrenicoabdominal a. (dorsally) and v. (ventrally)
|
|
|
Check out that broad's ligament! What are the parts of this?
|
Broad ligament =
mesometrium mesovarium mesosaplinx |
|
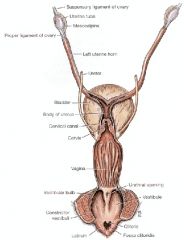
Identify this shiz.
|
A - Ovary
B - Uterine tube C - Uterine horn D - Uterine body E - Cervix F - Vagina G - Urethral orifice H - Vestibule of vagina I - Vulva w/clitoris |
|
|
What artery and vein course to/from the ovary? What structure does this course with?
|
Ovarian a. and v. course in the mesovarium.
|
|
|
T or F
The right ovary is more cranial than the left ovary. |
False.
Ha ha! I got ya! It's really true! Just like the kidneys and the testicles, the right ovary is more cranial. |
|
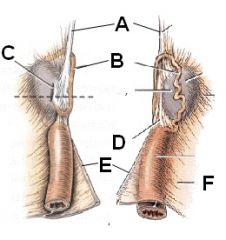
Identify this crap.
|
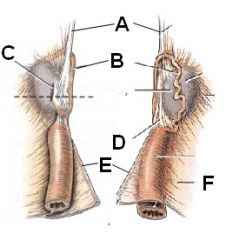
A - Suspensory ligament of ovary
B - Descending uterine tube C - Opening of ovarian bursa D - Proper ligament of ovary E - Round ligament of uterus F - Mesometrium |
|
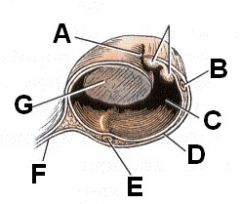
Identify this, yo! (cross-section at level of ovary)
|
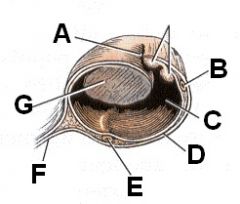
A - Opening of ovarian bursa
B - Ascending uterine tube C - Ovarian bursa D - Mesosalpinx E - Descending uterine tube F - Mesovarium G - Ovary |
|
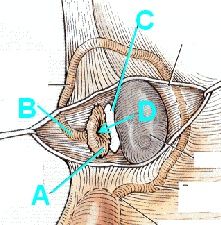
Identify or die!
|
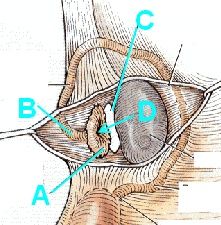
A - Infundibulum w/fimbria
B - Ampulla C - Opening of ovarian bursa D - Abdominal ostium |
|
|
What are the openings in the vestibule and where are they located with respect to one another?
|
Clitoral fossa is most ventral
Vagina is most dorsal Urethral opening is in the middle |
|
|
What is the boundary between the vagina and the uterus? What is the cranial ventral extension of the vagina called past this structure?
|
Cervix
Fornix is the region of the vagina that is cranial ventral to the cervix. |
|
|
Were do the ovarian vv. drain into?
|
Right ovarian v. - Caudal vena cava
Left ovarian v. - Left renal v. |
|
|
T or F
Fertilization commonly takes place in the tubouterine junction. |
False but close - fertilization occurs in the uterine tube
|
|

What does a bitch's uterus have in common with this metal hand?
|
They are both bicornuate
|
|
|
Describe how the female reproductive tract can provide external access to the abdominal cavity.
|
The opening of the ovarian bursa opens into the abdominal cavity. Thus, there is potential for entry into the abdominal cavity via the vagina/cervix/uterus/uterine tube/infundibulum/opening of ovarian bursa
|
|
|
Which structures are ligated in an ovariohysterectomy?
|
Ovarian a. and v.
Uterine a. and v. |

