![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the ventral and lateral boundaries of the abdominal cavity?
|
Ventral/Lateral - external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, transversus abdominis, costal arch (lateral)
|
|
|
What are the dorsal, cranial, and caudal borders of the abdominal cavity?
|
Dorsal - vertebrae and hypaxial mm.
Cranial - Diaphragm Caudal - Pelvic inlet |
|
|
What creates the rectus sheath? What is its function?
|
The aponeuroses of various abdominal muscles create the sheath. Fxn is to allow for rectus contraction/relaxation without hindrance.
|
|
|
What is the name for the serosa lining the abdominal cavity? what membrane lines the organs? What name is given to the space between these linings?
|
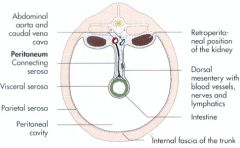
Parietal peritoneum
Visceral peritoneum Peritoneal cavity |
|
|
T or F
Kidneys are inside the peritoneal cavity but outside the abdominal cavity. |
FALSE YOU RETARD!!!!
Kidneys are inside the abdominal cavity but outside the peritoneal cavity. For this reason they are called retroperitoneal! No organs are technically within the peritoneal cavity. Kidneys are only covered by peritoneum on their ventral parts. |
|
|
What are the three types of connecting peritoneum.
|
Mesentery (eg: mesojejunum)
Ligament (eg: median ligament of bladder) Omentum |
|
|
What is a connecting peritoneum (define it, I mean)?
|
Double sheets of peritoneum extending between organs or connecting them to the parietal peritoneum
|
|
|
Describe the formation of mesenteric structures
|

1. Primitive mesentary forms on the median saggital plane containing stomach and spleen
2. Flips to the left ~180 degrees 3. Primitive dorsal mesentary = greater omentum 4. Primitive ventral mesentary = lesser omentum |
|
|
What are structures arising from the dorsal primitive mesentary?
|
Mesoduodenum
Greater Omentum Mesojejunum Mesoileum Mesocolon Mesorectum |
|
|
What organs are found within the omentum? Which leaves contain which organ?
|
Spleen - superficial leaf
Left limb of pancreas - deep leaf |
|
|
Why does Angus MacGyver like the omentum?
|
'cause it's better than even duct tape at warding-off infection
|
|
|
What is the space between the superficial and deep leaves of the greater omentum called? Why is this clinically important?
|
Omental bursa
Intestine can incarcerate here in large animals (via the epiploic foramen) |
|
|
What are the boundaries of the epiploic foramen?
|
Dorsal - caudal vena cava
Ventral - hepatic portal v. Caudal - hepatic a. Cranial - liver |
|
|
What structures arise from the primitive ventral mesentary?
|
Lesser omentum
Falciform ligament (remnant) Median ligament of the bladder (remnant) |
|
|
What ligament does the falciform ligament enclose? What is this a remnant of?
|
Round ligament of the liver
Remnant of umbilical v. |
|
|
What are the openings in the diaphragm? What courses through each opening?
|
Caval foramen - caudal vena cava
Esophageal hiatus - esophagus, vagus nn. Aortic hiatus - descending aorta, azygos v., thoracic duct Lumbocostal arch - Sympathetic trunk and major splanchnic n. |
|
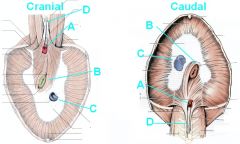
Identify these structures
|
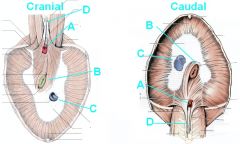
A - Aortic hiatus
B - Esophageal hiatus C - Caval foramen D - Crura of diaphragm |
|
|
What is the most cranial organ in the abdomen?
|
The liver
|
|
|
What are functions of the liver?
|
Metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Bile production. Blood storage and filtration. Excretion of bilirubin Detoxification |
|
|
What are the four general lobes of the liver?
|
Left hepatic lobe
Caudate lobe Quadrate lobe Right hepatic lobe |
|
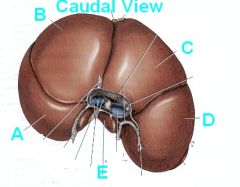
Identify the parts of the liver NOW!
|
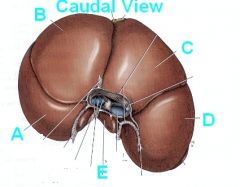
A - Left Lateral Lobe
B - Left Medial Lobe C - Right Medial Lobe D - Right Lateral Lobe E - Papillary process of Caudate Lobe |
|
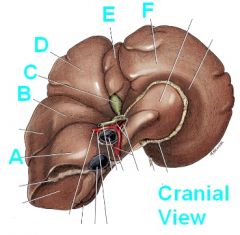
Identify these hepatic structures PUNK!
|
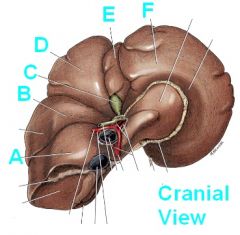
A - Caudate process of caudate lobe
B - Right lateral lobe C - Gall Bladder D - Right Medial lobe E - Quadrate lobe F - Left medial lobe |
|
|
What are the borders of the quadrate lobe of the liver?
|
From falciform ligament to the gall bladder.
|
|
|
What carries blood to the liver?
What carries blood away from the liver? |
Two vessels carry toward:
Hepatic artery (oxygen) Portal vein (nutrition) Away: Hepatic veins |
|
|
Which lobes are the gall bladder snuggled between? How 'bout the falciform ligament?
|
Gall bladder - R medial and quadrate lobes
Falciform lig - L medial and quadrate lobes |
|
|
Where do the diaphragmatic crura attach?
|
L3 and L4 vertebrae
|
|
|
What are the ligaments of the liver and what is their function?
|
Hold the liver in place
Right and Left triangular ligament Coronary ligament |
|
|
Where does bile drain into the GI tract?
|
The major duodenal papilla in the duodenum
|
|
|
What is the function of the spleen?
|
RBC storage, RBC destruction, immune system, blood filtration
|
|
|
Around which structure does the intestine rotate during fetal GI development?
|
Root of the mesentary around the cranial mesenteric a.
|
|
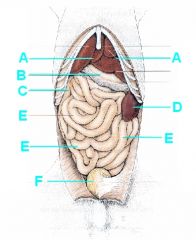
Identify this!
|
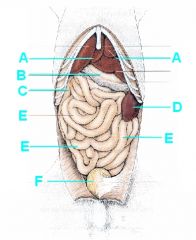
A - Liver
B - Stomach (greater curvature) C - Duodenum (descending) D - Spleen E - Jejunum, jejunum, jejunum F- Urinary bladder |
|
|
What is the origin for the abdominal quadrants?
|
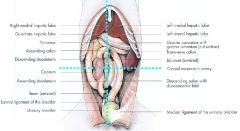
Root of mesentary at cranial mesenteric a.
|
|
|
In which abdominal quadrant(s) would the liver be found? The gall bladder?
|
Liver - left and right cranial
Gall bladder - right cranial |
|
|
In which abdominal quadrant(s) would the spleen be found?
|
Left cranial/left caudal in dorsal and left lateral recumbency.
Left cranial/left caudal/right cranial in right lateral recumbency. |
|
|
What are the parts of the GI tract located in the abdominal cavity?
|
Stomach
Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum |
|
|
Which region of the stomach is the best place to cut? What attaches here?
|
Greater curvature (omentum attaches here).
Lesser curvature is the opposite side. |
|
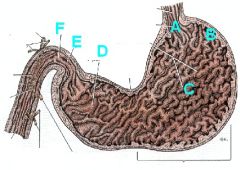
Identify the regions of the stomach and give their abdominal quadrant of location.
|
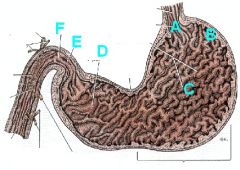
A - Cardia (L Cranial)
B - Fundus (L Cranial) C - Body (L Cranial) D - Pyloric part (pyloric antrum - R Cranial) E - Pyloric canal (R Cranial) F - Pylorus (pyloric sphincter - R Cranial) |
|
|
What are the folds within the stomach called? What is their function?
|
Rugae
Permit expansion. |
|
|
T or F
The only secretory region of the stomach is the fundus and body. |
False, silly!
The fundus and body are the regions of GASTRIC glands. The cardiac and pyloric regions secrete mucus. |
|
|
What are the regions of the small intestine?
|
Duodenum
Jejunum Ileum |
|
|
Describe the path of the duodenum with respect to the cranial mesenteric a.
|
The duodenum wraps around the cranial mesenteric a. caudally.
|
|
|
Name the regions of the duodenum and their abdominal quadrant.
|
Cranial duodenal flexure - R cranial
Descending part - R cranial Caudal duodenal flexure - R&L caudal Ascending part - L caudal Duodenojejunal flexure - L caudal |
|
|
In which quadrant is the jejunum located? How 'bout the Ileum?
|
Jejunum - all quadrants!
Ileum - L & R caudal |
|
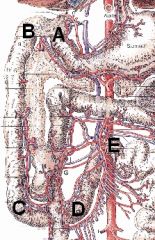
What is A > E?
A > B? B > C? C > D? D > E? What is E? |
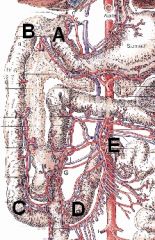
A > E - Duodenum
A > B - Cranial duodenal flexure B > C - Descending part C > D - Caudal duodenal flexure D > E - Ascending part What is E - Duodenojejunal flexure |
|
|
What are the parts of the large intestine? In which quadrants are they located?
|
Cecum - R caudal
Colon - all quadrants Rectum - L caudal |
|
|
What allows ingesta from the ileum to the colon?
|
Ileocolic orifice and sphincter muscle
|
|
|
What is the communication between the colon and the cecum called?
|
Cecocolic orifice
|
|
|
Describe the parts of the colon and which quadrant each part is located in .
|
Ascending colon - R caudal/cranial
Right Colic flexure - R cranial Transverse colon - R/L cranial Left colic flexure - L cranial Descending colon - L cranial/caudal |
|
|
Where is the transverse colon with respect to the cranial mesenteric artery?
|
Cranial to the cranial mesenteric a.
|
|
|
Where is the caudal duodonal flexure with respect to the cranial mesenteric artery?
|
Caudal to the cranial mesenteric a.
|
|
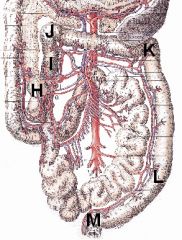
Name the following structures/regions:
H I > L I > J J J > K K K > L L > M |
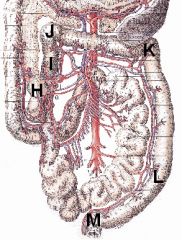
H - Cecum
I > L - Colon I > J - Ascending colon J - Right colic flexure J > K - Transverse colon K - Left colic flexure K > L - Descending colon L > M - Rectum |
|
|
At which duodenal structure(s) might a pancreatic duct empty? Name the pancreatic duct associated with each structure.
|
Major duodenal papilla (pancreatic duct)
Minor duodenal papilla (accessory pancreatic duct) |
|
|
T or F
Dogs and cats always have a pancreatic duct associated with the major duodenal papilla. |
False!
Cats always do but dogs may be reduced or absent. Dog empty their pancreas through the accessory pancreatic duct associated with the minor duodenal papilla (only present in 20% of cats) |
|
|
What are the regions of the pancreas and where are they located?
|
Body - located near pylorus of stomach
Right lobe (limb) - in mesoduodenum Left lobe (limb) - in deep leaf of greater omentum |
|
|
What are the functions of the pancreas?
|
Exocrine portion produces digestive proenzymes
Endocrine portion produces insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, gastrin, etc. |
|

Identify:
1 2 2' 3 4 |

1 - Liver
2 - Pyloric part of stomach 2' - descending duodenum 3 - Spleen 4 - Os Penis |
|
|
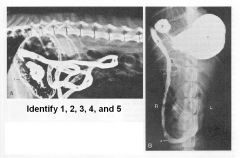
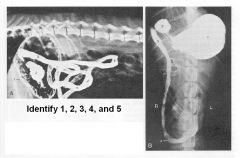
1 - Stomach
2 - Pyloric part of stomach 3 - Descending duodenum 4 - Caudal flexure of duodenum 5 - Jejunum |
|
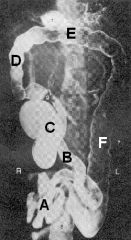
Identify A thru F
|
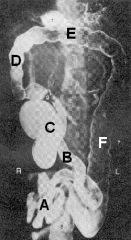
A - Jejunum
B - Ileum C - Cecum D - Ascending colon E - Transverse colon F - Descending colon |

