![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the available methods to detect dental caries?
|

1. Visual
2. Touch and Feel 3. Imaging 4. Dyes |
|
|
What classification involves the proximal surfaces of anterior teeth?
|

Class III
|
|
|
Which classification involves the gingival 1/3 of facial or lingual surfaces regardless of which tooth it is on?
|

Class V
|
|
|
What classification involves proximal and incisal edge of anterior teeth?
|

Class IV
|
|
|
What instruments are used for smoothing floors of cavity preps?
|

Chisel
Hatchet Margin Trimmer |
|
|
Which instrument is good to detect and remove decay when close to pulp?
|
Spoon Excavator
|
|
|
Which instrument is good to detect and remove decay when close to pulp?
|

Spoon Excavator
|
|
|
What does the first number on the hand instrument indicate?
|
How Wide the Cutting Edge is in 10ths of mm
i.e. 13 = 1.3 mm |
|
|
What is the cutting head shape of these burs?
1/4, 1/2, 2, 4, 6, 8 |
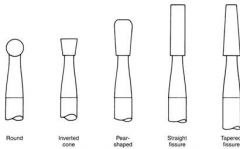
Round
|
|
|
What is the cutting head shape of these burs?
33 1/2, 34, 35 |
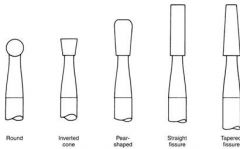
Inverted Cone
|
|
|
What are two different types of Straight fissure (cylinder) burs?
|
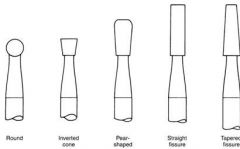
Cross Cut (556, 557, 558)
Non cross cut (56, 57, 58) |
|
|
What is the cutting head shape of these burs?
330 & 245 |
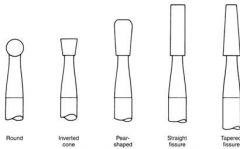
Pear Shaped
|
|
|
What is the cutting head shape of these burs?
7104, 7404, 7801 |
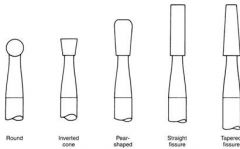
Finishing burs
|
|
|
What is the fastest speed you can polish with?
|
40,000 RPM
|
|
|
What are polishing discs useful and NOT useful for?
|
Cannot do class II. Not good for grooves.
Good for composite veneers. Useful for line angles |
|
|
What is the polishing order?
|
Coarse, Medium, Fine, Superfine
Green, Yellow, White Use goat hair brush with diamond last |
|
|
What determines the design of a cavity preparation?
|
Location of caries
Dental material used |
|
|
What is the definition of outline form?
|

The outline of the cavity as it meets the external surface. Determined by the extent of caries.
|
|
|
Define Retention form
|

Resist forces that tend to dislodge or draw the restoration along the long axis of the tooth (tensile forces)
|
|
|
What method of retention do grooves, converging walls, dovetails, and pins provide?
|

Mechanical Retention
|
|
|
What type of retention is provided by bonding/adhesion as in Composite Resin?
|

Micromechanical
|
|
|
What type of retention is provided by glass ionomer?
|

Chemical retention
|
|
|
Define Resistance form
|

Resistance form resist forces that tend to displace the restoration by torquing or tipping.
The ability of the preparation and tooth structure to resist fracture |
|
|
What does convenience form allow for?
|

Caries removal
Visibility Preparation and restoration |
|
|
What are the steps in cavity preparation?
|

...
|
|
|
T/F
When curing composite the outermost layer does not cure completely if it is not covered by the mylar strip. |
True
This is called the air inhibited layer or the oxygen inhibited layer |
|
|
What is a benefit of the air inhibited layer of composite?
|
You may add more composite to this layer without bonding
|
|
|
What are the factors affecting adhesion to tooth structure?
|
1. Physiochemical properties of the adherend and the adhesive (good wetability, good curing light)
2. Surface contaminants (clean substrate) 3. Oral environment |
|
|
What are the contents of the smear layer?
|
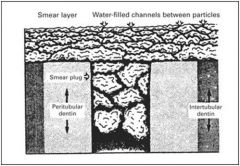
Smear Layer (0.5 - 5.0 um)
1. Pulverized hydroxyapatite 2. Altered collagen 3. Bacteria 4. Saliva |
|
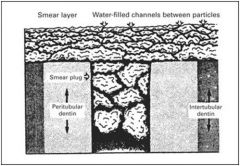
How does the smear layer affect bonding to the tooth?
|

The smear layer will NOT provide a good bond to the tooth, so it needs to be removed
|
|
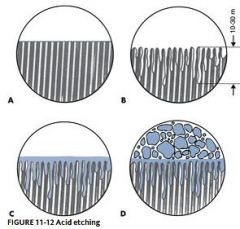
What is the purpose of acid etch?
|

Decalcifies - creates mechanical undercuts
Cleans - Phosphate detergent, removes smear layer |
|
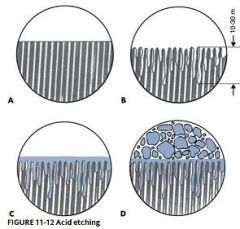
What do we use to etch teeth?
|

Phosphoric acid 35%
|
|
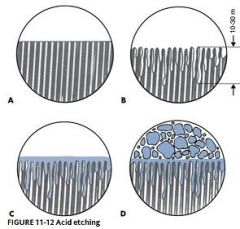
What are the Objectives of Bonding agents?
|

1. Minimize tooth preparation
2. Reduces microleakage 3. Reinforces tooth structure 4. Sealing |
|
|
What are the Characteristics of ideal dentin bonding agents?
|

...
|
|
|
What are the indications for bonding agents?
|

...
|
|
|
What is the composition of dentin bonding agents?
|

Hydrophilic resins & Solvent carrier (acetone or alcohol)
|
|
|
What is the bonding mechanism for bonding agents?
|

Mostly Micromechanical
|
|
|
T/F
No matter the bonding agent, you will always have a hydrophilic and hydrophobic part. |
True
|
|
|
What is the hybrid layer?
|
Resin interlocking with collagen fiber
-when you etch, you'll expose collagen fibers. adhesives will inflitrate and interlock with collagen fibers. This is what gives us our micromechanical retention. When it infiltrates, there is a layer that is adhesive and tooth structure (organic, collagen fibers). This is a hybrid of tooth and material. The more stable hybrid layer the stronger the bond) |
|
|
What does the primer do?
|

Primer transforms the hydrophilic dentin surface into a hydrophobic state that allows the adhesive resin to penetrate into collagen network.
|
|
|
What does the adhesive resin/bonding agent?
|

1. Hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties
2. Stabilize the hybrid layer 3. Forms the resin tags for retention |
|
|
How should the dentin be prior to application of bonding agent?
|
moist from water (but no blood or saliva)
|
|
|
When, why and where do we place a bevel?
|
Class V - incisal/occlusal cavosurface line angle - 0.5-1.0 mm bevel (note: never apply a bevel on the gingival, because the enamel is very thin. You want at least 2.0 mm)
Class II - Facial and Lingual Proximal surface - 0.5 mm - 45 deg |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Three step Total Etch system?
|
Excellent enamel and dentin bond
But, takes longer to do and primer is very hydrophilic, so you need 20-30 seconds to allow the solvent to evaporate. |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Two Steps Total Etch?
|
Good enamel and dentin bond, primer & adhesive mixed into one bottle (this is what we use at Case)
But, still takes 20 sec to allow primer in bottle to grab water and evaporate |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Two Steps Self Etch?
|
Has self-etching primer bottle and adhesive bottle
But, collagen is exposed but does not completely remove smear layer |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of One Step Self-Etch (all in one)?
|
Incompatible with self-cure resin
Poor enamel etch and poor bond |
|
|
What is the composition of composite?
|

1. Resin Matrix
2. Inorganic filler particles 3. Coupling agents 4. Activator-initiator system 5. Optical modifiers |
|
|
What makes up the resin matrix?
|

Bis-GMA & TEGDMA
|
|
|
What is a coupling agent and what is its function?
|

Provides bonding of the inorganic filler particles to the resin matrix. usually an organosilane
|
|
|
How do filler particles affect the material?
|

...
|
|
|
How are composite resins classified?
|

Method of polymerization & Particle size
|
|
|
What size are the microfil resins?
|

0.04 micron colloidal silica microfill
|
|
|
In what situation would you use Microfill over Hybrid resin?
|

Microfill - Preferred for smooth surface caries lesions or veneers
|
|
|
When would you use a Hybrid over microfill resin?
|

Hybrid - Anterior restorations including class IV and stress bearing restorations
|
|
|
How do you control shrinkage? Can you eliminate it?
|
Layer
No. The only way you can eliminate shrinkage is if you cure composite 100% outside (i.e. in the lab) then cement in the mouth. |
|
|
What is rebonding?
|
If you need to add more composite and there is no air inhibited layer then you need to etch and rebond. This is also true if you need to seal an area off.
|
|
|
What are the advantages of posterior composite restorations?
|
1. Aesthetics
2. Conservation of tooth structure 3. Adhesion to tooth 4. Low thermal conductivity 5. Elimination of galvanic current 6. Radiopacity |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of posterior composite restorations?
|
1. Polymerization shrinkage
2. Postoperative sensitivity 3. Marginal leakage 4. Technique sensitive 5. Isolation 6. Time consuming 7. Discoloration |
|
|
What are the indications for posterior composites?
|
Indications
1. Aesthetics 2. Class V 3. Small to moderate class I and class II if amenable to isolation 4. Repair |
|
|
What are the contraindications for posterior composites?
|
Contraindications
1. Adequate isolation not possible 2. Loss of excessive tooth structure 3. Subgingival margins 4. All contacts on restoration |
|
|
When do you use calcium hydroxide prior to etching?
|
only in areas close to the pulp
|
|
|
How do you deal with subgingival margin if restoring with composite?
|
If you cannot isolate, don't do the composite! Take impression and make composite onlay or inlay, then cement in place. Otherwise it may break or debond. Also it can leak, have open margin, leading to decay underneath.
|

