![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Perichondrium |
The connective tissue that surrounds cartilage where it isn't a joint; feedsthe cells in the cartilage matrix via its blood vessels |
|
|
Appositional Growth |
newtissue is laid down on the outside of the existing structure; Cartilagegrows from the outside
|
|
|
Intersitinal Growth |
newtissue is created within the matrix of existing cartilage; Cartilagegrows from within |
|
|
Axial Skelton |
Composed of the skull, vertberae, ribs (thoracic cage) and coccyx |
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton |
Includes limb bones (arms and legs), pelvic and shoulder girdles |
|
|
Diaphysis |
Shaft of longs bones |
|
|
Epiphyses |
Head of bone |
|
|
Periosteum |
Double-layeredmembrane that surrounds bone
|
|
|
Endosteum |
coversinternal bone surfaces (trabeculaeinspongy bone and canals through compact bone)
|
|
|
Trabeculae |
anastomosing bony spicules in cancellous bone which form a meshwork of intercommunicating spaces that are filled with bone marrow.
|
|
|
Foramina |
an opening, hole, or passage, especially in a bone.
|
|
|
Dipole |
Spongy bone in flat bones |
|
|
Hematopoetic |
Red marrow |
|
|
Osteoclasts |
bone destroying cells |
|
|
Osteocytes |
A branched cell embedded in the matrix of bone tissue.
|
|
|
Osteoblasts |
addto bone thickness (appositional growth)
|
|
|
Osteon |
atube or cylinder of bone matrix
|
|
|
Haversian Canal |
any of the minute tubes that form a network in bone and contain blood vessels
|
|
|
Canaliculi |
Connectingadjacent osteocytes
|
|
|
Interstitial Lamellae |
Liebetween proper osteons to fill gaps mayhave been an osteon that was “remodeled” during growth from injury
|
|
|
Circumferential lamellae |
Formthe outer layers of the diaphyses oflong bonesH
|
|
|
Osteiod |
composedof collagen and glycoproteins, which are made by osteoblasts
|
|
|
Wolff's Law |
bone in a healthy person or animal will adapt to the loads under which it is placed.
|
|
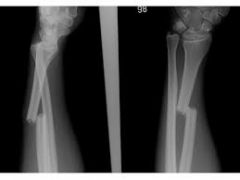
|
displaced fracture |
|
|
Osteoporosis |
Whenbone resorptionoutpaces bone deposit
|
|
|
Rickets |
bones not sufficiently mineralized
|

