![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
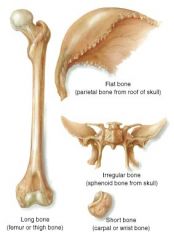
Types of Bone - Diagram
|
|
|
|
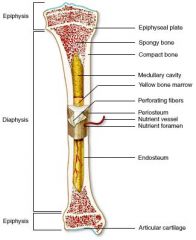
Bone Structure - Diagram
|
|
|
|
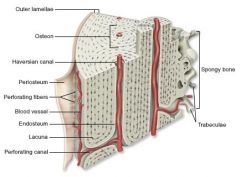
Bone Histology - Diagram
|
|
|
|
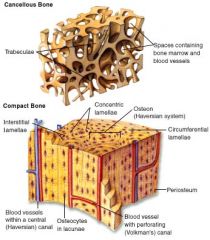
Spongy & Compact Bone Histology - Diagram
|
|
|
|
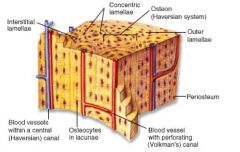
Compact Bone Histology - Diagram
|
|
|
|
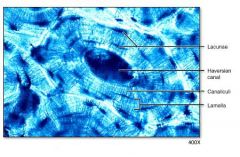
Cross Section of Dried Compact Bone - Diagram
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 main types of bone?
|
Compact, or cortical and spongy, or cancellous
|
|
|
What is Wolff's Law of Bone Adaptation?
|
Bone models and remodels in response to the mechanical stresses it experiences so as to produce a minimal-weight structure that is "adapted" to its applied stresses
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of ossification?
|
Intramembranous and endochrondral
|
|
|
What is intramembranous ossification?
|
When a bone develops from a fibrous membrane & results in the formation of cranial bones of the skull & clavicles. Mostly flat bones; starts ~ week 8 of development in mesenchymal cells
|
|
|
What is endochrondral ossification?
|
An embryonic process in which hyaline cartilage functions as a pattern for bone formation; forms all the bones of the body except clavicles and skull; begins in 2nd month of development
|
|
|
What are the 6 bone groups w/ examples?
|
1. Flat, ex. sternum
2. Irregular, ex. vertebrae 3. Long, ex. humerus 4. Sesamoid, ex. patella 5. Sutural (Wormian), ex. lambdoid suture in skull |
|
|
What is the axial skeleton?
|
The long axis of the body; includes skull, vertebral column and rib cage
|
|
|
What is the appendicular skeleton?
|
Bones of the upper and lower limbs and the girdles that attach them
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of bone markings?
|
1. Cavities
2. Depressions 3. Projections |
|
|
Sinus
|
A cavity w/in a bone, filled w/ air and lined w/ mucus membrane
|
|
|
Fissure
|
A narrow, slit-like opening
|
|
|
Foramen
|
A round or oval opening through a bone
|
|
|
Fossa
|
A shallow, basin-like depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface
|
|
|
Groove
|
A furrow in a bone
|
|
|
Meatus
|
A canal-like passageway
|
|
|
Condyle
|
A rounded articular projection
|
|
|
Crest
|
A narrow ridge of bone, usually prominent
|
|
|
Epicondyle
|
A raised area on or above the condyle
|
|
|
Facet
|
A smooth, nearly flat articular surface
|
|
|
Head
|
A bony expansion carried on a narrow neck
|
|
|
Line
|
A narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest
|
|
|
Process
|
Any bone prominence
|
|
|
Ramus
|
An arm-like bar of bone
|
|
|
Spine
|
A sharp, slender, often pointed projection
|
|
|
Trochanter
|
A very large blunt, irregularly shaped process
|
|
|
Tubercle
|
A small rounded projection or process
|
|
|
Tuberosity
|
A large rounded projection; may be roughened
|
|
|
Articular cartilage
|
Covers the ends of most bones at movable joints
|
|
|
Diaphysis
|
A tube, or shaft forming the long axis of the bone
|
|
|
Endosteum
|
Delicate connective tissue membrane covering the internal surfaces of long bone
|
|
|
Epiphyseal line
|
Between the diaphysis and each epiphysis
|
|
|
Epiphyseal plate (growth plate)
|
On long bone; A disc of hyaline cartilage that grows during childhood to lengthen the bone
|
|
|
Epiphysis
|
End of long bone
|
|
|
Medullary cavity
|
"Middle;" marrow cavity in long bone
|
|
|
Nutrient foramen
|
An opening in long bone for nerve fibers, lymphatic vessels, and blood vessels
|
|
|
Periosteum
|
A glistening white, double-layered membrane covering the external surface of long bone, except joint surfaces
|
|
|
Trabecula (ae)
|
Honeycomb of small needle-like or flat pieces making up spongy bone
|
|
|
Red marrow
|
Hematopoietic tissue typically found w/in the trabecular cavities of spongy bone of long bones and in deploe of flat bones
|
|
|
Yellow marrow
|
Fat found in long bones
|
|
|
Canaliculi
|
In compact bone; tiny canals radiating outward from a central canal to the lacunae of the 1st lamella and then from lamella to lamella
|
|
|
Haversian canal
|
Also "central canal;" runs through core of an osteon in compact bone and contains small blood vessels and nerve fibers
|
|
|
Lacunae
|
Small spaces at junctions of lamellae in compact bone; occupied by osteocytes
|
|
|
Lamellae
|
Matrix tubes composing osteon in compact bone; tubes layered around each other like rings on a tree
|
|
|
Osteoblast
|
Bone-forming cells
|
|
|
Osteoclast
|
Large cells that resorb or break down bone matrix
|
|
|
Osteocyte
|
Mature bone cell; spider-shaped; occupying lacunae
|
|
|
Osteon (Haversian system)
|
Structural unit of compact bone; elongated cylinder oriented parallel to the long axis of the bone; group of hollow tubes of bone matrix
|
|
|
Volkmann's canals
|
Lie at right angles to the long axis in compact bone and connect the blood and nerve supply of the periosteum to those in the central canals and medullary cavity
|
|
|
Bronchial cartilage
|
Reinforces the bronchia; hyaline
|
|
|
Costal cartilages
|
Connect the ribs to the sternum; hyaline
|
|
|
Intervertebral discs
|
Discs between vertebrae; fibrocartilage
|
|
|
Laryngeal cartilages
|
Reinforce the larynx; hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
Nasal cartilage
|
Supports the external nose; hyaline
|
|
|
Tracheal cartilages
|
Reinforce the trachea; hyaline
|
|
|
Perichondrium
|
Fibrous connective tissue membrane covering the external surface of cartilaginous structures
|
|
|
Elastic cartilage
|
Contains more stretchy elastic fibers than hyaline cartilage and so are better able to stand up to repeated bending; only found in the external ear and the epiglottis
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage
|
Highly compressible w/ great tensile strength; parallel rows of chondrocytes alternating w/ thick collagen fibers; found in menisci of the knee and discs between vertebrae
|
|
|
Hyaline cartilage
|
Provides support w/ flexibility and resilience
|
|
|
Scoliosis
|
Abnormal lateral curvature of the vertebral column that occurs most often in the thoracic region
|
|
|
Kyphosis
|
Hunchback; dorsally exaggerated thoracic curvature of the vertebral column
|
|
|
Lordosis
|
Swayback; accentuated lumbar curvature
|
|
|
Atlas vertebra
|
C1; has no body and no spinous process
|
|
|
Axis vertebra
|
C2; has knob-like "dens" projecting superiorly from body
|
|
|
Dens of C2
|
Knob-like projection; acts as pivot for atlas rotation
|
|
|
What are the 3 groups of vertebrae and how many are there in each group?
|
1. Cervical (neck) - 7
2. Thoracic - 12 3. Lumbar - 5 |
|
|
Nucleus pulposus
|
Inner gelatinous; gives disc its elasticity and compressibility
|
|
|
Annulus fibrosus
|
A strong collar composed of collagen fibers
|
|
|
True ribs
|
Superior 7 rib pairs that attach directly to the sternum
|
|
|
False ribs
|
Inferior 5 pairs of ribs that attach indirectly to the sternum or entirely lacking a sternal attachment
|
|
|
Vertebrochondral ribs
|
Rib pairs 8-10 that attach to sternum indirectly
|
|
|
Floating ribs
|
Rib pairs 11 & 12; they have no anterior attachments
|
|
|
7 bones that make up the orbit
|
"Master Zeus Palpatates Seven Foxy Ladies Everyday"
1. Maxillary 2. Zygomatic 3. Palatine 4. Sphenoid 5. Frontal 6. Lacrimal 7. Ethmoid |

