![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
epiphysis pathology |
chondroblastoma, giant cell tumor |
|
|
metaphysis pathology |
osteosarcoma, enchondroma, osteochondroma, aneurysmal bone cyst |
|
|
diaphysis pahtology |
adamantinoma, osteoid osteoma, chondromyxoid fibroma, fibrous dysplasia, fibrosarcoma, fibrous cortical defect, bone cyst, round cell lesions |
|
|
osteoblast maturation |
osteoprogenitor cells exposed to Runx2, Wnt, BMP |
|
|
Dwarfism - achondroplasia |
reduce chondrocyte proliferation in growth plate; AD; short proximal extremity, normal trunk, enlarged head; GOF mutation FGF receptor 3 |
|
|
Dwarfism - thanatophoric dwarfism |
rare, lethal; FGFR3 mutation, shortened limbs & small chest => resp. insufficiency |
|
|
osteogenesis imperfecta |
brittle bone disease; problem w/ type 1 collagen production; very fragile skeleton; AD; see blue sclera, blue teeth, multiple fractures in utero and at birth |
|
|
osteopetrosis |
osteoclast dysfunction; reduced bone resorption & diffuse skeletal sclerosis; fracture like chalk; very rare |
|
|
Osteoporosis |
age related bone loss; very common; incr. porosity of the skeleton |
|
|
Paget's disease (osteitis deformans) of bone |
regions of osteoclastic bone resorption followed by marked bone formation = thick bone; AD pattern, late adulthood |
|
|
Paget's disease etiology |
environmental & genetic factors; SQSTM1 gene mutation that incr. NF-KB activation of osteoclasts |
|
|
Paget's disease - histology |
mosaic patterns of lamellar bone (osteosclerotic phase); also osteolytic and mixed phases |
|
|
Hyperparathyroidism |
osteitis fibrosa cystica; brown tumor + sheets of osteoclasts; no inflammation, bone is replaced w/ cysts & fibrous tissue |
|
|
fracture healing |
blood clot -> neutrophils -> macrophages -> soft tissue callus -> activate osteoblasts -> boney callus -> excess bone cartilage and fibrous tissue -> remodel callus along stress liens |
|
|
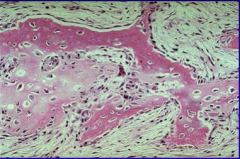
fracture callus |
|
|
avascular necrosis (osteonecrosis) |
common; located in medullary cavity; caused by vascular interruption, corticosteroids, thrombosis & embolism, vessel injury, venous HTN |
|
|
osteomyelitis |
acute or chronic; S. aureus most common; draining sinus; dead bone separates (sequestrum) |
|
|
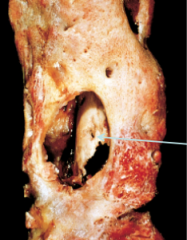
osteomyelitis w/ sequestrum necrotic bone |
|
|
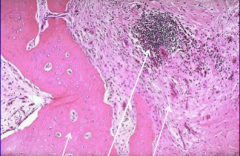
chronic osteomyelitis w/ reactive bone, inflammation & fibrosis |
|
|
Osteoma |
benign; immobile tumor of mature bone (skull, facial) |
|
|
Osteoid osteoma |
<2cm diameter; teens + 20s; M>F; 50% in femur or tibia; present w/ severe nocturnal pain |
|
|
osteoblastoma |
like osteoid osteoma, >2cm, mostly in spine; present w/ dull pain |
|
|
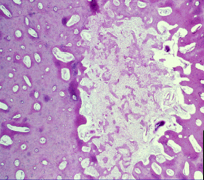
osteoid osteoma |
|
|
osteoid osteoma |
|
|
osteosarcoma |
malignant mesenchymal tumor producing bone matrix; mostly <20 yo; in metaphyseal region of long bones; most common in knee |
|
|
osteosarcoma presentation |
painful bone or fracture; 20% w/ pulmonary mets; lytic & blastic mass that breaks thru cortex; Codman triangle (lifted periosteum) |
|
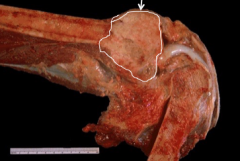
|
osteosarcoma - gross |
|
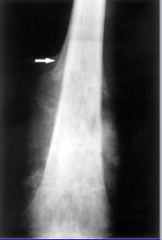
|
osteosarcoma - xray |
|
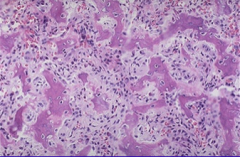
|
osteosarcoma histology; see malignant disorganized osteoblasts w/ large bizarre nuclei |
|
|
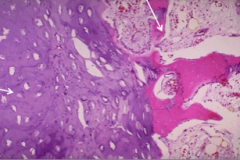
Osteochondroma |
benign cartilage-capped tumor; MC benign bone tumor; most solitary; formed by exostosis (bony outgrowth) |
|
|
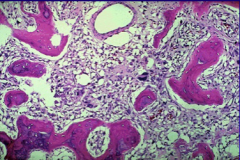
osteochondroma - histology |
|
|
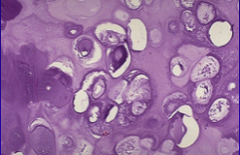
Chondroma |
benign tumor of hyaline cartilage; most solitary; in medullary cavity = endchondroma |
|
|
Ollier's disease |
multiple chondromas |
|
|
Maffucci's syndrome |
chondroma a/w hemangioma |
|
|
chondroma |
|
|
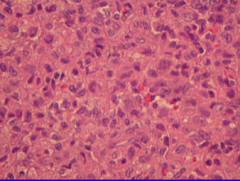
chondroblastoma |
rare, young, painful, benign; F>M, usually around knee |
|
|
chondroblastoma |
|
|
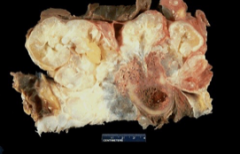
chondrosarcoma |
produce neoplastic cartilage; can be intramedullary or juxtacortical; diff histologies (hyaline, clear cell, dedifferentiated, mesenchymal); involve central skeleton, mets to lungs & skeleton |
|
|
chondrosarcoma epidemiology |
40+ y/o, M>F; arise along w/ endchondroma, fibrous dysplasia or Pagets |
|
|
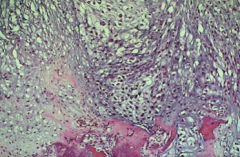
chondrosarcoma - gross |
|
|
chondrosarcoma - histology |
|
|
chondromyxoid fibroma |
rare, young; 3-8cm w/ cartilage, fibrous & myxoid areas; present w/ dull pain; benign |
|
|
Fibrous cortical defect (non-ossifying fibroma) |
very common; children >2y/o; developmental defect in tibia & femur; mostly asympomatic, resolve |
|
|
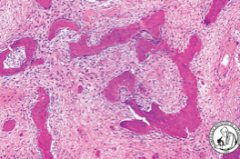
fibrous dysplasia |
benign; normal bone that doesn't mature properly; can enlarge and distort the bone; chinese letter trabeculae; present in 20-40 y/o |
|
|
McCune-Albright syndrome |
polyostotic fibrous dysplasia + cafe-au-lait skin + pigmentations + endocrinopathy |
|
|
fibrous dysplasia |
|
|
Fibrosarcoma (Malignant fibrous histiocytoma) |
older patients; collagen-producing tumor, malignant |
|
|
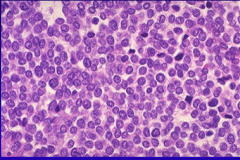
Ewing sarcoma |
small round cell tumor; have neurophenotype, c-myc oncogene; 2nd MC bone tumor in kids; translocation of EWS fusion protein; present w/ painful mass & low grade fever; mass in femur, flat bones of pelvis |
|
|
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor |
like Ewing sarcoma but in adults; extraskeletal presentation |
|
|
Ewing sarcoma |
|
|
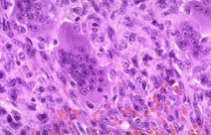
Giant cell tumor |
benign locally aggressive; proliferating osteoclasts; incr. RANKL promotes osteoclast precursor proliferation; epiphyses & metaphyses affected; knee; 20-40 y/o; pain and fractures; recur if not totally removed |
|
|
giant cell tumor of bone |
|
|
Aneurysmal bone cyst |
benign tumor; multiloculated blood-filled cystic spaces; a/w 17p13 translocation; first 2 decades; metaphyses of long bones & vertebral bodies |
|
|
MC malignancy in bone? |
metastatic tumors |
|
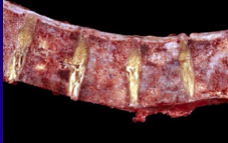
|
metastatic lesion - lytic |
|
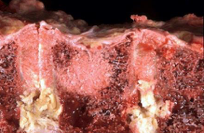
|
metastatic lesion - blastic |
|
|
Osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease) |
erosion of articular cartilage; caused by aging (primary), trauma (secondary, younger); women = hands/knees, men = hips; osteophytes impinge spinal nerves; Heberden nodes on fingers |
|
|
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) |
chronic systemic infl. autoimmune disorder w/ nonsuppurative proliferative synovitis -> articular cartilage destroyed, ankylosis |
|
|
Joints in RA |
synovium thick & hyperplastic (pannus), perivascular infiltrate, lymphoid follicles; eventual fibrosis & joint destruction (ankylosis) |
|
|
Skin in RA |
rheumatoid nodules; subQ granulomas that are firm and non-tender w/ central fibrinoid necrosis surrounded by macrophage rim |
|
|
Blood vessels affected in RA |
small to medium size arteries (not kidney) |
|
|
autoantibodies in RA |
Fc portion of autologous IgG (rheumatoid factors), citrulline-modified peptide antibodies |
|
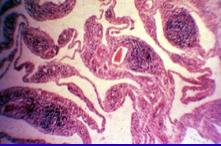
|
RA - pannus; histology |
|
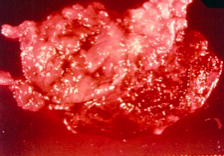
|
RA - pannus; gross |
|
|
stages of RA symptoms |
early = swollen fingers, hyperpigmentation & reducible deformities advanced = ulnar deviation, subluxation of M-P joints |
|
|
ankylosis of joints - RA |
|
|
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis - Juvenile RA |
2:1 female; oligoarthritis more common, systemic onset; large joints affected; RF positive or negative, positive ANA |
|
|
seronegative spondyloarthropathies |
ankylosing spondyloarthritis, negative RF, pathologic change in ligamentous attachments, boys>girls; HLA-B27 positive |
|
|
Reiter syndrome |
reactive arthritis of fingers, toes, low back pain; conjunctivitis; men in 20s and 30s; HLA-B27; many have ankylosing spondolysis |
|
|
Enteropathic arthritis |
cause = bowel infection; HLA-BL2 positive; abrupt arthritis involving knee & ankles; no ankylosing spondylitis |
|
|
Psoriactic arthritis |
chronic infl. arthropathy a/w psoriasis; peripheral & axial joints & ligaments/tendons; HLA-B27 & HLA-Cw6; 30-50 y/o; DIP joints |
|
|
infectious arthritis |
suppurative (staph, strep, GC), sickle cell patient (salmonella); one joint is swollen & hot |
|
|
Gout |
hyperuricemia; urates deposited into joints & tissue (tophi) |
|
|
Pseudogout |
over 50, esp. >85 yo; Ca pyrophosphate crystals released into joint, cause infl. |
|
|
ganglion cyst |
near joint capsule or tendon, common, myxoid degeneration of CT; benign |
|
|
giant cell tumor of tendon sheath |
clonal proliferation of synovocytes, giant cells & histiocytes; knee; benign but can recur |
|
|
villonodular synovitis (giant cell tumor) |

