![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the central nervous system (CNS) organs? |
brain and spinal chord |
|
|
What is the neuron? |
The conducting cell that transmits electrical signals called nerve impulses and is the primary form of communication in the CNS. |
|
|
What are nerve impulses? |
electrical signals that travel along an axon because there is a difference in electrical potential inside and outside the axon like a tiny battery
|
|
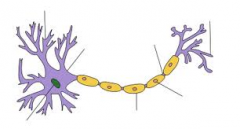
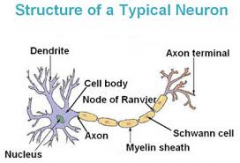
Label the neuron |
|
|
|
Neurons are made up of a cell body, dendrites, axon, axon terminal and a myelin sheath. What functions do each of these conduct? |
cell body - contains nucleus and other organelles similar to body cells and collects info from the dentrites and passes it along to the axon. dentrites - extends cell body and receive a nerve impulse fromanother neuron. Many dentrites extend from the cell body in order to increase the neuronal connections with other nerves. axon - a long membrane bound extension to the cell body that passes the nerve impulse onto the next cell myelin sheath - a fatty layer of cells that cover the axons of most neurons in order to insulate and protect the axon and also speed up transmission through the axon
|
|
|
What do the dentrites do? |
They receive information and take it TO the cell body, which gathers it and the axon takes the message AWAY from the cell body and passes it onto the next cell. |
|
|
What is a synapse? |
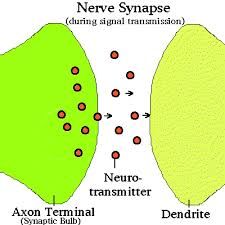
it's a small gap separating neurons - found at the end of the axon terminal and helps connect a single neuron to thousands of other neurons |
|
|
In a synapses there are neurotransmitters, what are they and what do they do? |
-chemical messages released at the synapse and passes the ' message' (impulse) onto the next neuron or other type of cell - neurotransmitter molecules are made inside the pre synapse neuron and stored in the axon terminal - when an impulse reaches the axon terminal, the neurotransmitter is released into the synapse space and travels across to receptors on the postsynaptic nerve of another cell |
|
|
What is a reflex?
|
an involuntary, unconscious, instantaneous reaction to a stimulus and carried out through a reflex arc e.g knee jerk reaction when patella tendon is hit or pupils of the eyes dilute in dim light or the dark and constrict in bright light |
|
|
What is a conditioned reflex? |
voluntary or conscious or learned e.g. sport technique |
|
|
What is a simple reflex? |
involuntary/ unconscious or rapid |
|
|
What's a reflex arc, what parts is it made up of? |
a neural pathway that controls an action reflex and is made up of three parts - sensory neuron carries the stimulus message from the receptor to the - interneuron or relay neuron in the CNS - neuron carries the response message FROM the CNS to the effector (muscle or gland) |
|
|
What do all sense organs have? |
receptors that are specific for certain stimuli |
|
|
What are hormones? |
chemical messages produced in the endocrine glands. They speed up or slow down the processes in the body and slow down or stop processes and stimulate growth |
|
|
How do hormones move throughout the body? |
released to the circulatory system which carries them through the body |
|
|
Why is the hypothalamus considered the Control centre of the endocrine system? |
It regulates activities of the other endocrine glands |
|
|
Define endocrine system |
regulates and controls varowus body functions and activities |
|
|
Define exocrine glands |
responsible for tears, sweat or digestive juices and they are located in the body near the organs they affect |
|
|
Define hypothatamus |
controls whole endocrine system and is considered the control centre - linked to the nervous system |
|
|
Name the glands of the endocrine system |
hypothalamus, pituitary,parathyroid, thyroid, thymus, adrenal, pancreas (Islets of Langerhans), ovaries, testes |
|
|
Define Pituitary |
controls blood pressure, chemical and physical activities, growth, sexual development, reproduction and controls other glands
|
|
|
Define thymus |
involved in the development of the immune system produces white blood system during infancy |
|
|
define thyroid
|
controls metabolism in the body, production of protein, development of nervous system and affects growth rate of children |
|
|
Define Parathyroid |
regulates blood calcium and phosphate levels |
|
|
Define adrenal |
produces the hormone adrenaline, increases heart rate, breathing blood sugar/pressure. this happens because you need more enjoy aka 'flight or fight ' hormone |
|
|
Define Islets of Langerhans |
inside pancreas and produces insulin and glucagon which controls the blood sugar levels |
|
|
Define ovaries and testes |
ovaries - create oestrogen which create wider hips, enlarge breasts, body hair
testes - androgen which produces deeper voices, body hair, enlarges muscles and bones |
|
|
Explain how the reflex arc works |
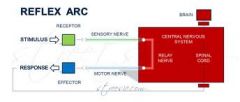
|
|
|
An example of a reflex arc would be a person pulling away their hand from a flame. Explain what happens |
pain sensors in hand impulse to sensory neuron |
|
|
What happens if a motor neuron is damaged? |
It will be sent on sensory pathway Control Neutral Centre, wahich will send the impulse to a different motor neuron and she will pull her arm away but at a slower rate. |
|
|
Define Insulin, what does it do. |
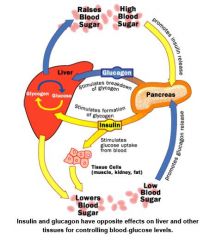
It lowers sugasr levels, helps cells use sugar as energy, excess sugar stored as glycogen (opposite to glucasgone) |
|
|
What can diabetes lead to? |
Heart disease, kidney failure and blindness |
|
|
What is negative feedback? |
It's a pathway of responses that result in changing the original stimulus in order to reestablish homeostasis
Process whereby the body sense a change from the set point - every system in body has set point - of the internal condition and activates a process to work against that change |
|
|
What is homeostasis? |
A process of maintaining a stable internal environment desite variations in external conditions. "Homeo" is same and "stasis" is to stay or stand
Cells work best when the surrounding conditions are kept constant or within an optium/limited range |
|
|
Why is homeostasis important? |
It keeps the body systems working
Factors that need to be controlled are blood PH, blood pressure, water/salt balance, oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations, blood glucose/sugar levels, body temperature |
|
|
Why are enzymes important to homeostasis? |
Enzymes change the rate of chemical reactions in the body. Changes to internal conditions can affect enzyme initiated chamica reactions A decrease in enzyme activity can lead to a decrease in essential compounds in the body |
|
|
How do organisms respond to stimuli? |
Organisms need to monitor changes in the external and internal environments in order to maintain homeostasis.
Internal and External stimuli help the body monitor changes to the internal or external environments |
|
|
What are the internal and external physicsal factors of stimuli? |
External - light or chemical factors such as Oxygen and CO2 concentration.
Internal - Core body temp or chemical factors such as changes in CO2 levels |
|
|
How are changes of the environment detected and what are the internal and external ones. |
They are detected by receptors. External receptors include ears, eyes, nose, tongue and skin. Internal receptors are the nerve cells. |
|
|
Where and what is the core temperature of the body detected by? |
It's detected by nere cells situated in the hypothalumus part of the brain |
|
|
Blood glucose levels regulate in mammals with the hormone insulin and glugagon, produced by the pancreas and help the body to do what?If the body is unable to produce this what will happen. |
regulate the metabolism of glucose. If the body is unable to produce enough insulin or is resistant to its effect, diabetes will result |
|
|
Responses to the environment that maintain internal stability are called? What brings these? Some of these responses asre very rapid known as the...? |
Homeostatic responses
Effectors bring about these responses
withdrawl reflex e.g. pull away when you touch something hot |
|
|
What is an example of negative feedback relating to air conditioners? |
Analogy is the thermostat in an airconditioner which reponds to the changing air temp by turning the air conditioner on or off to maintain a constant air temperature. |
|
|
Explain the stimulas pathway |
stimulus is detected by a receptor> signal sent to control centre such as brain> sends signal to nervous or hormonal system> sends a message to an effector ( muscle or gland) wahich carries the desired response |
|
|
What is the stimulus? |
a thing or event that evokes a specific functional reaction in an organ or tissue. |
|
|
Which effects are slower, hormonal or nervous responses? |
The hormonal effects are slower but the effects are longer in duration than the effects of the nerves. |
|
|
How does homeostasis work? |
In animals homeostasis is carried out by the nervous and endocrine systems, which are most highly developed in mamals
Nervous system coordinates rapid responses to stimuli
Endocrine sstem uses hormones to maintain the activity of tissues and organs. Hormones asre produced in specialized glands.
Hypothalumus is th control centre for homeostasis and is linked to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. |
|
|
What is a nephron? |
It's the basic structure and functional part of the kidney |
|
|
What are the functions of the nephron? |
Concentrates water and soluble substsances to filter out waste
Controls the electolytes and metabolites
Regulates blood volume and blood pressure |
|
|
Define glomerulus |
small molecules are forced by pressure from blood into BowMan's Capsule |
|
|
Define Bowman's capsule |
collects the filtraste ( collects good and bad salts) |
|
|
Define Looop of Henle |
reabsorbs "good" salts from filtrate back into blood |
|
|
Define Collecting Duct |
reabsorbs water only if ADH is present |
|
|
Define ureter |
Transports urine from the kidneys to bladder |
|
|
Define bladder |
stores urine |
|
|
define urethra |
transports urine from bladder to outside body |
|
|
Define renal artery and vein(blood vessels) |
Takes deoxgenated blood and filters blood back to heart |
|
|
Define ADH |
ADH (pituitary gland)is the chemical that tells the kidneys how much water to conserve. ADH constantly regulates and balances the amount of water in the blood. Higher water concentration increases the volume and pressure of the blood. Anti Divretic Hormone
If there's no ADH no water is absorbed |
|
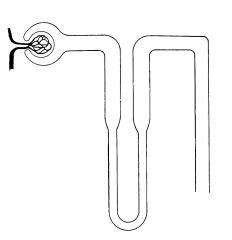
Label the structure of a nephron |
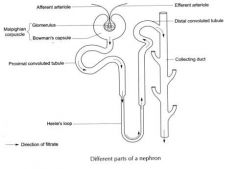
|
|
|
What happens during the fitration process? |
Blood pressure forces fluid through the capilary walls in the glomerus. Large molecules are left behind and the remainder that passes through is called the filtrate. This is collected by the Bowman's Casule and enters tubules |
|
|
What happens during the reabsorbtion? |
About 90% of the blood filtrate is reabsorbed in the first region of the nephron. Reabsorbtion allows useful substances such as glucose viatamins, amino acids are essential ions to be retained. |
|
|
What happens during secretion? |
The kidney is able to rid the body of unwanted substances. Like drugs, by sacrating them into the tuble just before the urine enters the linal region of the nephron, collecting duct. |
|
|
What is diffusion? |
It's the process wherby molecules in a concentrated pocket of gas or liquid spread evenly throughout the meduim in which they are found. Molecules move from an area with a high concentration to a low concentration |
|
|
What is a semi permeable membrane? |
a membrane that will allow some molecules to pass but not others |
|
|
What is Osmosis? |
It is the movement of water across a membrane from areas of high water concentration eg. dilute solutions to areas of low concentration e.g. concentrated solutions |
|
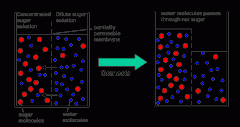
Which side is hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic? |
Hypotonic is the side with less sugar but more water, so the water would flow out of this side Has low concentration of solute molecules high concentration of water molecules and low osmotic pressure
Hypertonic is more sugar but less water so water would flow into this side. It has high concentration of solute molecules, low concentration of water molecules and high osmotic pressure
Isotonic is equal concentrations of sugar on each and there is no movement of water |
|
|
Why are cells smal but have a larger surface area? |
They are small because they need nutrients and oxygen and they need to get the waste products out. Alos if the cell is small then the products won't have to travel far to goin and out of the cell. The cells have a large surface area becuase of the many folds which increase the surface areas example alveoli in the lungs or villi i the small intestine. |

