![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Unilateral renal agenesis associations |
Men: 20% have ipsilateral epididymis/vas deferens absent, or seminal vesicle cyst
Women: Unicornuate uterus (Mayer Rokitansky) |
|
|
What is the Potter Sequence? |
In-utero insult (ACE inhibitors?), kidneys don't form, no urine, no lungs (pulmonary hypoplasia) |
|
|
What is Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser? |
Unilateral renal agenesis and absence or atresia of the uterus |
|
|
Pancake adrenal |
Used to differentiate between surgical vs congenital absent kidney |
|
|
Teel me about Horseshoe kidney |
Recurrent infections = increase risk of TCC Increased risk of Wilms (8x higher) Associated with Turners syndrome |
|
|
Crossed fused renal ectopia |
More often the left kidney crosses The ectopic kidney is inferior |
|
|
Calcifications in a fatty renal mass? |
RCC until proven otherwise |
|
|
Risk factors for RCC? |
Tobacco, chronic dialysis, family history |
|
|
Medullary RCC is associated with what disease? |
Sickle cell trait (very aggressive) |
|
|
Chromophobe RCC is associated with what disease? |
Birt-Hogg-Dube |
|
|
Clear cell RCC is associated with what disease? |
VHL |
|
|
Papillary RCC is associated with what disease? |
Hereditary papillary renal carcinoma |
|
|
RCC stage 1? |
Limited to kidney and <7cm |
|
|
RCC stage 2? |
Limited to kidney but >7cm |
|
|
RCC stage 3 (a, b and c)? |
Vein invasion but limited to Gerota's Fascia A: Renal vein B: IVC below diaphragm C: IVC above diaphragm |
|
|
RCC stage 4? |
Beyond Gerota's fascia |
|
|
ADPKD increased risk for RCC? |
No, unless the patient is on dialysis |
|
|
What is a benign renal tumor with a central scar? |
Oncocytoma (spoke wheel on US)
-Associated with Birt-Hogg-Dube -Treated like RCC until proven otherwise -Hotter than surrounding renal parenchyma on PET (unlike RCC) |
|
|
Renal macroscopic fatty tumor? |
Angiomyolipoma
(associated with Tuberous Sclerosis) (can bleed if >4cm) (lipid poor if they are T1 dark) |
|
|
Renal mass with non-communicating, fluid filled locules which protrudes into the renal pelvis? |
Multilocular cystic nephroma |
|
|
Typical occurrence of Multilocular Cystic Nephroma? |
Bimodal: 4 year old boys 40 year old women (Michael Jackson) |
|
|
Bosniak? Simple cyst, no enhancement |
Class 1 |
|
|
Bosniak? Hyperdense (<3cm), thin calcifications, thin septations |
Class 2 |
|
|
Bosniak? Hyperdense (>3cm), minimally thickened calcifications |
Class 2F (5% chance of cancer) |
|
|
Bosniak? Thick septations, mural nodule |
Class 3 (50% chance cancer) |
|
|
Bosniak? Any enhancement |
Class 4 |
|
|
Ddx for a T2 dark renal cyst? |
Hemorrhagic cyst Lipid poor AML Papillary RCC |
|
|
Tell me about ADPKD? |
Adult 70% get liver cysts Berry aneurysms (risk of RCC only if on dialysis) |
|
|
Tell me about ARPKD? |
Hypertension Congential hepatic fibrosis Echogenic kidneys with loss of corticomedullary differenetiation
Could show large abdomen with small chest (pulmonary hypoplasia) |
|
|
Explain VHL? |
Autosomal dominant 50-75% have renal cysts 25-50% develop RCC (clear cell)
Pancreas: cysts, neuroendocrine tumors, serous microcystic adenomas
Adrenal: Pheochromocytomas
CNS: Hemangioblastomas, endolymphatic sac tumors
Epididymal cystadenomas |
|
|
Explain Tuberous Sclerosis? |
Autosomal dominant. Hamartomas everywhere
Renal: AMLs, RCC in younger patients Lung: LAM Cardiac: Rhabdomyosarcoma Brain: SEGA, subcortical tubers, subependymal nodules |
|
|
Bipolar patient with multiple tiny renal cysts? |
Lithium nephropathy |
|
|
Tiny cysts in utero or newborn, oligo? |
MCDK
(Non-communicating cysts, no functional renal tissue)
Dismal prognosis is bilateral Conservative treatment if unilateral |
|
|
Renal cyst originating from the renal sinus and looks like hydro? |
Peripelvic cyst |
|
|
Renal cyst originating from the parenchyma, compresses the collecting system? |
Parapelvic cyst |
|
|
Striated nephrogram ddx? |
Pyelonephritis Medullary sponge kidney Acutely after contusion Acute ureteral obstruction Radiation nephritis Acute renal vein thombosis
|
|
|
Diabetic patient with echogenic foci and dirty shadowing on US? |
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (really bad!) |
|
|
"Bear paw" sign with staghorn calculus and psoas abscess? |
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis (Struvite calculus) |
|
|
Most common cause of papillary necrosis? |
Diabetes!
Others: Pyelonephritis, sickle cell (analgesic use), TB, cirrhosis |
|
|
Shrunken calcified kidney with cavitary lung mass? |
Renal TB |
|
|
Prepuberty uterus and streaky ovaries? |
Turner Syndrome
(also coarctation and horseshoe kidney) |
|
|
Mullerian agenesis with renal agenesis or ectopia? |
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser |
|
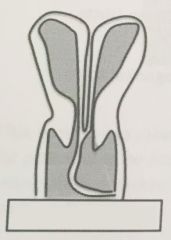
|
Uterus Didelphys (complete uterine duplication |
|
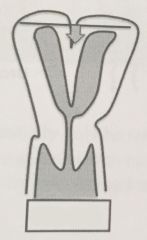
|
Bicornus
(unicollis or bicollis) (separation of uterus by deep myometrial cleft) |
|
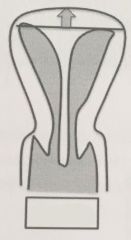
|
Septate
(two endometrial canals separated by muscular or fibrous septum) (has a higher fundal apex contour) |
|
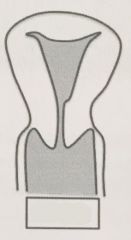
|
Arcuate uterus
(normal variant) |
|
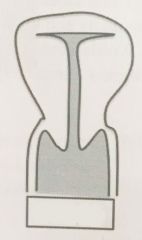
|
T-shaped
(DES related, vaginal clear cell carcinoma) |
|
|
Infertile patient with multiple diverticula involving the fallopian tube? |
Salpingitis isthmica nodosa |
|
|
High velocity serpiginous structure in myometrium in a patient with prior D&C (or abortion, c-section, multiple pregnancies)? |
Uterine AVM |
|
|
Intrauterine filling defects on HSG, or T2 dark bands on MRI in infertile patient? |
Ashermans or endometrial synechia
(due to D&C, surgery, pregnancy, or infection...TB) |
|
|
Order of fibroids (by location)? |
Intramural, subserosal, submucosal |
|
|
Fibroid without enhancement, T2 dark? |
Hyaline degeneration |
|
|
Fibroid without enhancement with peripheral rim of T1 high signal, pregnant woman? |
Red (carneous) degeneration
(due to venous thrombosis) |
|
|
Fibroid with minimal gradual enhancement, T2 bright? |
Myxoid degeneration |
|
|
thickening of the junctional zone, thickened posterior wall, foci of T2 high signal in uterus? |
Uterine adenomyosis |
|
|
HNPCC causes increased risk of what cancer other than colon? |
Endometrial |
|
|
What ovarian tumor secretes estrogen and can cause a thickened endometrial stripe? |
Granulosa Cell tumor |
|
|
Limit for post-menopausal endometrial stripe on and not on Tamoxifen? |
4mm in a normal patient 8mm with Tamoxifen use |
|
|
Cervical cancer Stage IIA? |
Spread beyond cervix but NO parametrial invasion
Surgery only |
|
|
Cervical cancer Stage IIB? |
Parametrial involvement but NO pelvic sidewall extent.
Chemo/Radiation and Surgery |
|
|
Main type of cervical cancer? |
Squamous cell |
|
|
Vaginal mass with a history of mom using DES? |
Clear cell adenocarcinoma
(plus a T-shaped uterus) |
|
|
Most common vaginal cancer in children? |
Rhabdomyosarcoma (age 2-6 and 14-18) |
|
|
A met to the anterior wall upper 1/3 vagina came from where? |
Genital tract |
|
|
A met to the posterior wall lower 1/3 vaginal came from where? |
GI tract |
|
|
Cyst in the cervix? |
Nabothian |
|
|
Cyst in anterior lateral wall of upper vagina? |
Gartner duct cyst |
|
|
Cyst in vagina below pubic symphysis? |
Bartholin gland cyst |
|
|
Most common cause of genital ambiguity in females? |
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
|
|
Patient with meningitis and adrenal hemorrhage? |
Waterhouse-Friderichsen Syndrome |
|
|
What is the organ of Zuckerkandl? |
An area of extra adrenal tissue located near the origin of the IMA. A pheochromocytoma can present here. |
|
|
What is the "Rule of 10s" for pheochromocytomas? (5) |
10% are extra-adrenal 10% are bilateral 10% are in children 10% are hereditary 10% are NOT active |
|
|
What conditions are associated with pheochromocytomas? |
VHL MEN IIa and IIb NF-1 Sturge Weber Tuberous Sclerosis Carney Triad |
|
|
Whats the difference between the Carney Triad and the Carney Complex? |
Carney Triad: Extra-adrenal pheo, GIST, pulmonary chondroma
Carney Complex: Cardiac myxoma, skin pigmentation |
|
|
Common mets to adrenal gland? |
Lung, breast, melanoma |
|
|
What are the adrenal washout equations? |
Absolute: E-D ----- x 100 >60% is Adenoma E-U
Relative: E-D ----- x 100 >40% is Adenoma E |
|
|
Bilateral enlarged calcified adrenal glands with hepatosplenomegaly? |
Wolman Disease |
|
|
MEN? Pituitary adenoma, parathyroid hyperplasia, pancreas (gastrinoma) |
MEN I (PiParPanc) |
|
|
MEN? Medullary thyroid cancer, parathyroid hyperplasia, pheochromocytoma |
MEN IIa (PMP) |
|
|
MEN? Medullary thyroid cancer, marfanoid habitus/mucosal neuroma, pheochromocytoma |
MEN IIb (PMMM) |
|
|
Carcinoid syndrome implies mets to where? |
Liver |
|
|
What type of thyroid cancer contains microcalcifications? |
Papillary |
|
|
Enhancing nodule in a thyroglossal duct cyst? |
Papillary thyroid cancer |
|
|
Most common location for ectopic thyroid tissue? |
Lingual thyroid |
|
|
Most common cause of hyperthyroidism and goiter? |
Graves (autoimmune disease, antibody against TSH receptor) |
|
|
Increased uptake of I-123 with %RAIU 50-80%? |
Graves |
|
|
Most common cause of hypothyroidism and goiter? |
Hasimotos |
|
|
Woman with a painful thyroid gland after an upper respiratory infection? |
Subacute thyroiditis |
|
|
%RAIU during acute phase of subacute thyroiditis? |
Low |
|
|
What are the IgG4 associated diseases? |
Reidels thyroiditis Orbital pseudotumor Retroperitoneal fibrosis Sclerosing cholangitis |
|
|
Where could the infection have started in a child that has acute suppurative thyroiditis? |
4th brachial cleft anomaly via a pyriform fistula |
|
|
Comet artifact on thyroid US? |
Colloid nodule |
|
|
Type of thyroid cancer that produces calcitonin? |
Medullary |
|
|
What types of thyroid cancer do NOT respond to I-131? |
Medullary, Anaplastic and Hurthle cell |
|
|
What types of thyroid cancer respond well to I-131? |
Papillary and Follicular |
|
|
What is the classic pattern of thyroid cancer mets to the lungs? |
Miliary |
|
|
Risk of treating metastatic thyroid cancer to the lung with I-131? |
Pulmonary fibrosis |
|
|
What factors does sestamibi parathyroid imaging depend on? |
Mitochondrial density and blood flow |
|
|
What is the cumulus oophorus? |
Collection of cells in a mature dominant follicle, signals imminent ovulation |
|
|
Ovary with multilocular "spoke-wheel" appearance? |
Theca lutein cysts, related to overstimulation by bHCG.
1. Multifetal pregnancy 2. Molar pregnancy 3. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome |
|
|
Patient with theca lutein cysts, ascites, and pleural effusions? |
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome |
|
|
Best time to perform a PET scan on a woman in regards to menstrual cycle? |
First 7-10 days of the cycle |
|
|
Size cutoff of a postmenopausal woman with ovarian cyst who needs further workup? |
7cm needs MRI or surgical evaluation |
|
|
Round mass with homogenous low-level echoes and increased through transmission? (Uterus) |
Endometrioma |
|
|
Risk factor for an endometrioma for turning into a cancer? |
1. Size > 6-9cm 2. Age > 45 years old |
|
|
How to differentiate between an endometrioma and a hemorrhagic cyst? |
Re-image in 1-2 menstrual cycles, the cyst will get smaller or go away |
|
|
Most likely diagnosis for a large, simple-appearing, unilocular cyst in a postmenopausal woman |
Serous ovarian cystadenoma |
|
|
Psuedomyxoma peritonei comes from what? |
Ruptured mucinous tumors: 1. Appendiceal mucinous adenocarcinoma 2. Mucinous ovarian cystadenocarcinoma |
|
|
What is Meigs syndrome? |
Pleural effusion, ascites and benign ovarian tumor (usually fibroma) |
|
|
What is a Krukenberg tumor? |
Mets to the ovary that secrete mucin, usually from GI source |
|
|
Benign ovarian tumor with calcification? |
Brenner tumor |
|
|
Osteochondrosis of the tarsal navicular? |
Kohler |
|
|
Osteochondrosis of the 2nd metatarsal head? |
Freiberg infraction |
|
|
Most common carpal coalition? |
Lunotriquetral |
|
|
Management for simple adnexal cyst >5 and <7cm? |
Almost certainly benign, annual follow up ultrasound |
|
|
Management for simple adnexal cyst >7cm? |
Not definitively benign, MRI or surgical consult follow up |

