![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
clinical definition of HTN
|
systolic > 140
and/or diastolic > 90 |
|
|
2 main things that determine pressure
|
CO and inc'd PVR
|
|
|
t/f: catecholamines and Ang II decrease PVR
|
F, inc
|
|
|
% of primary HTN cases
|
95%
|
|
|
mnemonic for the secondary HTN's
|
Renal --> most common 2ndary
Endocrine Neurologic Aortic Labile |
|
|
complication mnemonic for HTN
|
Heart hypertrophy
Eye changes (retinopathy) Aortic Dissection/Aneurysm Renal Disease Thalamic Hemorrhage (strokes) |
|
|
what direct effect does renal artery stenosis cause
|
renal hypoperfusion
|
|
|
some examples of 2ndary labile HTN
|
psycogenic
stress post-op |
|
|
Genetic d/o's causing inc mineralocorticoids ==> HTN
|
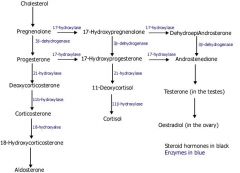
GRA
11B hydroxylase deficiency 17a hydroxylase deficiency |
|
|
inc'd mineralocorticoid receptor activity is weird side effect of what candy
|
licorice
|
|
|
which type of HTN (chronic/malignant) affects ALL arteries and arterioles
|
chronic
|
|
|
chronic HTN AKA
|
benign HTN
|
|
|
chronic htn causes hyaline changes in ______
|
arterioles
|
|
|
chronic htn causes thickening of the media d/t inc'd amts of collagen, elastic tissue, smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts where (arteries or arterioles)
|
muscular arteries
|
|
|
malignant htn causes what type of changes
|
hyperplastic arteriolar accompanied by fibrinoid necrosis
|
|
|
"onion skinning" is assoc. w/ which type of htn
|
malignant
|
|
|
acute/severe elevations of BP cause what?
|
hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis
|
|
|
htn is the most important risk factor for IHD over what age
|
45
|
|
|
atherosclerotic aneurysms mostly found in which part of the aorta
|
abdominal
|
|
|
cirsoid aneurysms are caused by?
|
atherosclerosis of splenic artery
|
|
|
berry aneurysms related to defect in muscle layer of
|
cerebral arteries
|
|
|
syphilitic aneurysms usually occur in the _____ aorta
|
thoracic
|
|
|
false aneurysms most often assoc. w/
|
post MI (ventricular TI)
|
|
|
definition of true aneurysm
|
affects entire wall of artery
|
|
|
initial dilation of aneurysm is usually saccular or fusiform
|
fusiform
|
|
|
which is more often assoc. w/ aneurysm complication salmonella or staph
|
salmonella then staph
|
|
|
t/f clinical presentation of AA can be Asx w/ only prominent abdominal aortic pulsations
|
t
|
|
|
aneurysm risk of rupture related to size:
<4cm = ? 4-5cm = ? 5-6cm = ? >6cm = ? |
no risk
1% 11% 25% |
|
|
what size aneurysm is surg indicated in
|
>5cm
|
|
|
t/f aortoenteric fistulas are not a late complication of reconstructive aortic surg
|
f, they are
|
|
|
better prognosis: thoracic or abdominal
|
abdominal
|
|
|
arteriosclerotic aneurysms of ateries in extremities are rare except in what 2 LE arteries
|
popliteal and femoral
|
|
|
7 factors assoc. w/ dissecting aneurysms
|
1. htn
2. marfan's 3. pregnancy 4. bicuspid aortic valve 5. trauma 6. atherosclerosis 7. inflammatory injuries |
|
|
dissection usually begins w/ a _____ _____ tear assoc. w/ an intimal plaque located in the _____ or _____
|
transverse intimal
ascending aorta or upper descending thoracic aorta near subclavian artery |
|
|
atherosclerosis _____
|
SUCKS!!!!
|
|
|
t/f dissection usually involves just a portion of the aorta as it progresses distally
|
f, entire circumference of aorta
|
|
|
what is arterial dilation most likely initiated by
|
loss of elasticity of recoil strength in arterial wall
|
|
|
what is usually found in the sacculation
|
laminated clot
|
|
|
type I aortic dissection location
|
ascending aorta extending beyond
|
|
|
type II aortic dissection location
|
ascending aorta only
|
|
|
type IIIA aortic dissection location
|
begins in descending aorta but stops above diaphragm
|
|
|
type IIIB aortic dissection location
|
begins in descending aorta and extends below diaphragm
|
|
|
dissecting aneurysms also classed according as? (3)
|
subacute, acute, chronic
|
|
|
varicosities usually involved in what venous system
|
saphenous
|
|
|
what other veins are affected?
|
perianal and pampiniform plexus
|
|
|
primary cause of varicose veins
|
inherent weakness in vessel wall (43% FHx)
|
|
|
2ndary cause of varicose veins? (2)
|
xs back pressure
weakening of wall by inflammation (vasculitis) |
|
|
6 things that predispose you to venous thrombosis
|
1. cardiac failure
2. neoplasia 3. pregnancy or post partum 4. obesity 5. prolonged stasis 6. hypercoag states (factor V leiden) |
|
|
what website did he get his facts about DVT and air travel?
|
continental
|
|
|
90% of DVT's come from where
|
deep veins of LE's
|
|
|
what vein is the usual suspect in DVT's?
|
popliteal
|
|
|
DVT can present clinically by (3)
|
local LE pain
tenderness erythema at DVT site |
|
|
migratory thrombophlebitis assoc. w/ pancreas, colon, lung CA AKA
|
trousseau
|
|
|
phlegmasia alba dolens AKA ____ occurs in ____ vein during what conditions _(3)__
|
milk leg
iliofemoral 3rd trimester, postpartum, or pelvic surg |
|
|
Vena Caval obstruction (VCO) is DVT variant caused by external occlusion usually in the ____ vena cava
|
external occlusion (tumors, aneurysms)
superior |
|
|
VCO caused by internal obstruction more commonly found in the _____ vena cava from the _____ and ____ veins
|
inferior
lower limbs and renal |
|
|
cystic hygroma(turner's syndrome), lung lymphedema, or cystic lymphangectasis and familial milroy's dz are what?
|
congenital conditions causing lymphatic obstruction
|
|
|
acquired obstructive lymphadema caused by (6)
|
1. lymphangitis
2. parasites 3. metastasis 4. irradiation 5. trauma 6. surg |
|
|
extreme LE lymphadema refered to as
|
elephantiasis
|

