![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
175 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
blood is 3-4 times more viscous than
|
h2o
|
|
|
most blood cells form in
|
red bone marrow
|
|
|
types of blood cells are
|
red blood cells, white blood cells
|
|
|
cellular fragments of blood are
|
platelets
|
|
|
formed elements of blood are
|
red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
|
|
|
blood volume varies with
|
body size, changes in fluid, electrolyte concentrations, amount of adipose tissue
|
|
|
blood volume is about ------- of body weight
|
8%
|
|
|
an average-size adult has ------ liters of blood
|
5
|
|
|
hematocrit is
|
percentage (packed cell volume)
|
|
|
a blood sample is usually -----% red blood cells and remaining -----% plasma
|
45.....55
|
|
|
plasma is a mixture of
|
h2o, amino acids, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, vitamins, hormones, electrolytes, cellular wastes
|
|
|
less than 1% of formed elements of blood are ----- and 99% are -----
|
white blood cells and platelets..... red blood cells
|
|
|
blood cells originate in ----- from -----
|
red bone marrow..... hematopoietic stem cells or hemocytoblasts
|
|
|
a stem cell can differentiate into
|
more stem cells
|
|
|
thrombopoietin stimulates
|
large cells-megakaryocytes
|
|
|
red blood cells are also called
|
erythrocytes
|
|
|
red blood cells are ----- in shape
|
distinct (tiny, biconcave, thin middles, and thick outer rim)
|
|
|
the biconcave shape of red blood cells allow them to
|
squeeze through narrow capillaries
|
|
|
hemoglobin is
|
oxygen carrying
|
|
|
each red blood cell is about ----- hemoglobin by volume
|
1/3
|
|
|
oxyhemoglobin is
|
(bright red) hemoglobin combines with oxygen
|
|
|
deoxyhemoglobin is
|
(bluish) oxygen is released
|
|
|
red blood cells extrude their ----- as they mature
|
nuclei
|
|
|
because red blood cells lack mitochondria they must produce ATP through
|
glycolysis only, use none of the oxygen they carry
|
|
|
as red blood cells age, they become ----- and are more likely to be damaged and are removed by -----
|
less active.....the spleen and liver
|
|
|
a red blood cell count is
|
number of red blood cells in a microliter
|
|
|
a healthy adult male has a red blood cell count between
|
4,600,000 to 6,200,000 per microliter
|
|
|
a healthy adult female has red blood cell count between
|
4,200,000 to 5,400,000 per microliter
|
|
|
a healthy child has a red blood cell count between
|
4,500,000 to 5,100,000 per microliter
|
|
|
the number of red blood cells reflects the bloods
|
oxygen carrying capacity
|
|
|
erythropoiesis is
|
red blood cell formation
|
|
|
initially, red blood cell formation occurs
|
in yolk sac, liver, and spleen
|
|
|
after an infant is born. red blood cells are produced
|
by tissue lining the spaces in bones, filled with red bone marrow
|
|
|
hemocytoblasts in red bone marrow gives rise to ----- that give rise to erythocytes
|
erythroblasts
|
|
|
reticulocytes are
|
young red cells containing net-like structure
|
|
|
the average life span of a red blood cell is
|
120 days
|
|
|
erythropoietin controls ----- and is released primarily from -----
|
rate of red blood cell formation.....kidneys (a lesser extent from liver)
|
|
|
when the availability of oxygen decreases ----- is released and red blood cell production -----
|
erythropoietin (EPO) .....increases
|
|
|
two vitamins needed for red blood cell production are
|
B complex vitamin B12 and folic acid (iron)
|
|
|
two B complex vitamins are needed for
|
red cell production - DNA synthesis
|
|
|
intrinsic factor is needed for
|
absorption of B12
|
|
|
iron is needed for
|
hemoglobin synthesis
|
|
|
anemia is
|
deficiency of red blood cells or reduction in amount of hemoglobin
|
|
|
damaged red blood cells rupture as they pass through
|
spleen or liver
|
|
|
in the liver and spleen ----- destroy worn out red blood cells
|
Macrophages (big eaters)
|
|
|
hemoglobin molecules are broken down into
|
four component poly peptide "globin" chain (surrounding heme group)
|
|
|
heme decomposes into
|
iron and biliverdin
|
|
|
ferritin is
|
iron protein complex
|
|
|
biliverdin is converted into
|
bilirubin
|
|
|
bilirubin and biliverdin are excreted in
|
bile
|
|
|
the poly peptide globin chains break down into
|
amino acids
|
|
|
white blood cells are also called
|
leukocytes
|
|
|
white blood cells function to
|
protect against disease
|
|
|
granulocytes have ----- whereas agranulocytes -----
|
granular cytoplasm..... without cytoplasmic granulations
|
|
|
examples of granulocytes are
|
Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
|
|
|
Neutrophil granules appear ----- in acid/base stain
|
purple
|
|
|
Neutrophils have nuclei that are
|
lobed and consist of 2-5 segments connected by a thin strand of chromatin
|
|
|
Neutrophils phagocytize
|
bacteria, fungi, and some viruses
|
|
|
Neutrophils account for about ----- of white blood cells in a blood sample
|
54-62%
|
|
|
eosinophil granules stain ----- in an acid stain
|
deep red
|
|
|
the nucleus of an eosinophil is usually
|
two lobes (bilobed)
|
|
|
eosinophils moderate
|
allergic reactions and defend against parasitic worm infestation
|
|
|
eosinophils make up ----- of the total number of circulating white blood cells
|
1-3%
|
|
|
basophil granules stain ----- in a basic stain
|
deep blue
|
|
|
basophils migrate to ----- where they release
|
damaged tissues..... histamine and heparin
|
|
|
histamine promotes
|
inflammation
|
|
|
heparin functions to
|
inhibit blood clotting
|
|
|
basophils usually account for ----- of leukocytes
|
Less than 1%
|
|
|
examples of agranulocytes are
|
monocytes and leukocytes
|
|
|
the largest of the white blood cells are
|
monocytes
|
|
|
the nuclei of monocytes are
|
spherical, kidney shaped, and oval lobed
|
|
|
monocytes can leave the ----- to become
|
bloodstream..... Macrophages and phagocytize (eat) bacteria, dead cells, and other debris
|
|
|
monocytes usually make up ----- of white blood cells in a blood sample
|
3-9% (live for several weeks or years)
|
|
|
a typical lymphocyte contains ----- nucleus surrounded by a ----- of cytoplasm
|
large..... thin layer
|
|
|
the major types of lymphocytes are
|
T-cells, B-cells
|
|
|
T-cells attack
|
microorganisms,tumor cells, and transplanted cells
|
|
|
B-cells produce
|
antibodies (proteins that attack foreign molecules)
|
|
|
lymphocytes account for ----- of the circulating white blood cells
|
25-33% (live for many years)
|
|
|
Diapedesis is
|
movement of leukocytes squeezing between cells that form the walls of the smallest vessels
|
|
|
amoeboid motion is
|
self propulsion
|
|
|
the most mobile and active phagocytic leukocytes are
|
Neutrophils and monocytes
|
|
|
when microorganisms invade human tissues basophils respond by
|
releasing bio chemicals that dilate local blood vessels
|
|
|
positive chemotaxis is
|
damaged cells releasing chemicals that attract leukocytes (when combined with Diapedesis it quickly bring many white blood cells into inflamed areas)
|
|
|
pus is
|
bacteria, leukocytes, and damaged cells accumulate in inflamed tissue (thick fluid)
|
|
|
a white blood cell count is normally between
|
4500-10000 per micro liter
|
|
|
leukocytosis is ----- and is often caused by
|
white blood cell count above 10000 per microliter .....acute infection (appendicitis) , follows vigorous exercise, emotional disturbance, or great loss of body fluid
|
|
|
leukopenia is ----- and is often caused by
|
white blood cells below 4500 per microliter..... typhoid fever, influenza, measles, mumps, chickenpox, Aids, poliomelitis, anemia, or lead, arsenic, mercury poisoning
|
|
|
a differential white blood cell count lists
|
percentages of various types of leukocytes in a blood sample
|
|
|
the number of Neutrophils increases during ----- and eosinophils increase during
|
bacterial infections..... parasitic infections and allergic reactions
|
|
|
platelets are also called
|
thrombocytes
|
|
|
platelets arise from cells called
|
megakaryocytes
|
|
|
a normal platelet count is normally between
|
150000-450000 per microliter
|
|
|
platelets help repair ----- by sticking
|
damaged blood vessels..... to broken surfaces
|
|
|
platelets release ----- which
|
serotonin..... contracts smooth muscles in vessel walls, reducing blood flow
|
|
|
plasma is
|
clear straw colored liquid part in which cells and platelets are suspended
|
|
|
about ----- of plasma is water
|
92%
|
|
|
functions of plasma include
|
transporting nutrients, gases, and vitamins (helping to regulate fluid and electrolyte balance maintaining favorable pH)
|
|
|
the three main plasma protein groups are
|
albumin, globulins, fibrinogen
|
|
|
albumin are ----- and are synthesized
|
the smallest of plasma proteins..... in the liver, because they are plentiful they determin osmotic pressure
|
|
|
albumins function to
|
maintain osmotic pressure, regulate water movement between blood and tissues
|
|
|
globulins can be divided into the following three groups
|
alpha, beta, gamma globulins
|
|
|
alpha and beta globulins are synthesized ----- and function to
|
in the liver..... transport liquids and fat soluble vitamins
|
|
|
Gamma globulins are synthesized ----- and function as
|
in the lymphatic tissues..... antibodies in immune response
|
|
|
fibrinogen is synthesized ----- and functions to
|
in the liver..... coagulate blood
|
|
|
the most important blood gases are
|
O2, CO2
|
|
|
the plasma nutrients are
|
amino acids, simple sugars, nucleiotides, and lipids absorbed from digestive tract
|
|
|
types of non protein substances in plasma are
|
amino acids, urea, uric acid, creatine, and creatinine
|
|
|
urea is produced when
|
protein and nucleic acid catabolize
|
|
|
uric acid is produced when
|
protein and nucleic acid catabolize
|
|
|
creatinine is produced from
|
metabolism of creatine
|
|
|
creatine phosphate is
|
in muscle, brain tissues, and blood as energy in phosphate bonds much like ATP molecules
|
|
|
about half of the NPN substances in blood are
|
urea
|
|
|
plasma electrolytes include
|
sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, bicarbonate phosphate, and sulfate ions
|
|
|
----- are the most abundant plasma electrolytes
|
sodium chloride ions
|
|
|
hemastasis refers to
|
the process that stops bleeding (vitally important when blood vessels are damaged)
|
|
|
three actions that may prevent blood are
|
blood vessel spasm( Vasoconstriction), platelet plug formation, blood coagulation
|
|
|
vasospasm is
|
constriction of smooth muscles in the walls of small blood by vessels
|
|
|
following vasospasm blood loss ----- and the ends of the severed vessel may
|
lessens..... close completely
|
|
|
platelets adhere to
|
exposed ends of injured blood vessels
|
|
|
a platelet plug is formed when
|
the contact collagen
|
|
|
the function of the platelet plug is to
|
control blood loss from a small break
|
|
|
coagulation causes
|
blood clots
|
|
|
the extrinsic clotting mechanism is triggered by
|
releasing of bio chemicals from broken blood vessels or damaged tissues
|
|
|
serotonin
|
aids in reduction of blood loss
|
|
|
the intrinsic clotting mechanism is triggered by
|
blood contact with foreign surfaces in the absence of tissue damage
|
|
|
clotting factors are
|
complex and use many biochemicals
|
|
|
vitamin ----- is necessary for some clotting factors to function
|
K
|
|
|
procoagulants promote ----- and anti coagulation inhibits
|
coagulation.....coagulation
|
|
|
normally -----prevail and the blood does not clot
|
anticoagulants
|
|
|
the major even in blood clot formation is
|
conversion of the soluble plasma protein fibrinogen into insoluble threads of protein fibrin
|
|
|
the extrinsic clotting mechanism is triggered when
|
blood contacts damaged blood vessel walls or tissues outside blood vessels
|
|
|
tissue thromboplastin is
|
associated with disrupted cell membranes
|
|
|
the series of reactions in the extrinsic clotting mechanism are dependent on ----- ions
|
calcium
|
|
|
prothrombin activator converts ----- to -----
|
prothrombin..... thrombin
|
|
|
the function of trombone is to
|
catalyze a reaction that fragments fibrinogen
|
|
|
once fibrin threads form, they stick to
|
exposed surfaces of damaged blood vessels creating meagerly that entraps blood cells and platelets
|
|
|
a blood clot is composed of
|
fibrin threads and platelets
|
|
|
blood clotting is enhanced by ----- system
|
positive feedback
|
|
|
normally blood clot formation is prevented by
|
blood flow throughout the body (by rapidly carrying excess thrombin away and keeping its concentration too low to promote further clotting)
|
|
|
blood clotting mechanisms
|
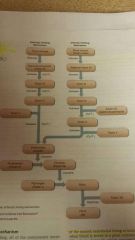
|
|
|
the ----- factor initiates clotting in the intrinsic clotting mechanism
|
hageman
|
|
|
the intrinsic clotting mechanism occurs when blood is exposed to
|
a foreign surface such as collagen in connective tissue instead of the smooth endothelial lining of intact blood vessels or when blood is stored in glass container
|
|
|
the reactions of the intrinsic clotting mechanism depend on ----- ions
|
calcium
|
|
|
most of the steps of blood clot formation in the intrinsic clotting mechanism are the same as
|
extrinsic mechanism
|
|
|
after blood clot forms it soon begins to
|
retract
|
|
|
serum is
|
plasma minus fibrinogen and clotting factors
|
|
|
platelet derived growth factor stimulates
|
smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts to repair damaged blood vessel walls
|
|
|
fibroblasts produce ----- which help strengthen and seal
|
connective tissue..... vascular breaks
|
|
|
plasmin is released from ----- and functions to
|
plasminogen..... digest fibrin threads and other proteins associated with blood clots
|
|
|
a thrombus is
|
a blood clot abnormally forming in a vessel
|
|
|
atherosclerosis is
|
accumulations of fatty deposits change arterial linings sometimes initiating inappropriate clotting
|
|
|
thrombosis in veins is usually caused by
|
atherosclerosis
|
|
|
the smooth lining of blood vessels discourages
|
platelets and clotting factors from accumulating
|
|
|
antithrombin inactivates
|
additional thrombin binding to it and blocking its action on fibrinogen
|
|
|
heparin is
|
interferes with formation of prothrombin activator prevents the action of thrombin on fibrinogen and promotes removal of thrombin by antithrombin and fibrin absorption
|
|
|
agglutination is ----- and is due to
|
clumping of red blood cells..... reaction between red blood cell surface molecules
|
|
|
avoiding the mixture of certain kinds of ----- prevents adverse transfusion reactions
|
antigens and antibodies
|
|
|
a person with only antigen B has type ----- blood
|
B
|
|
|
a person with both antigen A and antigen B has type ------ blood
|
AB
|
|
|
a person with neither antigen A nor antigen B has type ----- blood
|
O
|
|
|
a person with type A blood has ----- antibody in their plasma
|
B
|
|
|
a person with type B blood has ----- antibody in their plasma
|
A
|
|
|
a person with type AB blood has neither ----- antibodies in their plasma
|
A and B
|
|
|
a person with type O has both ----- antibodies in their plasma
|
A and B
|
|
|
antibodies anti-A and anti-B do not cross the
|
placenta
|
|
|
the major concern in blood transfusion procedures is that
|
the cells in donated blood not clump due to antibodies in the recipients plasma
|
|
|
a person with type AB blood is called a universal recipient because
|
they lack both anti-A and anti-B antibodies
|
|
|
type O blood is the universal donor because
|
they lack antigens A and B
|
|
|
a person with type A blood cannot receive type B blood because
|
type A has B antibodies if they receive type B blood their antibodies would kill off blood
|
|
|
the rH blood group was named after
|
rhesus monkey
|
|
|
blood is said to be rH positive when
|
antigen D or rH antigens are present on RBC membranes
|
|
|
blood is said to be rH negative when
|
red blood cells lack rH antigens
|
|
|
anti rH antibodies form only in rH negative persons when
|
there is a response to the presence of RBC with rH antigens
|
|
|
when rH negative woman is pregnant with an ------ fetus she will produce
|
rH positive..... anti-rH antibodies
|
|
|
erythroblastosis fetalis occurs when
|
(hemolytic disease) anti-rH antibodies cross placental membrane and destroy fetal red blood cells
|

