![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define the three types of hemolysis:
|
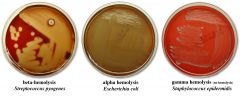
alpha-hemolysis
-green to light-brown halo is seen around the colonies; bacteria partially break down hemoglobin leaving a green pigment (biliverdin) beta-hemolysis -clearing is seen around the colonies; bacteria produce a "beta-hemolysin" (streptolysin O or S), which lyses red blood cells in the medium gamma-hemolysis (no hemolysis) -no hemolysis is observed; bacteria do not produce a hemolysin |
|
|
What is MacConkey's Agar good for?
|
Selective for: gram-negative bacteria
-growth of gram-positive bacteria (e.g.: Staphylococcus aureus in the image below) is inhibited by the crystal violet dye and **bile salts** in the media Neutral red pH indication turns red in the presence of acid by-products of lactose fermentation. Cloudiness is caused by precipitation of bile salts by acids. Bile salts inhibit gram positive and non-enteric rods. |
|
|
Ways to determine antibiotic sensitivity (2)
|
Disc Diffusion method (Kirby-Bauer)
Minimun Inhibitory Concentration Test tube dilution method. |
|
|
Nitrocefin Test
|
Rapid test to detect B-lactamase production in bacteria.
Hydrolysis of B-lactam ring in nirtocefin creates cephalosporanic acid (pink) Postive test goes from pale yellow to pink. Staph aureus often produces lactamase at too low of levels to detect by this method. |
|
|
Catalase Test
|
Detects enzyme that degrades hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen.
Positive test when bubbles appear after applying hydrogen peroxide to bacteria. Streptococci (Negative) Staphylococci (Positive) -Many others also product catalase so gram stain first. Platinum and blood can cause false positives |
|
|
Oxidase Test
|
Used to detect the presence of cytochrome c oxidase.
(Positive test turns purple, normally colorless) Neisseria (positive) Pseudomonas (positive) Enterobacteriaceae (negative) |
|
|
Indole Test
|
Tests if bacteria can produce indole by reductive deamination of tryptophan.
Positive test turns pink. E. coli (positive) |
|
|
E. coli morphology:
|
Small, gram - rod, pleomorphic
|
|
|
Staph aureus morphology:
|
Small, gram + cocci in clusters
|
|
|
Srep agalactiae
|
Gram + cocci in chains
|

