![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are three examples of animal steroids?
|
Sterols (cholesterol)
Bile acids Steroir Hormones |
|
|
Where are most steroid hormones derived from?
|
Cholesterol
|
|
|
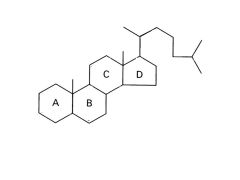
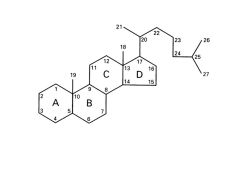
What is the typical structure of a steroid?
|
Fused Ring: 6-6-6-5
|
|
|
|
|
|
What does androstane give rise to?
|
Androgens
|
|
|
What does pregnane give rise to?
|
Progesterone
|
|
|
What does estrane give rise to?
|
Estrogens
|
|
|
What is the action of 5-a-reductase?
|
Reduces 5-C double bond in testosterone
Creates 5a-dihydrotestosterone (ACTIVE ANDROGEN) |
|
|
Where in the body is cholesterol synthesized?
|
All tissues
Particularly high in liver, adrenal cortex, gonads, placenta |
|
|
Provide the basic pathway for steroid synthesis. List all enzymes necessary. List rate limiting step.
|
AcCoa + NADH + ATP-->HMGCoA
via HMG CoA Synthase HMG CoA --> Mevalonate via HMG CoA Reducatse THIS IS RLS! --> --> Cholesterol --> --> Steroid |
|
|
What are the controls on HMG CoA Reductase?
|
Genetic level control: When low [sterol], increased transcription of gene
Activity level control: via phosphorylation |
|
|
True/False: Cholesterol is the precursors for all steroid hormones.
|
False; exception is vitamin D
|
|
|
Can cholesterol be metabolized?
|
No, it cannot. It is excreted in feces as bile salts and bile acids.
|
|
|
Describe the localization of steroid hormone synthesis.
|
Cholesterol synthesized in sER and cytoplasm
Enters mitochondria for side-chain cleavage (via p450 SCC enzyme) Leaves mitochondria as pregnenolone -Enters SER and leaves cell as sex steroid (gonads) OR -Enters SER, then mito, and leaves cell as glucocorticoids or mineralocorticoids (adrenal cortex) |
|
|
What is sER content like in steroid secreting cells?
|
Steroid secreting cells have ABUNDANT sER
|
|
|
What is the reaction catalyzed by cytochrome P450?
|
R + O2 + NADPH + H+
---> R-OH + H2O + NADP+ (insertion of an OH group onto an R group and reduction of other O to Water) |
|
|
How does cholesterol become cortisol/aldosterone?
|
Cholesterol-->Progesterone
via P450 scc Progesterone --> Cortisol/aldosterone via P450c 17, 21, 11; 21, 11, 18 respectively |
|
|
How does cholesterol become estrone?
|
Cholesterol-->Progesterone
via P450 scc Progesterone --> Androstenedione via P450 c17 Androstenedione-->Estrone via P450 aromatase |
|
|
How does cholesterol become estradiol?
|
Cholesterol-->Progesterone
via P450 scc Progesterone --> Androstenedione via P450 c17 Androstenedione-->Testosterone Via (unlisted) Testosterone-->Estradiol via P450 aromatase |
|
|
What hormone influences the production of cortisol and aldosterone? How?
|
ACTH regulates P450 enzymes
|
|
|
What hormone influences the production of estrone and estradiol? How?
|
LH regulates P450 aromatase
|
|
|
What is the role of StAR protein? What step in cholesterol synthesis is it required for?
|
Steroid Acute Regulatory Protein: facilitates transfer of cholesterol across both outer and inner mitochondrial membranes
Required for SCC; p450 scc is in inner mitochondria--where metabolism to pregnenolone |
|
|
What would a mutation in StAR lead to? Clinical manifestations?
|
Lipoidal Congential Adrenal Hyperplasia
Genetic loss of steroidogenesis Cellular damage from accumulated choelsterol No steroid hormones can be synthesized ALL individuals are PHENOTYPIC females with severe salt-losing (absence of androgen) |
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome? How does this disease come about?
|
Mental retardation, AMBIGUOUS GENITALIA (can't produce andorgens) in males, low circulating cholesterol
Defect/Deficit of C7-Reductase: req'd for 7-dehydrocholesterol-->cholesterol (very upstream) |
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia? Cause?
|
Virilization of females (formation of male genitalia) because of excess androgen production, salt-wasting
Tx: glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid replacement Cause: Defect/deficit in C21-hydroxylase; req'd for Progesterone --> cortisol/aldosterone produce excess androgens! |
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of a 5a-reductase deficiency?
|
Undervirilized males, virilize at puberty
May have blind vaginal pouch--testes suppress Mullerian derivatives Remember: 5a-reductase required for testosterone to act on target tissues |
|
|
What determines the biological actions of steroid hormones?
|
Specificity and tissue localization of steroid hormone receptors
|
|
|
Explain how steroid hormone receptors interact with heat shock protein, coactivators, and DNA binding elements.
|
Steroid binds receptor, induces conformational change and phosphorylation
HSP released from receptor Steroid-bound receptors dimerize Dimer binds Steroid Response Coactivator (SRC; the coactivator) SRC-dimer binds DNA, begins transcription |
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of complete androgen insensitivity? Cause?
|
AKA Testicular Feminization
Cause: Mutation in Androgen Receptor Gene Breast development at pubrerty, absence of menstrual flow (amenorrhea), scant or abscent pubic/axillary hair Genitalia: Female with blind vaginal pouch Wolffian derivatives usually absent Mullerian derivates usually absent or vestigial Gonads: testes |
|
|
If testosterone is normally at a concentration that nearly saturates the androgen receptors in target tissues, how do anabolic steroids increase muscle mass?
|
Two theories:
1) Fully saturating would fully activate androgen receptors 2) Inhibiting glucocorticoid receptor with anabolic steroids; cortisol binds these receptors and stimulates protein degradation |

