![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
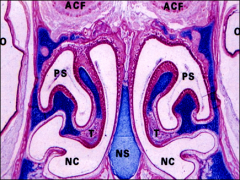
Paranasal Sinuses
are cavities in the = 3ct |
maxillary
ethmoid sphenoid connected with the nasal cavity. |
|
|
|
Paranasal Sinuses
are lined with a thinner = |
ciliated respiratory epithelium with few _______ cells
|
goblet
|
|
|
Paranasal Sinuses
lamina propria is thin and contains few small glands and lies on |
periosteum of the bone.
Erectile or cavernous tissue is not present. |
|
|
|
*Paranasal sinuses are often a site of
|
painful inflammation
, sinusitis. pic |
|
|
|
Nasopharynx
is lined by |
typical respiratory epithelium
In areas subjected to abrasions, a _____ ___ ___ may occur. |
nonkeratinizing stratified squamous
|
|
|
Nasopharynx
Underlying connective tissue contains |
mucous, serous
mixed glands. |
|
|
|
Nasopharynx
The lymphatic tissue is irregularly scattered throughout and also form |
tonsillar structures
(pharyngeal tonsils or adenoids) on the posterior wall. |
|
|
|
Nasopharynx
palatine and lingual tonsils at the junction of the oral cavity and pharyngeal tonsil in the nasopharynx collectively forms a protective ring________ ________ guarding access to the lower reaches of respiratory and oral cavities. |
(Waldeyer’s ring)
(upper respiratory tract infection) is a aka = |
*Sore throat
|
|
|
Larynx
The two main functions of the larynx are |
to produce sound
2. to close the trachea during swallowing to prevent food and saliva from entering the airway. |
|
|
|
Larynx
The wall of the larynx is made up of the |
thyroid and cricoid hyaline cartilage and the elastic cartilage core of the epiglottis extending over the lumen
|
|
|
|
Extrinsic laryngeal muscles attach the larynx to the hyoid bone to
|
raise the larynx during swallowing.
|
|
|
|
Intrinsic laryngeal muscles
|
abductor
adductors tensors link the _____ & _____ = |
thyroid
cricoid cartilages When intrinsic muscles contract, the tension on the vocal cords changes to modulate phonation. |
|
|
The larynx can be subdivided into three regions:
|
supraglottis,
glottis subglottis Stratified unkeratinized & keritanized & vocal cord change |
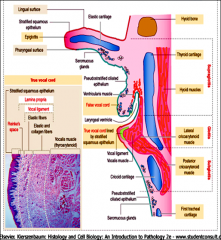
The supraglottis, which includes the epiglottis, false vocal cords (or folds), and laryngeal ventricles.
The glottis, consisting of the true vocal cords (or folds) and the anterior and posterior commissures. The subglottis, the region below the true vocal cords, extending down to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage. During forced inspiration, vocal cords are abducted, and the space between the vocal cords widens. |
|
|
supraglottis,
|
epiglottis
false vocal cords the epiglottis, false vocal cords (or folds), laryngeal ventricles. |
|
|
|
glottis
|
true vocal cords (or folds) and
anterior commissures posterior commissures. During forced inspiration, vocal cords are = |
abducted,
and the space between the vocal cords widens. |
|
|
subglottis
|
the region below the true vocal cords, extending down to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage.
|
|
|
|
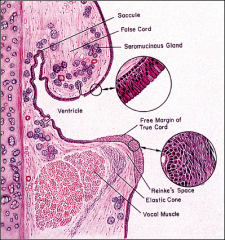
Larynx
vocal cords a cover consisting of |
-stratified squamous
-superficial layer of the lamina propria, aka = Elsewhere, the epithelium is pseudostratified ciliated, with goblet cells. = |
Reinke's space
pseudostratified ciliated, with goblet cells. |
|
|
Larynx
Laryngeal seromucous glands are found throughout the lamina propria, except at the level of the = |
true vocal cords.
pic |
|
|
|
Larynx
Laryngea contains l________ glands |
seromucous
|
|
|
|
lamina propria of the true vocal cords consists of three layers:
|
superficial =
intermediate = deep = |
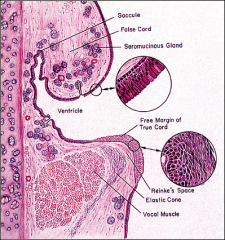
-extracellular matrix
-few elastic fibers -abundant elastic and collagen fibers |
|
|
_____ _______ are responsible for vocal cord vibration.
|
Reinke's space
& the epithelial covering |
|
|
|
Reinke's edema
|
viral infection
, trauma (laryngeal endoscopy), severe coughing cause what to occur |
fluid to accumulate in the superficial layer of the lamina propria.
|
|
|
Reinke's space
Both the intermediate and deep layer of the lamina propria constitute the |
vocal ligament.
The lamina propria is usually rich in = |
mast cells
|
|
|
Mast cells participate in
|
hypersensitivity reactions leading to edema and laryngeal obstruction, a potential medical emergency.
|
|
|
|
Croup designates a
|
laryngotracheobronchitis
in children, in which an inflammatory process = |
narrows the airway and produces inspiratory stridor.
|
|
|
Epiglottis
projects from the rim of the |
larynx
extends into the = |
pharynx
and has both a lingual and a laryngeal surface. |
|
|
Epiglottis
entire lingual surface and the apical portion of the laryngeal surface are covered with |
stratified squamous epithelium.
|
|
|
|
Epiglottis
Toward the base of the epiglottis on the laryngeal surface, the epithelium undergoes a transition into |
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
|
|
|
|
_______ & __________ glands are found beneath the epithelium. Core contains elastic cartilage.
|
Mixed mucous glands
serous glands pic |
|
|
|
The trachea is the continuation of the larynx.
T/F Thin walled tube. |
T
10 cm long branches to form the = |
right and left primary bronchi entering the hilum of each lung.
|
|
|
The hilum is the region where the
|
primary bronchus
pulmonary artery pulmonary vein nerves lymphatics enter and leave the lung. |
|
|
|
Secondary divisions of the bronchi and accompanying connective tissue septa divide
|
each lung into lobes.
|
|
|
|
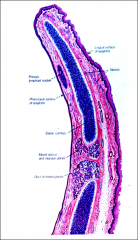
The wall of the trachea consists of
4ct |
Mucosa
Submucosa Cartilagenous layer Adventitia |
|
|
|
Trachea Epithelium is
|
typical respiratory
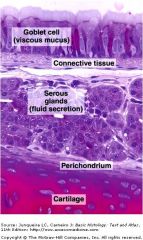
lying on basal lamina. The lamina propria contains = submucosa displays _______ & _______ glands. |
elastic fibers.
serous glands mucus glands |
|
|
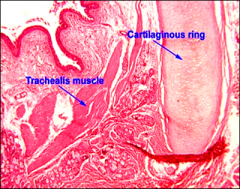
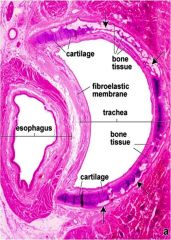
The framework of the trachea and extrapulmonary bronchi consists of a stack of =
|
C-shaped hyaline cartilages
each surrounded by a __________ layer blending with the perichondrium. |
fibroelastic
In the trachea and primary bronchi, the open ends of the cartilage rings point posteriorly to the esophagus. |
|
|
The lowest tracheal cartilage is the =
|
carinal cartilage.
|
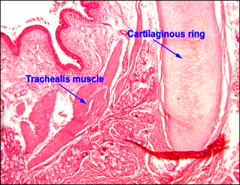
|
|
|
Trachea
Transv_______ _____ trachealis muscle attach to the inner ends of the cartilage. |
erse fibers of the
|
|
|
|
Trachea
layers top to Bottom = |
Epithelium
Lamina propria {Submucosa Seromucous glands} Cartilage Adventitia |
|

