![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Development of female genital ducts and glands
Mesonephric ducts regress because of absence of |
testosterone
|
|
|
|
Paramesonephric duct develops because of absence of =
|
MIS
|
|
|
|
Derivatives of paramesonephric duct
|
-Broad ligament of uterus
-uterine tubes -Uterus from and -vagina from = |
uterovaginal primordium
|
|
|
Note the paramesonephric duct -- produces =
|
uterine canal.
|
|
|
|
By week 12, female and male characteristics can be recognized. By week __ phenotypic sexual differentiation is complete.
|
20
|
|
|
|
By week 12, female and male characteristics can be recognized. By week 20,
|
phenotypic sexual differentiation is complete.
|
|
|
|
Early in the 4th week, proliferating mesenchyme produces a
|
genital tubercle
in both sexes at the cranial end of the |
cloacal membrane.
|
|
|
Labioscrotal swellings and urogenital folds soon develop on each side of the =
|
cloacal membrane
|
|
|
|
_______ _________ & ________ _________
soon develop on each side of the cloacal membrane |
Labioscrotal swellings
and urogenital folds The genital tubercle soon elongates to form a |
primordial phallus.
|
|
|
Labioscrotal swellings and urogenital folds soon develop on each side of the cloacal membrane
The genital tubercle soon elongates to form a |
primordial phallus.
|
|
|
|
►proliferating mesenchyme produces a genital tubercle in both sexes at the =
|
cranial end of the cloacal membrane
|
|
|
|
Masculinization of the indifferent external genitalia is induced by
|
testosterone
produced by the = |
interstitial cells of the fetal testes.
|
|
|
Masculinization of the indifferent external genitalia is induced by testosterone produced by the
|
interstitial cells of the fetal testes.
|
|
|
|
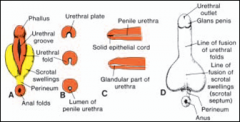
As the phallus enlarges and elongates to become the penis, the urogenital folds form the lateral walls of the =
|
urethral groove
on the ventral surface of the penis. |
|
|
|
As the phallus enlarges and elongates to become the penis, the urogenital folds form the lateral walls of the urethral groove on the ______ _________ of the penis.
|
ventral surface
|
|
|
|
The urogenital folds fuse with each other along the ventral surface of the penis to form the =
|
spongy urethra.
|
|
|
|
______ ______ fuse with each other along the ventral surface of the penis to form the spongy urethra.
|
urogenital folds
|
|
|
|
The urogenital folds fuse with each other along the ____ _____ of the penis to form the spongy urethra.
|
ventral surface
|
|
|
|
The surface ectoderm fuses in the median plane of the penis, forming the
|
penile raphe
|
|
|
|
During the twelfth week a circular ingrowth of $ ______ occurs at the periphery of the glans penis
|
ectoderm
When this ingrowth breaks down, it forms the = |
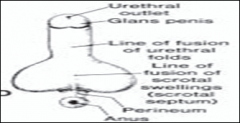
prepuce (foreskin)
|
|
|
.
|
|
|
|
The labioscrotal swellings grow
toward each other and fuse to form the = |
scrotum
The line of fusion of these folds is clearly visible as the = |
scrotal raphe.
|
|
|
The____ ____ grow toward each other and fuse to form the scrotum
The line of fusion of these folds is clearly visible as the scrotal raphe. |
labioscrotal swellings
|
|
|
|
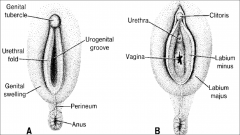
Development of Female External Genitalia
Growth of the primordial phallus gradually ceases and it becomes the |
clitoris
|
|
|
|
The unfused parts of the urogenital folds form =
|
labia minora.
|
|
|
|
Most parts of the labioscrotal folds remain unfused and form two large folds of skin, the =
|
labia majora
which are homologous to the |
scrotum
|
|
|
.
|
|

