![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Fetal testes produces 2 hormones:
|
Testosterone
Antimullerian hormone |
|
|
|
Testosterone production stimulated by =
|
human chorionic gonadotrophin
(hCG) |
|
|
|
AMH suppresses development of the =
|
development of the paramesonephric (mullerian) ducts, which form the uterus and uterine tubes.
|
|
|
|
The walls of the seminiferous tubules are composed of two kinds of cell: =
|
Sertoli cells
Spermatogonia, Sertoli cells derived from = Spermatogonia, primordial sperm cells derived from the = |
surface epithelium of the testis
primordial germ cells. |
|
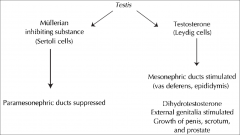
Influence of the sex glands on further sex differentiation
|
.
|
|
|
|
Development of Ovaries
Gonadal development occurs _______ in female embryos The ovary is not identifiable histologically until about the __week |
slowly
10th |
|
|
|
Development of Ovaries
Gonadal cords do not become prominent but they extend into the ________ and form a rudimentary _____ _______ = |
and form a rudimentary
rete ovarii. |
|
|
|
Development of Ovaries
primordial germ cells form in the wall of the |
yolk sac during week __ =
primordial germ cells later migrate into the developing _____ and differentiate into the _______ _____ ____ |
4
gonads definitive germ cells. |
|
|
Development of Ovaries
As the gonadal cords (cortical cords) increase in size, ____ ____ cells are incorporated in them |
primordial germ
At about __ weeks these cords begin to break up into isolated = |
16
cell clusters - primordial follicles |
|
|
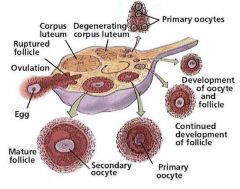
Each primordial follicle consists of an
|
oogonium
derived from a = surrounded by a single layer of flattened follicular cells derived from the = |
primordial germ cell
surface epithelium |
|
|
_______ ________ consists of an oogonium, derived from a primordial germ cell, surrounded by a single layer of flattened follicular cells derived from the _____ _______=
|
primordial follicle
surface epithelium |
|
|
|
Active mitosis of
oogonia occurs during |
fetal life
producing thousands of primordial follicles. No oogonia form |
postnatally
|
|
|
.
|
|
|
|
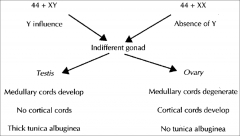
Development of Genital Ducts
|
mesonephric
paramesonephric ducts |
(wolffian - medial)
mullerian - lateral |
|
|
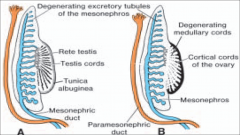
►Genital ducts in the sixth week in the male (A) and female (B). The mesonephric and paramesonephric ducts are present in both.
|
pic +
|
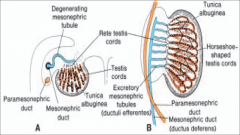
Transverse section through the testis in the eighth week
|
|
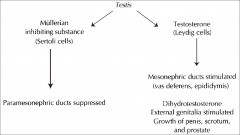
Fig: Influence of the sex glands on further sex differentiation
|
.
|
|
|
|
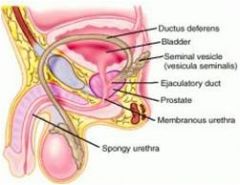
Derivatives of mesonephric duct in males
3ct |
Epididymis
Ductus deferens Ejaculatory duct In female fetuses the mesonephric ducts almost completely disappears. |
|
|
|
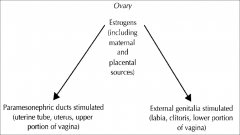
The paramesonephric ducts develop lateral to the =
|
gonads
mesonephric ducts |
|
|
|
The paramesonephric ducts
They develop from the = |
mesothelium
|
|
|
|
The paramesonephric ducts plays an essential role in the development of the
= |
female reproductive system.
|
|
|
|
The paramesonephric ducts pass, parallel to the =
|
mesonephric ducts
until they reach the future = |
pelvic region of the embryo
|
|
|
The paramesonephric ducts pass, parallel to the mesonephric ducts, until they reach the future pelvic region of the embryo
Here they cross ventral to the mesonephric ducts, approach each other in the median plane, and fuse to form a Y-shaped = |
uterovaginal primordium.
|
|
|
|
This tubular structure projects into the dorsal wall of the urogenital sinus and produces an elevation - the sinus =
|
(paramesonehric) tubercle.
|
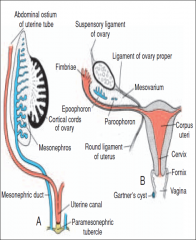
|
|
|
Note the paramesonephric duct -- produces
|
uterine canal.
|
|
|
|
Note the paramesonephric duct -- produces =
|
uterine canal.
|
|
|
|
The fetal testes produce masculinizing hormones
|
(testosterone)
a mullerian inhibiting substance (MIS) |
|
|
|
Sertoli cells secrete =
|
MIS
|
|
|
|
Interstitial cells secrete
|
Testosterone
|
|
|
|
A lateral outgrowth from the caudal end of each mesonephric duct gives rise to the =
|
seminal gland (seminal vesicle)
|
|
|
|
what glands produces a secretion that nourishes the sperms =
|
seminal gland (seminal vesicle)
|
|
|
|
Prostate is derived from = ____ ____
arise from the prostatic part of the urethra. |
endodermal outgrowths
|
|
|
|
Prostate is derived from endodermal outgrowths arise from the =
|
prostatic part of the urethra.
|
|

