![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Right and left thyroid lobes connected by
|
Isthmus
|
|
|
Isthmus located just below
|
Cricoid cartilage
|
|
|
Bottom of thyroid usually goes to ___ vertebral level
|
C4 or C6
|
|
|
Remnant of embryonic thyroglossal duct
|
Pyramidal lobe
|
|
|
Foramen cecum
|
Where thyroid pierces through tongue through the thyroglossal duct
|
|
|
____ (3) occurs when thyroid is enlarged
|
Dysphagia
Dispnea Infection |
|
|
Dysphagia
|
difficulty or discomfort in swallowing, as a symptom of disease
|
|
|
Right and left thyroid lobes connected by
|
Isthmus
|
|
|
Dyspnea
|
difficult or labored breathing
|
|
|
Potential sites of abberant thyroid glandular tissue/thyroglossal duct tissue (3)
|
Superior/infront of thyroid cartilage
Superior/in front of hyoid bone Superior to hyoid bone - root of mouth |
|
|
Blood supply to thyroid
-2 arteries --Occasional 3rd |
1. Superior thyroid (from ext. carotid)
2. Inferior thyroid (from thyrocervical trunk) --3. Thyroid Ima (from subclavian) |
|
|
Vascular supply to thyroid
-3 veins -____ drain into internal jugular -____ drain into brachiocephalic |
1. Superior thyroid - Int. jug.
2. Middle thyroid - int. jug. 3. Inferior thyroid - brachiocephalic |
|
|
Surgical relations to thyroid gland
|
Inferior thyroid a. to recurrent laryngeal n.
|
|
|
Parathyroid glands located ____ on thyroid
|
Posterior
|
|
|
C cells produce
|
Calcitonin
|
|
|
Calcitonin
|
Reduces blood calcium levels by stimulating calcium resorption by the bone (osteoblasts)
|
|
|
Function of thryoid gland
|
Endocrine gland that produces thyroid hormone & calcitonin
|
|
|
Follicular cells produce _____ under control of _____
|
Thyroid hormone; anterior pituitary
|
|
|
Anterior pituitary under control of
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
Thyroid hormone works in conjunction with ____ to stimulate ____
|
Growth hormone; cellular metabolism
|
|
|
Thyroid hormone
-Increases -Important in -Crucial in normal development of |
-Metabolism
-Body growth -NS |
|
|
____ is essential diet component for TH
|
iodine
|
|
|
Hyperthyroidism cause
Hyperthyroidism presentation (4) |
Too much TH
Skinny Jittery Nervous Dry skin |
|
|
Hypothyroidism cause, presentation (3)
|
Too little thyroid hormone
Fat Sluggish Tired |
|
|
Calcitonin stimualtes osteo____
|
Blasts
|
|
|
PTH stimulates osteo____
|
plasts
|
|
|
____ is an antagonist to calcitonin
|
PTH
|
|
|
____ increases blood calcium
|
PTH
|
|
|
PTH stimulates Ca+ release from ____; conservation by ___, activation of
|
bone; kidney; Vitamin D
|
|
|
Parathyroid in relation to thyroid capsule
|
Within
|
|
|
Low calcium levels lead to life threatening _____ disorders
|
neuromuscular
|
|
|
Parathyroid supplied by ____ a.
|
Inferior thyroid
|
|
|
-Goiter
-Usual cause worldwide -Usual US cause |
-Enlargement of thyroid gland
-Iodine deficiency -Hyper/hypothyroidism |
|
|
Enlargement of thyroid gland compresses
1. 2. 3. 4. (nerve) |
1. Trachea
2. Larynx 3. Esophagus 4. Recurrent laryngeal n. |
|
|
Grave's disease
|
Autoimmune disease; immune system overstimulates thyroid gland, causing hyperthyroidism
|
|
|
Extreme Hyperthyroidism symptoms
(PEG) |
Proptosis
exophthalmos Goiter |
|
|
exophthalmos
|
abnormal protrusion of the eyeball or eyeballs
|
|
|
Proptosis
|
abnormal protrusion or displacement of an eye or other body part
|
|
|
Hashimoto's Disease
|
Autoimmune disease; Chronic thryoiditis, thyroid is destroyed resulting in hypothyroidism & goiter
|
|
|
-Antibody implicated in Grave's disease
-Role |
-Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin
-Binds to thyroid cells, mimics TSH |
|
|
Dangers of thyroidectomy
|
Bleeding
Damage to recurrent pharyngeal |
|
|
Hyper & Hypoparathyroidism
|
Remember PTH is antagonist to TH
|
|
|
Carotid Triangle Boundaries
|
Posterior digastric
Superior Omohyoid Anterior border of SCM |
|
|
Carotid sheath extends from ___ to ___
|
Base of skull to root of neck
|
|
|
Carotid sheath contributed to from:
|
All fascial layers of neck
|
|
|
Investing layer of deep cervical fascia
-Surrounds -Splits into 2 layers to enclose: |
-Entire neck
-Trapezius/SCM & Supra/infrahyoid mm. |
|
|
Prevertebral fascia
-Surrounds -Becomes continuous with ____ at _____ |
-Everything except trap and SCM
-Endothoracic fascia; anterior longitudinal ligament |
|
|
Sympathetic trunk covered by ____ fascia
|
Prevertebral
|
|
|
50% of retropharyngeal abscesses occur in pt. _____ age; 96% occurring before
|
6-12 months; 6 year
|
|
|
Retropharyngeal abscess symptoms in children
|
Irritability
Lymphadenopathy Torticollis Poor oral intake Sore throat Drooling |
|
|
Torticollis
|
a condition in which the head becomes persistently turned to one side
|
|
|
Retropharyngeal abscess symptoms in adults
|
Pain
Dysphagia Snoring Nasal obstruction Anorexia |
|
|
General Retropharyngeal abscess symptoms
|
Dyspnea
Respiratory distress Lateral or posterior oropharyngeal wall bulge |
|
|
Retropharyngeal abscess cause in children
|
Suppurative process in lymph nodes (nose, adenoids, nasopharynx, sinuses)
|
|
|
Suppurate
|
undergo the formation of pus; fester
|
|
|
Retropharyngeal abscess cause in adults
|
Trauma, instrumentation
|
|
|
Submandibular space abscess symptoms
|
Pain
Drooling Dysphagia Neck stiffness/anterior neck swelling Floor of mouth edema |
|
|
Cause of submandibular abscess is usually
|
Odontogenic origin
|
|
|
Ludwig's angina
|
Infection of the floor of the mouth (submandibular space) with secondary involvement of sublingual and submental spaces
|
|
|
___ gland surrounds the terminal portion of the submandibular duct
|
Sublingual gland
|
|
|
Sublingual gland supplied by ___ innervation
|
Parasympathetic (Secretomotor) from submandibular ganglion either directly or through lingual n.
|
|
|
Thoracic duct drains:
|
LE, L. UE, L. Head
|
|
|
Right lymphatic duct drains
|
R Head, R UE
|
|
|
Scalp/skin lesions with metastasize to ___ area
|
In front of ear
|
|
|
Oropharynx, hypopharynx lesions with metastasize to ___ area
|
Below ear
|
|
|
Nasopharynx lesions with metastasize to ___ area
|
Posterolateral neck
|
|
|
GI, UG, Pulmonary lesions with metastasize to ___ area
|
Root of neck
|
|
|
Oral cavity lesions with metastasize to ___ area
|
Body of mandible
|
|
|
Larynx, tongue, hypopharynx lesions with metastasize to ___ area
|
Anterior border of SCM
|
|
|
Recurrent laryngeal n. travels up between ___ and __ before reaching larynx
|
Esophagus; thyroid
|
|
|
Esophagus
Upper 1/3 is ____ m. Middle Lower |
Skeletal
Mix Smooth |
|
|
Root of the neck
|
Junction between neck and thorax
|
|
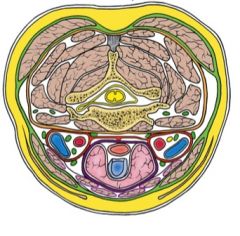
Green layer
Orange layer Purple Layer Red |
-Investing layer of deep cervical fascia
-Prevertebral fascia -Pretracheal fascia -Carotid sheath |
|
|
Superior thyroid a. supplies (SIS)
|
SCM
Infrahyoids Superior pole of thyroid |
|
|
Submandibular gland is 1 of 3 ____; secretes it's product into ____
|
Salivary glands; submandibular duct (Wharton's duct)
|
|
|
Innervation of submandibular gland
|
CN VII (Facial) via chorda tympani
|
|
|
-Type of secretions from parotid gland
-Type of secretions from Sublingual gland -Type of secretions from submandibular gland |
-Watery/serous
-Thick, mucousy -Mix of serous and mucous |
|
|
Parasympathetic stimulation of submandibular gland produces ___ saliva because
|
Watery; vessels dilate
|
|
|
Sympathetic stimulation of submandibular gland produces ___ saliva because
|
Thick mucousy; vessels constrict
|
|
|
Subclavian vessels
"Very Tired Individuals Sip Strong Coffee Served Daily" |
• Vertebral artery
• Thyrocervical trunk --Inferior thyroid --Superficial cervical --Suprascapular •Costocervical --Superior intercostal --Deep cervical |
|
|
Largest branch off aorta
|
Brachiocephalic trunk
|
|
|
Thoracic duct travels posterior to ____ before draining into ____
|
Carotid sheath; junction of L subclavian and L internal jugular
|
|
|
-Location of 1st part of subclavian
-Branches off 1st part of subclavian a. |
-Medial to anterior scalene
Vertebral Internal thoracic Thyrocervical trunk |
|
|
Vertebral a. travels through:
|
Foramina of C6-1
|
|
|
___ gives off anterior intercostal aa.
|
Internal thoracic
|
|
|
-2nd part of subclavian (location)
-Branches of 2nd part of subclavian |
-Posterior to anterior scalene
Costocervical trunk |
|
|
-Location of 3rd part of subclavian a.
-Branches |
Lateral to anterior scalene
Dorsal scapular |

