![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the generalized structure of an amino acid?
|
NH2-C(R)-COOH
|
|
|
What supplies the body's amino acid pool? What is this pool used for?
|
Supplied by absorption from diet (~100g/day)
Normal protein degradation (~400g/day) Synthesis of non-essential AA from precursors Pool used for: Protein synthesis (~400g/day) Synthesis of other products (e.g., epinephrine)--~30g/day Metabolism for energy production |
|
|
What is the role of pancreatic enzymes in the digestion of amino acids?
|
Break polypeptides into amino acids, dipeptides and tripeptides, which are then transported into the cell
|
|
|
How does the body know when to secrete and activate proteases? Provide examples of these proteases.
|
When food present, duodenum secretes CCK (in response to fats/prots) and secretin (in response to stomach acid)
CCK and secretin signal for release of pancreatic zymogens Zymogens are inactive precursors secreted into duodenum Ex: Trypsinogen-->Trypsin Chymotrypsinogen-->Chymotrypsin Proelastase-->Elastase Procarboxypeptidase A/B-->Carboxypeptidase |
|
|
How are pancreatic zymogens activated?
|
In response to food, duodenum release ENTEROPEPTIDASE which cleaves trypsinogen to trypsin (active)
Trypsin then activates all pancreatic zymogens (including more trypsinogen) |
|
|
What intestinal cells to amino acids enter? What forces exist that effect movement into these cells?
What becomes of most di- and tripeptides that are absorbed by these cells? And of free AA's? |
Enterocytes
Concentration gradient of Na+ for single AA Concentration gradient of H+ for di- and tripeptides Enterocyte peptidases within cytosol degrade them into AA's Free AA's go to hepatic portal circulation |
|
|
What is cystinuria? Symptom's?
|
diminished ability to transport dibasic AA's (in gut and kidney)
Leads to excess cystine in urine, resulting in KIDNEY STONES |
|
|
What is Hartnup's Disease? Symptoms?
|
Defect in uptake of tryptophan, neutral AA's
Tryptophan converted to Niacin, so resembles Pellagra (3D's: Dermatitis, Diarrhea, Dementia) |
|
|
In protein turnover, how does the body know which proteins are old/misfolded and need to be degraded?
|
Old/misfolded proteins tagged by UBIQUITIN (ATP-dependent)
Ubiquitin tagged molecules then are transported into proteasome where they are cleaved into AA's |
|
|
What becomes of excess amino acids?
|
Excess AA's are deaminated (nitrogen removed) and carbon skeletons used for energy in gluconeogenesis or ketogenesis
|
|
|
What intestinal cells to amino acids enter? What forces exist that effect movement into these cells?
What becomes of most di- and tripeptides that are absorbed by these cells? And of free AA's? |
Enterocytes
Concentration gradient of Na+ for single AA Concentration gradient of H+ for di- and tripeptides Enterocyte peptidases within cytosol degrade them into AA's Free AA's go to hepatic portal circulation |
|
|
What is cystinuria? Symptom's?
|
diminished ability to transport dibasic AA's (in gut and kidney)
Leads to excess cystine in urine, resulting in KIDNEY STONES |
|
|
What is Hartnup's Disease? Symptoms?
|
Defect in uptake of tryptophan, neutral AA's
Tryptophan converted to Niacin, so resembles Pellagra (3D's: Dermatitis, Diarrhea, Dementia) |
|
|
In protein turnover, how does the body know which proteins are old/misfolded and need to be degraded?
|
Old/misfolded proteins tagged by UBIQUITIN (ATP-dependent)
Ubiquitin tagged molecules then are transported into proteasome where they are cleaved into AA's |
|
|
What becomes of excess amino acids?
|
Excess AA's are deaminated (nitrogen removed) and carbon skeletons used for energy in gluconeogenesis or ketogenesis
|
|
|
What is the general formula for transamination in the biosynthesis of a non-essential amino acid?
Which amino acids make use of this method? What are their precursors? |
AA1 + alpha-keto acid 2<-->alpha-keto acid 1 + AA2
via Aminotransferase (needs Vit B6) Pyruvate-->Alanine OAA-->Aspartate a-ketoglutarate-->Glutamate |
|
|
How is cysteine formed?
|
Derived from homocysteine, which is product of methionine metabolism, and serine
Serine comes from intermediate of glycolysis |
|
|
How is tyrosine formed?
|
From Phenylalanine
|
|
|
Briefly describe the metabolism of phenylalanine.
|
Phenylalanine-->Tyrosine
via Phenylalanine DH -->Thyroid hormones, Pigmentation, Proteins, TCA, NT's |
|
|
What is PKU? How is it diagnosed? Symptoms? Treatment?
|
Phenylketonuria: defective phenylalanine hydroxylase; can no longer convert to tyrosine
Overflow of phenylalanine leads to phenylketones (detected in urine) Symptoms: elevated phenylalanine in blood, phenylketones in urine, TYROSINE IS NOW ESSENTIAL, hypopigmentation, mental retardation Tx: Lifelong restriction of phenylalanine, tyrosine supplementation |
|
|
What enzyme is defective in complete albinism? What does this result in?
What's another cause of albinism? |
Tyrosinase is defective
Tyrosine--->-->-->Melanin via Tyrosinase No pigmentation of skin, hair, eyes; visual defects (photophobia), increased skin cancer risk Other cause: defect in phenylalanine metabolism (e.g., defect in phenylalanine hydroxylase) |
|
|
How does alkaptonuria arise? Symptoms? Treatment?
|
Defective Homogentisic Acid Oxidase:
F-->Y-->Homogentisic Acid-->-->Fumarate + AcAc-->TCA Enzyme catalyzes step after formation of homogentisic acid Causes accumulation of homogentisis acid; results in pigmentation of sclera, large joint arthritis, homogentisic aciduria (urine turns dark), black onchronotic pigmentation of cartilage and collagenous tissue Tx: Low protein diet; diet low in F/Y |
|
|
How does alkaptonuria arise? Symptoms? Treatment?
|
Defective Homogentisic Acid Oxidase:
F-->Y-->Homogentisic Acid-->-->Fumarate + AcAc-->TCA Enzyme catalyzes step after formation of homogentisic acid Causes accumulation of homogentisis acid; results in pigmentation of sclera, large joint arthritis, homogentisic aciduria (urine turns dark), black onchronotic pigmentation of cartilage and collagenous tissue Tx: Low protein diet; diet low in F/Y |
|
|
Is methionine essential or non-essential? What does is help synthesize?
|
Essential
SAM (s-adenosylmethionine) for add'n of carbons to biol substrates Cysteine (via homocysteine) |
|
|
What are high levels of homocysteine associated with? What could possibly cause an increase in homocysteine levels? Treatment?
|

CVD
Deficiency in B12, Folate, Serine, Cystathionine synthase, or B6 could lead to high levels of cystathionine Tx: Restrict methionine intake, supplement B6, B12, folate |
|
|
Using methionine metabolism, explain the impacts of a B12 deficiency.
|
Decreased B12 (no longer can convert homocysteine to methionine) results in high homocysteine
No longer can convert CH3-THF to THF (THF needed for synthesis of dTMP from dUMP) Manifests itself as PERNICIOUS ANEMIA (causes nerological probs) |
|
|
What purpose does SAM serve? How is it synthesized?
|
SAM donates high energy carbon to biological substrates (ex: Norepi-->Epi)
Methionine + ATP-->S-Adenosyl-methionine + Pi + PPi (SAM = S-adenosyl-methionine) |
|
|
Briefly outline normal methionine metabolism.
|
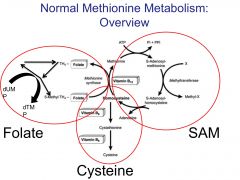
|
|
|
How is histamine formed? Synthesized from what aa? Effects of histamine?
|
AA Breakdown product (decarboxylation with pyridoxal phosphate)
Vasodilator by degranulating mast cells; mediates allergic and inflammatory rxns Synthesized from HISTIDINE |
|
|
Where is serotonin found? Functions? Synthesized from what aa?
|
Intestines, brain, platelets
Pain, sleep, body temp, BP Synthesized from tryptophan |
|
|
How is creatine formed? Purpose? What is creatine kinase a marker of?
|
Arginine & Glycine with methyl from SAM
Provides rapidly mobilized store of energy for muscle undergoing intense contraction Creatine Kinase is a marker of MI |
|
|
What are high levels of serum creatinine indicative of?
|
Falling kidney function (should have been removed by kidneys; shouldn't be allowed to accumulate)
|
|
|
How is histamine formed? Synthesized from what aa? Effects of histamine?
|
AA Breakdown product (decarboxylation with pyridoxal phosphate)
Vasodilator by degranulating mast cells; mediates ellergic and inflammatory rxns Synthesized from HISTIDINE |
|
|
Where is serotonin found? Functions? Synthesized from what aa?
|
Intestines, brain, platelets
Pain, sleep, body temp, BP Synthesized from tryptophan |
|
|
How is creatine formed? Purpose? What is creatine kinase a marker of?
|
Arginine & Glycine with methyl from SAM
Provides rapidly mobilized store of energy for muscle undergoing intense contraction Creatine Kinase is a marker of MI |
|
|
What are high levels of serum creatinine indicative of?
|
Falling kidney function (should have been removed by kidneys; shouldn't be allowed to accumulate)
|
|
|
How is histamine formed? Synthesized from what aa? Effects of histamine?
|
AA Breakdown product (decarboxylation with pyridoxal phosphate)
Vasodilator by degranulating mast cells; mediates ellergic and inflammatory rxns Synthesized from HISTIDINE |
|
|
Where is serotonin found? Functions? Synthesized from what aa?
|
Intestines, brain, platelets
Pain, sleep, body temp, BP Synthesized from tryptophan |
|
|
How is creatine formed? Purpose? What is creatine kinase a marker of?
|
Arginine & Glycine with methyl from SAM
Provides rapidly mobilized store of energy for muscle undergoing intense contraction Creatine Kinase is a marker of MI |
|
|
What are high levels of serum creatinine indicative of?
|
Falling kidney function (should have been removed by kidneys; shouldn't be allowed to accumulate)
|
|
|
What categories can amino acids be broken up into (based on where their carbon skeletons go)?
|
Glucogenic
Ketogenic Glucogenic and Ketogenic |
|
|
Where are most amino acids broken down? What about branched amino acids? Which amino acids are branched?
|
Most aa's broken down in liver
Branched Chain AA's degraded primarily in muscle BCAA = isoleucine, leucine, valine |
|
|
What causes Maple Syrup Urine Disease? Symptoms? Treatment?
|
Deficiency in Branched-Chain Ketoacid DH (helps break down BCAA's) results in accumulation of BCAA and their corresponding alpha-keto acids
Interferes with brain function Symptoms: Dehydration, feeding probs, maple syrup odor to urine Tx: Diet low in BCAA |
|
|
If free amino groups are toxic to the CNS, what must occur after breakdown of amino acids? Describe all events.
|
Nitrogen must be transported to the liver!
Transamination generates carrier molecule Peripheral tissues use glutamine as carrier Muscles use alanine Liver converts glutamine to glutamate Liver converts alanine to pyruvate |
|
|
How does glutamate donate its nitrogen for urea synthesis?
|
Deamination (release NH3 directly into mitochondria)
Transfer of amino group to OAA to form aspartate in cytoplasm |
|
|
How does alanine aminostransferase function differ in the muscle and liver?
|
TRANSAMINATION
Muscle: Pyruvate-->Alanine Liver: Alanine-->Pyruvate (High levels of Alanine Transferase indicate liver damage) |
|
|
What reaction does aspartate aminotransferase catalyze?
|
TRANSAMINATION
Glutamate-->Aspartate High levels of AST serum damage to liver cells |
|
|
How does glutamate dehydrogenase function differ in the muscle and liver?
|
DEAMINATION: Removes amino group from glutamate:
1) as ammonia in kidney (NH3) 2) as urea in liver |
|
|
What benefit does coupling transamination with deamination have?
|
Removes nitrogen from excess AA's
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the urea cycle? Briefly outline its steps.
|
dispose of toxic ammonia.
Nitrogen enters as GLUTAMATE in mitochondria and as ASPARTATE in cytoplasm NH4 (mito) + ATP + CO2--> CARBAMOYL PHOSPHATE (RATE LIMITING!) combines with Ornithine to become Citrulline, exits to cytosol, combines with Aspartate -->-->Arginine-->UREA (and Ornithine) Last step via ARGINASE |
|
|
Why would alpha-ketoglutarate levels decrease in response to elevated levels of free ammonia? What affect does this have on metabolism?
|
Free ammonia is toxic to the CNS
a-ketoglutarate can be used as nitrogen acceptor even if it means removing a TCA cycle intermediate and reducing ATP |

