![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Parallels of latitude run |
East and west |
|
|
|
Meridians of longitude run |
north and south and connect earth's poles |
|
|
|
A great circle is formed |
On the surface of a sphere by the intersection of a plane that passes through the center of the sphere; such a circle on the surface of the earth an arc of which connecting two terrestrial points constitutes the shortest distance on the earth's surface between them |
|
|
|
The equator measures... |
North-south distances *is a great circle* |
|
|
|
Great circle |
Equator Also any two opposing meridians of longitude make a great circle (each meridian is half of a g.c.) |
|
|
|
Parallels of latitude are a series of smaller _________ circles refered to as small circles |
East-west |
|
|
|
Parallels of latitude are |
Parallel to the Equator Used to measure distances north and south of the equator North pole is 90° north lat. South pole is 90° south lat. |
|
|
|
Longitude lines are used to measure angular distances.... |
East and west of the PM 0° - 180° east and west 180° east longitude and 180° west longitude are the same Meridian |
|
|
|
The places where Meridians and parallels cross are called |
Coordinates |
|
|
|
Coordinates are used for: |
Pilot charts, blocks of airspace, & airborne navigation systems *they are written in ATC without degree or minute symbology and do not include seconds |
|
|
|
Circular measurement |
A circle = 360° 1° = 60' (minutes) 60' = 60" (seconds ( |
|
|
|
Lattitude can not be used as a scale to measure distance except at the |
Equator |
|
|
|
1 minute of latitude is equal to |
1NM (measured along a line of longitude) |
|
|
|
*when coordinates are used to define a position, is latitude or longitude stated first?* |
Latitude |
|
|
|
*the reference line for measuring north-south distances is the ______* |
Equator |
|
|
|
*How many minutes are there in 1° of latitude?* |
60 minutes |
|
|
|
A great circle route is |
The shortest distance between two points on a sphere -most direct route -saves time and fuel -crosses every meridian at different angle (constantly changing true direction) |
|
|
|
A rhumn line |
Is a line which makes the same angles with each meridian of longitude and is longer than a great circle route -constant heading -more time & fuel -easier to navigate |
|
|
|
1 NM = |
1.15 SM |
|
|
|
1 SM = |
0.87 NM |
|
|
|
NMs and Kts are universal in ATC |
NMs and Kts are universal in ATC |
|
|
|
Conversion factors |
NM x 1.15 = SM SM x .87 = NM |
|
|
|
Coordinated universal time (UTC) is also known as |
Zulu time -used by the FAA for all operations but local time may be used in VFR |
|
|
|
There are ___ standard time zones. name them |
4 -eastern -central -Mountain -pacific |
|
|
|
Each time zone is divided into ___° of L_______ |
15° of Longitude |
|
|
|
Time is in Local standard time (LST) OR |
Daylight savings time (DST) |
|
|
|
The unit of measurement which equals 1 NM is ___SM |
1.15 |
|
|
|
A time zone is established for every |
15° of Longitude |
|
|
|
U.S. time conversion factors |
Eastern = +5 hrs. Central = +6 Mountain = +7 Pacific = +8 Alaska = +9 Hawaii = + 10 |
|
|
|
When DST is in effect, subtract 1 hr from the time conversion factors |
Eastern = +4 hrs. Central = +5 Mountain = +6 Pacific = +7 Alaska = +8 Hawaii = + 9 |
|
|
|
DST starts at _____ the 2nd Sunday in March, and ends at _____ the 1st Sunday in November |
2am 2am *some locations do not switch to DST |
|
|
|
Indicated airspeed (IAS) |
-shown on the a/c indicator -used in pilot/controller communications |
|
|
|
True airspeed (TAS) |
-relative to undisturbed air mass Used in: -flight planning -en route portion of flight |
|
|
|
Ground speed (GS) |
The speed of an a/c relative to the surface of the earth is true airspeed corrected fir the effects of wind |
|
|
|
Mach number (MACH) |
-ratio of true airspeed to the speed of sound, expressed in decimal form - example Mach 0.82 |
|
|
|
For a constant true airspeed, the indicated airspeed ______ with altitude and temperature |
Decreases |
|
|
|
In less dense air at higher altitudes, fewer air molecules enter the a/c's pitot tube, resulting in a _____ indicated airspeed |
Lower |
|
|
|
At high altitudes, an a/c's indicated airspeed is significantly _____than its true airspeed |
Lower |
|
|
|
Air becomes _____ dense as temperature increases |
Less |
|
|
|
An increase in temperature has the same effect on speed as an ______ in altitude |
Increase |
|
|
|
Unlike the effects of altitude on speed, the differenfe between IAS and TAS caused by changes in temperature are relatively ______ and are ________ to a controller |
Unlike the effects of altitude on speed, the differenfe between IAS and TAS caused by changes in temperature are relatively small and are less significant to a controller |
|
|
|
Time = |
Distance/Speed
Divide time by 60 to get decimals Note: 2.5 hrs is expressed as 2 +30 in ATC |
|
|
|
Speed |
Speed = Distance/Time |
|
|
|
Distance |
Distance = speed x time |
|
|
|
Like units for time, speed, distance |
NM and Knots SM and MPH |
|
|
|
Wind |
Is a mass of air moving over the Earth's surface in a definite direction -it is stated to include direction and velocity |
|
|
|
Wind does nof affect _____ airspeed, but it does affect __________ |
Wind does NOT affect true air speed, but it does affect ground speed |
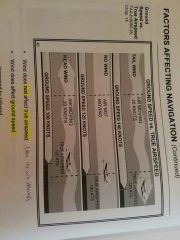
|
|
|
True course |
Represents the intended path of the a/c over the Earth's surface |
|
|
|
True heading = true course corrected for wind |
TH = TC +- WCA -the pilot attempts to fly true course -the wind pushes a/c off course -the track over the ground is not desired one -the difference is called drift angle |
|
|
|
Wind correction angle (WCA) |
The resulting angle when a pilot corrects heading toward direction from which the wind is coming coming coming |
|
|
|
It is the controller's responsibility to compensate for wind speed and direction when: |
-formulating estimates -issuing radar vectors |
|
|
|
The WAC is 20° and true course is 090° what is true heading? |
TH= 90-20 TH = 70° |
|
|
|
Variation is |
The angular difference between true north and magnetic north -measured in degrees from true north |
|
|
|
Isogonic lines are |
Lines of equal difference between true and magnetic north |
|
|
|
Agonic means |
Agonic line connects points of zero variation -there is only 1 agonic line |
|
|
|
Magnetic heading is |
Magnetic heading is true heading corrected for vatiation MH = TH + - VAR |
|
|
|
________ headings are used in pilot and controller communications |
Magnetic headings are used in pilot and controller communications |
|
|
|
For _____ variation, subtract degrees of variation
For ______ variation, add degrees of variation |
For east variation, subtract degrees of variation. For west variation, add degrees of variation |
|
|
|
The error of a magnetic compass due to magnetic influence in the structure and the equipment of an a/c is called |
Deviation -magnetic compass error may change as the a/c heading changes |
|
|
|
_______ heading is the magnetic heading corrected for deviation |
Compass heading is the magnetic heading corrected for deviation CH= MH + - DEV |
|
|
|
The angular difference between the true north and magnetic north at any given place is called |
Variation |
|
|
|
A line of equal magnetic variation is called |
An isogonic line |
|
|
|
What term defines a magnetic compass error that is caused by materials within the a/c which possess magnetic properties? |
Magnetic deviation |
|
|
|
True heading is true course corrected for the effects of |
Wind |
|
|
|
What is navigation of an a/c solely by means of computations based on airspeed, course, heading, wind direction, and speed, ground speed, and elapsed time |
Dead reckoning is navigation of an a/c solely by means of computations based on airspeed, course, heading, wind direction, and speed, ground speed, and elapsed time
-done with or without reference to the ground |
|
|
|
is the determination of position by identification of landmarks from their representation on a chart |
Pilotage is the determination of position by identification of landmarks from their representation on a chart -pilot flies landmark to landmark by visual references -useful only in VFR wx |
|
|
|
Navigation by reference to visible landmarks is called |
Pilotage |
|
|
|
What method of navigation reauires having to fly a predetermined course, taking into account the effects of wind? |
Deadreckoning |
|

