![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are petechiae and mucosal bleeding “classic” indicators of?
|
Platelet abnormality
|
|
|
What are the 4 main areas re: bleeding to cover when taking a patient’s history?
|
1. Current bleed: (when did it start, how much bld, trauma, etc)
2. PMHx: previous bleeds, surgeries, epistaxis, menstrual hx, melena, hemarthrosis 3. Meds: NSAIDS, ASA, also… ginko, garlic 4. FHx: Hemophilia, transfusions, hemorrhages |
|
|
What does a finding of hemarthrosis suggest?
|
Factor-type hemorrhage
|
|
|
What are the two main classes of bleeding?
|
1) Hematologic
2) Non-hematologic |
|
|
What is the overall classification of bleeds?
|
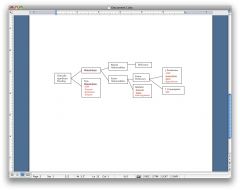
|
|
|
How can a bleed by platelets be further classified?
|
1) Qualitative:
2) Quantitative: |
|
|
What does INT/PT measure?
|
Extrinsic pathway
|
|
|
What does PTT measure?
|
Intrinsic pathway
|
|
|
If the PTT, INR and TT came back normal, what conclusion can you draw about the bleed?
|
It is due to non-hematologic factors
|
|
|
Interpret:
PTT 45 sec (N: 25-35) PT 11 (N: 10-13) TT 17 (N: <20) |
1) Problem with intrinsic pathway: (12,11,9,8)
2) Problem with inhibitor: lupus anticoagulant, heparin |
|
|
Interpret:
PTT 39 sec (N: 25-35) PT 26 sec (N:10-13) TT 19.0 (N: <20) |
- ↑ in both PTT and PT ∴ problem in both intrinsic and extrinsic pathway. Either factor deficiency or coagulation inhibitor.
- Unlikely inhibitor b/c wouldn’t see ↑ in both PT and PTT Either: • Multiple factor in both extrinsic (7) and intrinsic (12,11,9,8) • Def of factor in common pathway (10,5,2,1) ∴ either d/t vit K deficiency or liver disease. - Give Vit K to see if coagulation returns to normal, or test plasma factor levels. If level of both 5 and 7 are low – then problem is liver disease. If only 7 is low, then it is d/t Vit K deficiency. |
|
|
Interpret:
PTT 51 sec (N: 25-35) PT 11 sec (N: 10-13) TT 18 (N < 20) |
Problem with intrinsic pathway d/t inhibitor or deficiency.
|
|
|
A mixing study shows:
PTT (patient): 51 s PTT (control): 29 s PTT (50:50) mix: 48 sec Is this problem due to factor deficiency or presence of an inhibitor? |
Inhibitor (heparin or lupus anticoagulant)
|
|
|
Is lupus anticoagulant associated with bleeding?
|
No
|
|
|
What are the causes of ↑ factor consumption?
|
• Congenital (rare)
• Acquired (DIC) |
|
|
A deficiency in vitamin K would show what on the labs?
|
↑ PTT and PT
(normal TT b/c fibrinogen (factor 1) is not K-dependent) |
|
|
What factors are affected in vitamin K deficiency?
|
2,7,9,10
|
|
|
What can cause ↓ factor production?
|
• Congenital Deficiency: Hemophilia A (factor 8), Hemophilia B (factor 9), 12 (not assoc with bleeding), 11 (very rare), VWD (factor 8 ↓ as well)
• Acquired deficiency: liver disease, vit K deficiency |
|
|
What does a physical finding of Dupuytren’s contractures suggest?
|
Liver disease
|
|
|
What should the physical exam focus on?
|
1) Evidence of recent bleed
2) Evidence of underlying disease causing 2° bleeding |
|
|
(From quiz) A 72-year-old man with multiple medical problems develops extensive bruising. He had never before been noted to have any bleeding disorder. Laboratory testing reveals prolonged PT and PTT. The platelet count is normal. Which of the following is the MOST LIKELY finding on history?
a. Social history: extensive longstanding alcohol abuse b. Family history: maternal uncle with Hemophilia c. Past medical history: heavy bleeding following tooth extraction as a child d. History of presenting illness: febrile illness two weeks ago |
A. Social history: longstanding alcohol abuse
|
|
|
(From quiz) A 61-year-old man is brought by ambulance into the emergency department, unconscious. Initial labwork demonstrates that the PT and the PTT are abnormal. Your differential diagnosis for his coagulopathy should include:
a. immune thrombocytopenic purpura, secondary thrombocytopenia, marrow failure syndromes b. vitamin K deficiency, liver failure, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy c. Hemophilia A, Hemophilia B, von Willebrand`s Disease d. lupus anticoagulant, unfractionated heparin, aspirin |
B. Vitamin K deficiency, liver failure, DIC
|
|
|
What do you call a boomerang that doesn't come back?
|
A stick
|

