![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Parts of the brain needed for mocks |
Cerebral Cortex (two hemispheres)
Cerebellum Medula oblongata |
|
|
What does the cerebellum do? |
It controls balance + posture, as well as timing and fine motor skils. |
|
|
What does the medula oblongata control? |
Unconscious actions such as heart rate, breathing rate Reflexes such as vomiting, sneezing and swallowing (part of the CNS) |
|
|
Four Stages of Mitosis (+ Interphase) |
0. Interphase - cell copies all of its organelles, as well as making copies of the chromosomes so it has 2 pairs rather than 1. 1. Prophase - The nucleus begins to break down and the spindles begin to form 2. Metaphase - The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell and the spindles attach 3. Anaphase - the copies of each chromosome are separated by the spindles and moved to either end of the cell. 4. Telophase - The new nuclei form around the separated chromosomes. 5. Cytokinesis - the new cell surface membrane forms, creating two daughter cells from one parent cell. |
|
|
Stages of Meiosis |
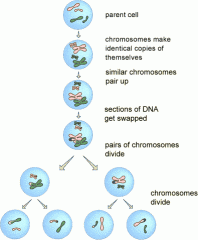
|
|
|
How does meiosis create genetic variation in the gametes? |
The crossing over of cells ensures that different parts of the genome are in each chromosome, creating genetic variation within the gametes |
|
|
How many daughter cells does meiosis produce? |
4 |
|
|
What are the 4 bases involved in DNA? |
Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine and Adanine |
|
|
What is the order of subunits of nucleotides, going from the outside inwards? |
Phosphate, sugar, base |
|
|
Which enzyme is used in transcription? |
RNA polymerase |
|
|
How does transcription and translation work? |
1. RNA polymerase attaches to DNA in front of a gene in a non-coding region. The RNA polymerase then separates the two DNA strands. 2. Moving from left to right, the RNA then adds complimentary RNA base pairings (nucleotides). HOWEVER, THE RNA USES URACIL (U) INSTEAD OF THYMINE (T) 3. All of these nucleotides then combine to form MESSENGER RNA (mRNA). 4. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus via nuclear pores (tiny holes) and enters the cytoplasm. 5. The mRNA then attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. 6. A ribosome then moves along an mRNA strand three bases at a time. Each triplet of bases (a codon) contains a molecule of transfer RNA (tRNA), where the complimentary base pairs line up. 8.This combo codes for a specific amino acid. The ribosome then joins up all of the amino acids to form a polypeptide. This is translation. 9. The polypeptide then folds up to form a protein (e.g. an enzyme) |
|
|
What is an allele? |
A form of a gene, which can have variation. |
|
|
Order of Classification |
Kingdom Phylum Class Order Genus Species |
|
|
What are the five kingdoms? (+ Extra sixth one) |
Animals
Plants Fungi Protista Prokaryotes +Archaea |
|
|
Explain the process of genetic modification using donor plasmids. |
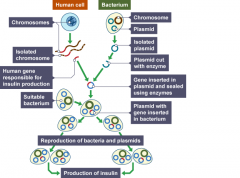
(DNA from chromosome cut using restriction enzymes and replaced into plasmid using DNA ligase) |

