![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
why are cells important?
|
- all organisms are made up of cells
- all living things have them |
|
|
what is the difference between HYDRO PHOBIC and HYDRO PHILIC
|
hydro phobic
*water hate hydro philic *water love |
|
|
what does the body mainly need?
|
h2o, glucose, o2 and co2
|
|
|
environment of cells
|

|
|
|
cell membrane
|

|
|
|
membrane structure
|

|
|
|
phospholipid bi-layer
|

|
|
|
aspects of tge internal environment that need to be regulated
|
- salt concentrations
- temperature - leveks of nutrition - ph - removal of waste - ion conentrations |
|
|
carbohydrates
|

|
|
|
movement into and out of a cell
|
- diffusion
- osmosis - facilitated diffusion - active transport - endocytosis and exocytosis |
|
|
diffusion
|

|
|
|
osmosis
|

|
|
|
active transport
|

|
|
|
bulk transport
|

|
|
|
whats in a plant cell?
|
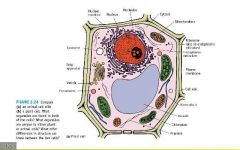
|
|
|
mitochondrion
|

|
|
|
nucleus
|
usually the largest oranelle in the cytoplasm of a cell. directs all activities of the cell.
|
|
|
what is in an animal cell?
|
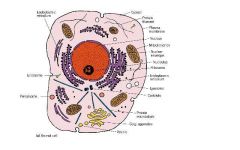
|
|
|
centriols
|

|
|
|
cell membrane
|
forms the outer boundary of the cell
|
|
|
cytoplasm
|

|
|
|
endoplasmic reticulum
|

|
|
|
golgi bodies
|
packaged and moved proteins
|
|
|
chloroplasts
|

|
|
|
vacuole
|

|
|
|
ribosome
|

|
|
|
lyosomes
|

|
|
|
cilia and flagella
|

|
|
|
why do we need enzymes?
|
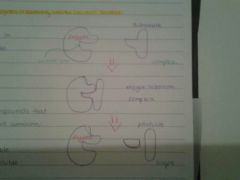
without it nothing works in our bodys.
|
|
|
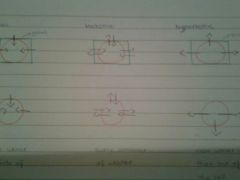
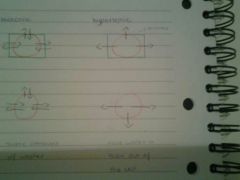
hypotonic
|
|
|
|
isotonic
|
|
|
|
hypertonic
|
|
|
|
hypothesis
if ............. then .............. |
if ....IV..... then .... DV.....
IV- what you control DV- result |

