![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 3 steps in Urine formation ? |
1.Filtration 2. Re absorption 3. Secretion |
|
|
Describe filtration |
movement of materials |
|
|
Describe Re-absorption |
transfer of solutes and water from nephron back into blood |
|
|
Describe secretion |
transfer of materials from blood into nephron |
|
|
During filtration, where do the blood enters ? which arteriole do they enters from ? |
glomerulus and afferent |
|
|
During filtration, where do the water and small solutes pass through ? |
Bowman's capsule |
|
|
What type of solutes does the glomerulus have that aren't in the bowman's capsule ? |
Plasma proteins and red blood cells |
|
|
where do re absorption occurs ? |
Proximal tubule, loop of henle, distal tubule and collecting duct |
|
|
What type of solutes get reabsorbed from the the proximal tubule and into the interstitial fluid ? |
Na+ , Cl-, water, glucose vitamin and amino acid |
|
|
where is the loop of henle located ? |
kidney |
|
|
Give an example of a substance that is permeable to the descending loop? |
water |
|
|
Give an example of a substance that is permeable to the ascending loop? |
salt |
|
|
Is the loop of Henle a hypotonic environment ? |
Yes,because it has a higher salt/urea concentration outside the tubule than the inside. |
|
|
Is the distal tubule a hypertonic environment ? |
Yes, because it has a higher salt/urea concentration inside the tubule than the outside . |
|
|
what types of solute get pumps out of the distal tubule? |
Na+, Cl-, HCO3-,water , urea |
|
|
In secretion, what substances flow from blood into nephron? and into where ? |
Substances: H+, K+ and drugs Locations :proximal and distal tubule lumen |
|
|
What hormone retains water in the body and constricts blood vessel? |
Anti-diuretic hormone(ADH) |
|
|
Where is the ADH located? |
pituitary gland |
|
|
What receptor detects the osmotic pressure in capillaries ? where is the receptor located ? |
Osmoreceptor Location :hypothalamus |
|
|
What receptor shrinks when water flow out? what happen after? |
Osmoreceptor. This cause the hypothalamus to send a nerve message to the pituitary gland to release ADH, which tell the kidney to reabsorb water , causing thirst. |
|
|
What role do the kidney plays? |
Regulate blood volume
|
|
|
What hormone increases the amount of Na and Cl- that is reabsorbed ?
Where is it located ? |
adrenal gland
aldosterone |
|
|
What special cells of the distal tubule releases renin? Where is it located ? |
juxtaglomerular apparatus afferent arteriole |
|
|
When do juxtaglomerular apparatus release renin? |
when blood pressure falls |
|
|
What is the function of the enzyme renin ? |
To convert the blood protein from angiotensinogen into angiotensin |
|
|
What happens when angiotensin increases?
|
Causes constriction of blood vessels therefore increases blood pressure Causes the adrenal gland to release aldosterone therefore increasing blood volume through an increase in water re absorption. |
|
|
In the proximal convoluted tubule, chloride ions are reabsorbed because of: |
the electrical attraction of sodium ions |
|
|
Which of the following promotes sodium retention and potassium loss from the blood of the distal convoluted tubule? A. renin B. angiotensin C. aldosterone D. angiotensin E. ADH. |
D |
|
|
Granular (juxtaglomerular cells) secrete _____ when there is a fall in _____ ion concentration A. renin / chloride B. carbonic anhydrase / sodium C. ATPase / potassium D. renin / sodium E. carbonic anhydrase / carbon dioxide. |
D |
|
|
Glucose is: a.Filtered, reabsorbed, and secreted b.Filtered, and reabsorbed, but not secreted c.Filtered, and secreted, but not reabsorbed d.Filtered, and neither secreted nor reabsorbed |
B |
|
|
The majority of reabsorption occurs in the: a.Renal capsule b.Proximal convoluted tubule c.Collecting duct d.Ascending limb of the loop of Henle |
B |
|
|
Which of the following is incorrect concerning ADH? a.Its production is regulated by plasma osmolarity b.Its activity is affected by alcohol c.It acts on the collecting duct and decreases its permeability to water. d.It is stored in the posterior pituitary |
c |
|
|
Which of the following parts is not found in the urinary system? a)Ureters b) Urethra c)Bladder d)Rectum |
D |
|
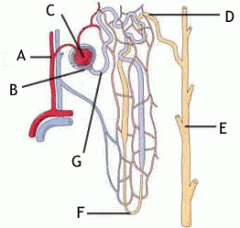
The structure B: A.cortex B.bowman's capsule C. collecting duct D.nephron |
B |
|
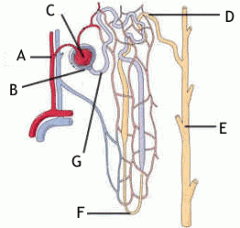
The structure G: A.renal artery B.renal vein C. proximal tubule D.distal tubule |
C |
|
|
Describe osmotic pressure |
concentration of solute in a solution.ability of a solution to draw water into itself across membrane |
|
|
Describe homeostasis |
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level |
|
|
In true dehydration, blood volume declines and sodium concentration rises. The increased osmolarity of the blood stimulates the hypothalamic receptors, which stimulate the posterior pituitary to release ____. |
ADH |
|
|
During ADH release, Sodium continues to be excreted as water is reabsorbed, so the ratio of sodium to water in the urine ____, and urine is more concentrated. Therefore water volume ___ (rate of volume decrease slows down) and ____ (concentration) of urine is increased. |
increases, increases, osmolarity |
|
|
_____ plays the primary role in adjustment of sodium excretion, by retaining salt. The primary effects of this hormone are that the urine contains less NaCl and more K+ and has a lower pH. |
Aldosterone |
|
|
How does the kidney regulate blood pressure? |
By the release of renin |
|
|
Does the release of Aldosterone increase the sympathetic or parasympathetic system? |
Sympathetic System (Fight or Flight) |
|
|
What is the primary stimulus to activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system? What is the end result? |
Low blood volume; Increased arterial pressure |
|
|
What organ(s) regulate the acid-base balance of the blood? |
Kidneys and lungs |
|
|
To remain healthy, our blood pH should stay with a range of ? |
7.3-7.5 |
|
|
What element help regulate the pH level of our blood? |
Hydrogen ions |
|
|
Give an example of a buffering systems |
Bicarbonic Acid Buffer system |
|
|
What is a buffer ?
|
A solution that resist changes in pH level.
|
|
|
What compound is formed ,when blood is too acidic? What happened to the compound if the blood is too basic? |
H2CO3 (carbonic acid) Carbonic dissociates forming hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions |
|
|
Filtration of the blood occurs at the ___________ an is collected by the ___________. |
Glomerulus ; bowman capsule |
|
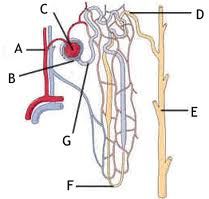
Structure E is the: A. outer medulla B. inner medulla C.This is Cancer D.Collecting Duct |
D |
|
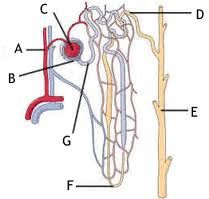
Structure D is the : A. Distal tubule B. Outer Medulla C. **** this **** D. loop of henle |
A |
|
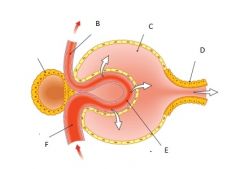
Structure B is the : A. Efferent arteriole B.NOT THIS ONE C.Secretion D. Bowman's capsule |
A |
|
|
Why do selective re-absorption occurs? |
changes in permeability of cells lining nephron changes in solute concentration of tissue surrounding nephron |
|
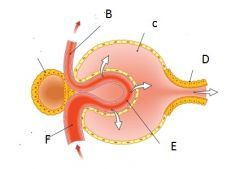
Structure F is the : A.Afferent Arteriole B. AHHHHHHHHH C. Glomerulus D. Blood |
A |

