![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Allele
|
An allele has one of 2 more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation
|
|
|
Multiple alleles
|
A multiple allele is one of a number of alternative forms of the same genetic gene
|
|
|
Dominant
|
The dominant gene produces the same phenotype in the organism
|
|
|
Recessive
|
The recessive gene produces its characteristic phenotype only when its allele is identical
|
|
|
Homozygous
|
The homozygous gene has identical alleles at corresponding chromosomal loci
|
|
|
Heterozygous
|
Heterozygoukeds has dissimilar alleles at corresponding chromosomal loci
|
|
|
Sex-linked
|
A sex-linked gene is the phenotype expression of an allele related to the chromosomal sex of the individual
|
|
|
Asexual
|
Asexual is an organism capable of producing offspring in the absence of a male
|
|
|
Sexual
|
Sexual is being of one sex or the other and capable of sexual reproduction
|
|
|
Cell Cycle
|
Cell cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its duplication and division
|
|
|
cell plate
|
the cell plate is a disc like structure that separates the 2 sets of chromosomes during cytokinesis
|
|
|
haploid
|
a haploid is a cell or organism that has 1/2 the number of chromosomes in somatic cells
|
|
|
diploid
|
Diploid is a cell or organism that has 2 sets of chromosomes one from the mom and one from the dad
|
|
|
mitosis
|
|
|
|
anaphase
|
anaphase is a stage in mitosis when the chromosomes move away from one another to opposite poles of the spindle
|
|
|
interphase
|
interphase is the resting phase between successive mitotic divisions of a cell
|
|
|
metaphase
|
metaphase is the second stage of cell division
|
|
|
prophase
|
prophase is the first stage of cell division
|
|
|
telophase
|
telophase is the final stage of cell dvision
|
|
|
centriole
|
the centriole is a minute cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells
|
|
|
chromatin
|
the chromatin is the material of which the material of which the chromosomes of organisms other than bacteria are produced
|
|
|
Meiosis
|
|
|
|
cytokinesis
|
cytokinesis is the cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis
|
|
|
cross over
|
crossover is the interchange of sections between pairing homologous chromosomes during prophase
|
|
|
spores
|
The spore is a dormant reproductive cell formed by certain organisms
|
|
|
Binary fission
|
Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction common among prokaryotes where a cell divides giving rise to two cells
|
|
|
Mendel
|
Mendel discovered how traits are transferred from the parents to their offspring
|
|
|
polygenic
|
Polygenic is a group of genes that produces a specific trait only when expressed together
|
|
|
Hemophilia
|
Hemophilia is the congenital tendency to uncontrolled bleeding and usually affects males transmitted from mother to son
|
|
|
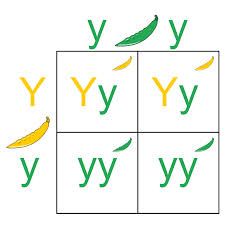
Punnet Squares
|
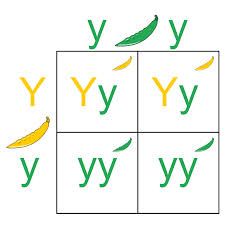
|
|
|
Phenotype
|
The phenotype is the set of observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment
|
|
|
Genotype
|
The genotype is the genetic constitution of an individual organism
|
|
|
Blood Type
|
|
|
|
Pedigree
|
Pedigree is an ancestral line or chart showing the lineage or descent of an individual and all the direct ancestors
|
|
|
Genetic Variation
|
Genetic variation are variations of genomes between members of groups/species thriving in different parts of the world as a genetic mutation
|
|
|
Inheritance
|
Inheritance are traits that are transmitted from parents to their child ex: blue yes/brown eyes, tall/short etc
|
|
|
Co-dominance
|
Co-dominance is a condition in which the alleeles of a gene pair in a hetrozygote are fully expressed resulting in offspring w/a phenotype that isn't dominant or recessive
|
|
|
Incomplete dominance
|
Incomplete dominance is a kind of dominance occurring in heterozygotes in which the dominant allele is only partially expressed
|
|
|
Independent assortment
|
independent assortment is the process of random segregation and assortment of chromosomes during anaphase resulting in genetically unique gametes
|
|
|
dihybrid
|
Dihybrid is the offspring of a dihybrid cross involving 2 gene loci each with 2 different alleles
|

