![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Catalyst |
A molecule which speeds up a chemical reaction, but remains unchanged at the end if the reaction |
|
|
Metabolic pathway |
A sequence of enzyme-controlled reactions in which a product of one reaction is a reactant in the next |
|
|
Active site |
Site on an enzyme with particular three-dimensional structure that permits binding with a substrate |
|
|
Enzyme-substrate complex |
Intermediate structure formed during an enzyme-catalysed reaction in which the substrate and enzyme bind temporarily, such that the substrates are close enough to react |
|
|
Activation energy |
The minimum energy that must be put into a chemical system for a reaction to occur |
|
|
Denatured |
An enzyme's active site is permanently distorted by the irreversible breaking of hydrogen bonds, preventing substrate binding and reducing the rate of reaction |
|
|
Inactivation |
Reversible reduction of enzyme activity at low temperature as molecules have insufficient kinetic energy to form enzyme-substrate complexes |
|
|
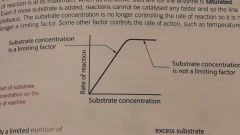
Limiting factor |
Factor is limiting when an increase in its value causes an increase in the rate of reaction |
|
|
Inhibitor |
A molecule or ion that reduces the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction |
|
|
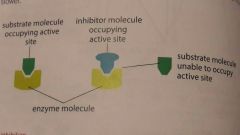
Competitive inhibition |
Reduction of the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction by a molecule or ion that has a complementary shape to the active site, and binds to the active site, preventing the substrate from binding |
|
|
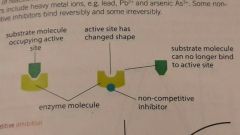
Non-competitive inhibition |
Reduction of the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction by a molecule or ion that binds somewhere other than the active site, altering the shape of the active site so the substrate cannot bind |
|
|
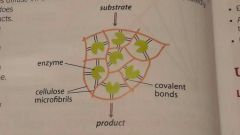
Immobilised enzyme |
Enzyme molecules bound to an inert material, over which the substrate molecules move |
|
|
Biosensor |
A device that combines a biomolecule, such as an enzyme, with a transducer, to produce an electrical signal which measures the concentration of a chemical |
|
|
Lock-and-key model |

|
|
|
Induced fit model |
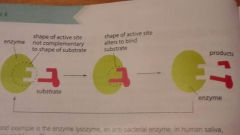
|
|
|
Activation energy graph |
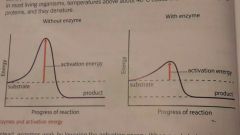
|
|
|
Temperature graph |
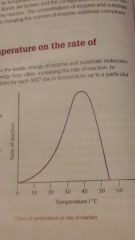
|
|
|
pH graph |
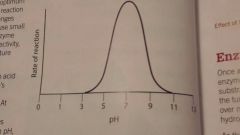
|
|
|
Substrate concentration graph |
|
|
|
Competitive inhibition |
|
|
|
Non-competitive inhibition |
|
|
|
Immobilised enzymes |
|
|
|
Immobilised enzyme graph |
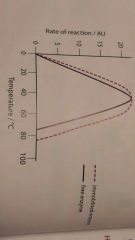
|

