![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the components of of the DNA structure |
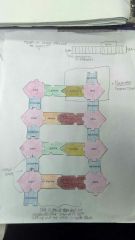
Sugar phosphate backbone plus a base (guanine, cytosine or thymine, adenine) |
|
|
What are nucleotides |
A section of the DNA that contain only a sugar, phosphate and a base |
|
|
What are genes |
A section of the DNA. Each gene tells us how to make a certain type of protein |
|
|
What are histones |
The proteins that the stands of DNA wrap around. |
|
|
What is a chromosome |
Condensed segments of DNA wrapped around histones |
|
|
Why do we have DNA |
Because DNA tell our bodies how to function. They are like the blueprints for our bodies. |
|
|
How is DNA different from species to species |
Different species have different genes |
|
|
Name all the steps in the cell cycle |
1) growth phase 2) "go" (happens during the growth phase) 3) checkpoint 1 4) synthesis phase 5) growth phase 6) checkpoint 2 7) checkpoint 3 8) mitosis |
|
|
Explain what happens during the growth phase of the cell cycle |
Cell increases in size and organelles increase in number |
|
|
Explain what happens during the "go" phase of the cell cycle |
The cells step out of the cell cycle for varying length of time to do their normal functions |
|
|
What happens during checkpoint 1 |
They check that the cell is at peak health |
|
|
What happens during the synthesis phase |
DNA replication |
|
|
What happens during the second growth phase of the cell cycle |
The cell makes components for mitosis |
|
|
What happens during checkpoint 2 and 3 of the cell cycle |
1) It checks that did it did DNA replication correct (92 chromosomes) 2) makes sure everything is correct before it divides (mitosis) |
|
|
What is the purpose of DNA replication |
To give the cell enough chromosomes (92) to be able to give both daughter cells enough chromosomes (46) when it divides later in mitosis |
|
|
When does DNA replication happen |
During the synthesis phase |
|
|
Explain the first step of DNA replication |
Enzyme helicase unzips the DNA (breaks the hydrogen bonds) |
|
|
Explain the second step of DNA replication |
New DNA nucleotides pair up with bases on the parental strand |
|
|
Explain the third step of DNA replication |
The enzyme DNA polymerase proof-reads the new DNA and joins the DNA backbone together |
|
|
What is helicase |
The enzyme that unzips the DNA strands |
|
|
What is DNA polymerase |
The enzyme that proof reads the new DNA and joins the DNA backbone together |
|
|
What is the purpose of mitosis |
To divide into 2 daughter cells that can replace it and do its job |
|
|
What is the different between mitosis and cytokinesis |
Cytokinesis divides the cell and mitosis divides DNA |
|
|
Explain the difference between cytokinesis in plants vs animals |
In animal cells it pinches in half and in plant cells a cell wall appears in the middle and it splits into two |
|
|
Name the steps of mitosis |
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase |
|
|
Briefly explain prophase |
-first step of mitosis -chromatin condense into chromosomes -aster and spindle fibres form |
|
|
Briefly explain metaphase |
-Sister chromatids line up along equator of the cell - spindle fibres attach to kinetochore on each chromatid |
|
|
Briefly explain anaphase |
Chromatids are pulled towards g be centrioles |
|
|
Briefly explain telophase |
-2 Nuclear membranes reform - chromosomes uncoil - cytokinesis begins and pinches cell into 2 |
|
|
Name the 5 different types of asexual reproduction |
Binary fission, budding, fragmentation, vegetation reproduction, spore formation |
|
|
Briefly explain binary fission |
Parent cell divides into 2 equal cells (offspring). Happens to animals that are single celled organism and bacteria |
|
|
Explain budding |
Unequal growth on parent eventually breaks off into an offspring. Happens to less complex multicellular organisms and plants like hydras and cactuses |
|
|
explain fragmentation |
A piece of the parent breaks off and grows into another adult (clone). Happens to to more complex plants and animals. Ex starfish |
|
|
Explain vegetative reproduction |
Specialized plants divide and grow into an offspring that is still attached to the parent by a specialized stem. Ex: blackberrys |
|
|
Explain spore formation |
Specialized cell forms with with a protective coating Happens to plants like mushrooms, mold, moss and ferns |
|
|
What are 2 advantages and 2 disadvantages to asexual reproduction |
1) less energy, few mutation and more offspring 2) too many offspring, too close together, all genetically the same |
|
|
How is DNA different within the same species |
The order of the bases (guanine, cytosine...) are different |
|
|
What are 2 advantages and 2 disadvantages to sexual reproduction |
1) offspring are genetically different so there is higher survival rate, fewer young so intense parental care (internal), less energy to find a mate (external) 2) finding mate takes energy (internal), more mutations, No protection for offspring (external) |
|
|
What is the difference between internal and external fertilization |
Internal= the gametes unite inside the females body and gets parental external=gametes unite outside the females body and generally does not get cared for by parents |
|
|
What is the purpose of meiosis |
To produce 4 gametes (reproductive cells) |
|
|
Explain what is different between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2 |
During metaphase 1 they do not line up on top of eachother but beside eachother to make a tetrad |
|
|
What is meiosis 2 designed to separate |
Sister chromatids |
|
|
What is meiosis 1 designed to separate |
Homologous chromosomes |
|
|
Where are the 2 places in meiosis that variation can occur |
Metaphase 1 and 2 |
|
|
What is a tetrad |
2 homologous chromosomes paired together. All 4 copies of the same chromosome number. |
|
|
Explain what happens in meiosis 1 |
Prophase: sister chromatids condense and pair up Metaphase: line up at equator and form tetrads *crossing over happens Anaphase: sister chromatids separate randomly towards centriole Telophase: splits into 2 cells |
|
|
How many cells are there at the end of meiosis 1 and how many chromosomes do they have each |
2 cells with 46 chromosomes each (23 pairs) |
|
|
Explain what happens during meiosis 2 |
Prophase: sister chromatids are paired up. Spindle fibres form Metaphase: Line up along equator. Variation occurs Anaphase: pulled towards centrioles Telophase: nuclear membrane reforms. Cytokinesis occurs |
|
|
How many cells are there at the end of meiosis 2 and how many chromosomes do they have |
4 haploid cells with 23 chromosomes each (single pieces) |
|
|
Which cells can do meiosis |
Gametes (reproductive cells) |
|
|
What does haploid (n) mean? |
They only have 1 copy of each chromosome |
|
|
What does diploid (2n) mean |
It has 2 copies of each chromosome |
|
|
What are homologous chromosomes |
Both copies of the same chromosome # paired together |

