![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Shape of the DNA structure
|
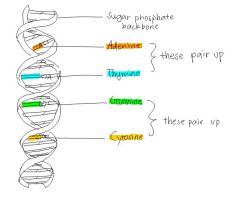
A double Helix |
|
|
Parts of the DNA structure
|
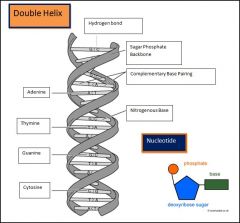
|
|
|
Base Pairing
|
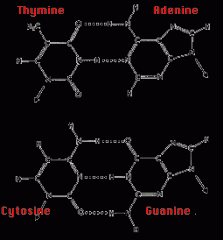
Thymine - Adenine Cytosine - Guanine |
|
|
Names of Bases
|
Thymine (T) Adenine (A) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) |
|
|
Parts of the Nucleotide
|
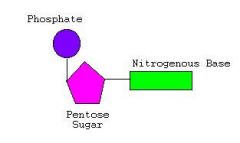
|
|
|
Haploid
|
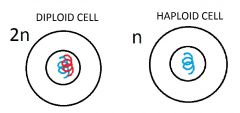
1 set of chromosome |
|
|
Diploid number
|
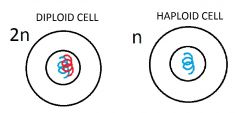
2 sets of chromosomes |
|
|
Difference between mitosis and meiosis
|
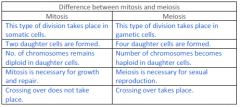
|
|
|
Number of cells produced - Mitosis
|
2 |
|
|
Number of cells produced - Meiosis
|
4 |
|
|
Number of Chromosomes compared to original cell - Mitosis |
Original - 46 Mitosis - 23 |
|
|
Number of Chromosomes compared to original cell - Meiosis |
Original - 46 Meiosis - 23 |
|
|
Define Homozygous |
When your alleles match. Eg. AA or aa Two genes of the same that control a particular trait |
|
|
Define Heterozygous |
Pair of genes of where one of is dominant or one is recessive - they're different E.g. Aa or aA |
|
|
Monoybrid Cross |
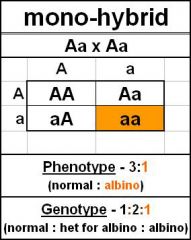
|
|
|
Dihybrid Cross |
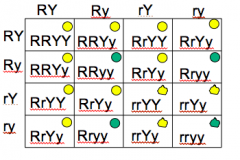
|
|
|
Mutations |
A mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. |

