![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
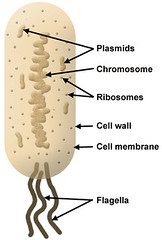
Prokaryote
|
No nucleus, No membrane bound organelles
|
|

Eukaryote
|
Nucleus, Membrane bound organelles
|
|

Homeostasis
|
balance
|
|
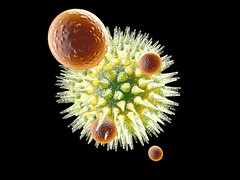
virus
|
infects host cells, contains genetic material,
non living |
|

lytic cycle
|
viral reproduces, kills the cell
|
|
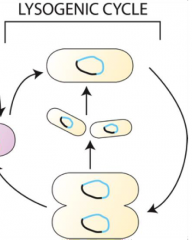
lysogenic cycle
|
virus enters cell, inserts genetic material
|
|
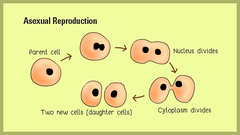
mitosis
|
cell division, identical cells produced
|
|
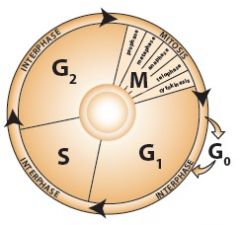
cell cycle
|
cell growth and division
|
|
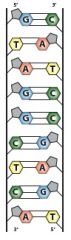
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
|
genetic code |
|
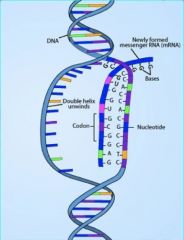
mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid)
|
copy of DNA code
|
|
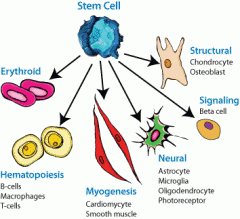
cell differentiation
|
specialization of cells,
(bone, muscle, nerve) |
|
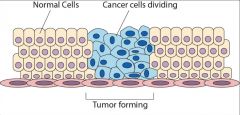
cancer
|
disease from uncontrolled growth and division of cells
|
|

carbohydrates
|
C, H, O
monosaccharide energy source glucose, starch |
|

lipids
|
C, H, O sometimes P
fatty acids energy storage fats, waxes, oils |
|

proteins
|
C, H, O, N
amino acids structural support, speeds reactions enzymes, collagen |
|

nucleic acids
|
C, H, O, N, P
Nucleotides genetic information DNA, RNA |
|

Nucleotide
|
link together to make DNA/RNA
|
|
transcription
|
DNA to mRNA
|
|
Translation
|
mRNA to protein
|
|
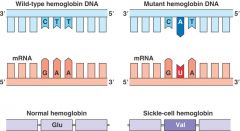
mutation
|
change in DNA
|
|
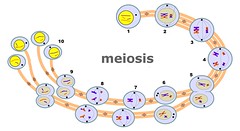
meiosis
|
produces gametes (eggs/sperm)
haploid |
|

genome
|
an organisms DNA
|
|
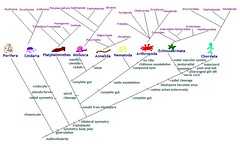
common ancestor
|
organism from which all others come from
|
|
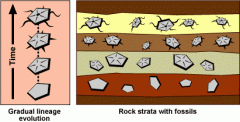
fossil record
|
fossil information about past organisms
|
|
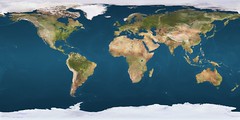
biogeography
|
geographical location of organisms
|
|
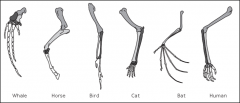
anatomical homologies
|
similar structures from common ancestor
|
|

molecular homologies
|
similar DNA from common ancestor
|
|
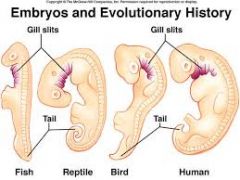
developmental homologies
|
similar development from common ancestor
|
|
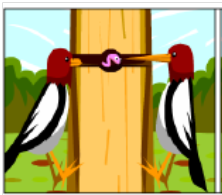
natural selection
|
survival of organisms
based on traits |
|
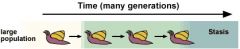
stasis
|
long time period no change in species
|
|
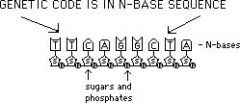
sequence
|
the order that something occurs
first, then, next, last |
|

genetic drift
|
changes in frequency of genes over time
|
|
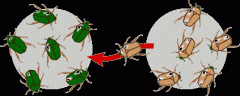
gene flow
|
moving genes from one population to another
|
|
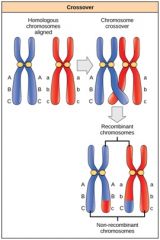
recombination
|
new gene combinations made during meiosis
|
|
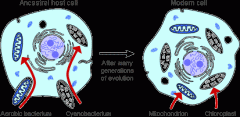
endosymbiosis
|
small prokaryotic cells engulfed by larger cells
|
|
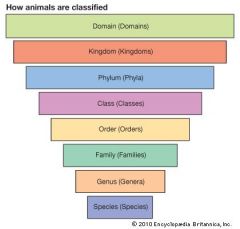
taxonomy
|
classifying organisms
|
|

photosynthesis
|
solar energy to chemical energy
makes glucose happens in chloroplast |
|
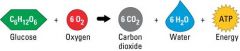
cellular respiration
|
glucose to ATP
happens in mitochondria |
|
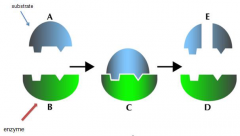
enzymes
|
protein
changes speed of chemical reaction |
|
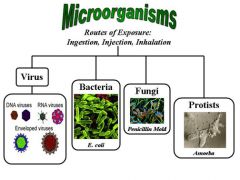
microorganisms
|
microscopic organisms
bacteria, protists |
|

primary succession
|
new ecosystem from nothing
|
|
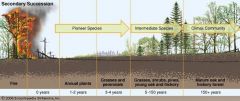
secondary succession
|
new ecosystem where one was devastated
|
|

predation
|
one animal eats another
|
|
parasitism
|
+/-
one benefits/one harms |
|

commensalism
|
+/0
one benefits/one neutral |
|

mutualism
|
+/+
both benefit |
|

competition
|
contest between two organisms for a resource
|
|
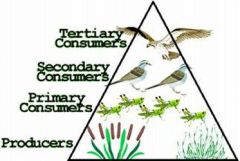
trophic levels
|
positions in a food chain
|
|
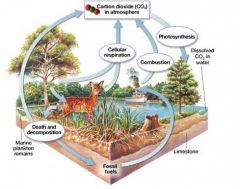
carbon cycle
|
moving carbon throughout an ecosystem
|
|
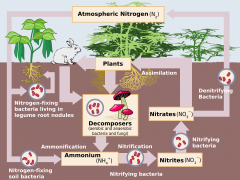
nitrogen cycle
|
movement of nitrogen throughout an ecosystem
|

