![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the ultimate source of energy for all livings things?
|
Sunlight
|
|
|
What is photosynthesis?
|
process plants use to capture light energy and make complex molecules
|
|
|
What are heterotrophs?
|
organism that consumes others for energy
|
|
|
Why is chlorophyll green?
|
it reflects green light (photons)
|
|
|
What causes the electrons of chlorophyll to be raised to a higher level? What do they enter when that occurs?
|
a. chlorophyll absorbs a photon of light
b. electron transport chain |
|
|
Where does oxygen gas come from during photosynthesis? How has that affected that atmosphere?
|
a, water
b. it's rich in oxygen gas |
|
|
Why is carbon fixation in plants important?
|
all organic molecules can be traced back to CO2 in the atmosphere
|
|
|
What happens to the excited electrons from Photosystem 1?
|
captured by NADPH
|
|
|
What are the products of the light reactions used in the dark reactions?
|
ATP and NADPH
|
|
|
What is the Calvin cycle? When does it occur?
|
a. a series of reactions that create carbohydrates
b. in both light and dark conditions |
|
|
Where does the energy to from ATP come from?
|
proton pumps in the thylakoid membrane
|
|
|
How does light intensity affect photosynthesis?
|
causes it to first increase, then decrease
|
|
|
What is ATP?
|
molecules essential for life
|
|
|
What is cellular respiration?
|
the release of energy from the breakdown of food
|
|
|
What is a connection between cellular respiration and photosynthesis?
|
oxygen
|
|
|
What is acetyl CoA?
|
formed from pyruvate, enters Krebs cycle, carbon dioxide
|
|
|
What happens to glucose in glycolosis? The products of glycolosis?
|
a. glucose splits
b. 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, and 2 NADH |
|
|
What is fermentation?
|
organic compounds broken down in absence of oxygen
|
|
|
Difference between glycolosis and aerobic respiration?
|
glycolosis = no oxygen (cytoplasm)
aerobic respiration = oxygen (mitochondrion) |
|
|
What is formed in muscles when oxygen isn't present?
|
lactic acid
|
|
|
Location of Krebs cycle and ETC?
|
mitochondrion
|
|
|
What are the parts of cellular respiration?
|
glycolosis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain
|
|
|
What is the end product of the ETC?
|
water
|
|
|
Name of equation, Molecule A?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + ADP + P <--- 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + MOLECULE A |
a. aerobic respiration
b. ATP |
|
|
What is ecology?
|
study of the interaction of living organisms with each other and their physical environment
|
|
|
What is a habitat?
|
physical location of an ecosystem in which a given species lives
|
|
|
What is a population?
|
a group of single species in an area at a specific time
|
|
|
What is a species?
|
the lowest classification level in biological taxonomy
|
|
|
Give an example of a relationship between a producer and a consumer?
|
a zebra eating grass
|
|
|
What is competition?
|
what occurs when organisms require the same food and space
|
|
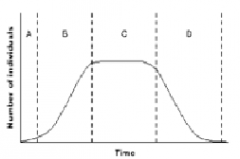
Identify the period where birth rate and death rate are equal and where there's negative growth in the graph.
|
a. C
b. D |
|
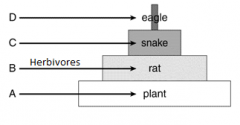
Identify the amount of energy available to level C.
|
10% of the level below it
|
|
|
What is commensalism?
|
one organism benefits, the other neither benefits nor is harmed
|
|
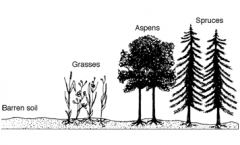
What is the process represented by the diagram below?
|
succession
|
|
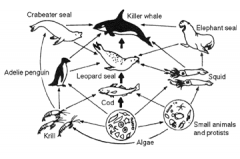
Identify the producer, the level of the leopard seals, and identify the name of the diagram.
|
a. algae
b. secondary and tertiary c. food web |
|
|
In the nitrogen cycle, what uses do plants use nitrates to form?
|
amino acids
|
|
|
What is a biome?
|
major ecosystems that occur over wide areas
|
|
|
What are examples of fossils?
|
traces of dead organisms, footprints, insects trapped in tree sap, shells, and old bones
|
|
|
On what island did Darwin conduct much of his research?
|
Galapagos
|
|
|
Darwin studies finches. What was his conclusion about them even though they had different shaped beaks?
|
descended and evolved from a common ancestor
|
|
|
According to Darwin, why does evolution occur?
|
species change over time due to natural selection
|
|
|
What is an important part of the ecological systems that causes natural selection to occur?
|
natural resources are limited and competition occurs for those resources
|
|
|
True or False - Organisms that share similar amino acid structures have a common ancestor.
|
True
|
|
|
What is the accumulation of differences between species?
|
divergent evolution
|
|
|
What is coevolution?
|
two or more species change in response to anouther
|
|
|
Plants and their pollinators have ____________ over the years.
|
coevolved
|
|
|
Why do peacocks have brightly colored tail feathers?
|
to attract potential mates
|
|
|
How do scientists use DNA sequences to determine evolutionary relationships?
|
more similar organisms share a more recent common ancestor
|
|
|
How do scientists use that fact that organisms have varying similarities in amino acid sequences in their proteins?
|
more similar organisms share a more recent common ancestor
|
|
|
What is gene flow?
|
movement of alleles into or out of a population
|
|
|
What is speciation?
|
formation of a new species
|
|
|
What affects allele frequencies in a population?
|
genetic drift, bottleneck, founder effect
|
|
|
What is crossing over?
|
homologous chromosomes exchange corresponding segments of DNA
|
|
|
When does crossing over occur?
|
Prophase I
|
|
|
What divides unequally in the formation of polar bodies in oogenesis?
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
What provides new genetic combinations?
|
random fertilization, crossing over, and independent assortment
|
|
|
What is a diploid cell?
|
two homologous of each chromosome, 2n, chromosomes found in pairs
|
|
|
If a diploid cell has 26 chromosomes, how many are in a haploid cell?
|
13
|
|
|
When does synapsis of homologous chromosomes into tetrads occur?
|
Prophase I
|
|
|
What is a mutation?
|
change in a gene due to damage or being copied incorrectly
|
|
|
What causes a frameshift mutation?
|
insertion or deletion - NEVER substitution
|
|
|
What is a mutation that involves one or a few nucleotides?
|
point mutation
|
|
|
What affect can a mutation have?
|
neutral, harmful, or helpful
|
|
|
How man chromosomes does a person with Down Syndrome have?
|
47
|
|
|
What is a trisomy?
|
having an extra chromosome
|
|
|
What is it called when a gamete has too many or too few homologues of a chromosome?
|
nondisjunction
|
|
|
What occurs when a gene has methyl groups attached?
|
genes are turned off
|
|
|
What occurs when a gene has acetyl groups attached?
|
genes are turned on
|
|
|
What are histones used for?
|
fold and package DNA
|
|
|
What is a situations in which gametes have one of each pair of homologues and are represented by n?
|
haploid
|
|
|
How are homologous chromosomes similar?
|
size, shape, genetic content
|
|
|
What are chromatids?
|
identical strands of DNA
|
|
|
How do spermatogenesis and oogenesis differ?
|
Spermatogenesis ends with 4 haploid sperm, oogenesis ends with 1 haploid ovum.
|
|
|
If and organism has 44 chromosomes in its diploid cells, how many possible variants can occur in their sperm or egg cells based on independent assortment.
|
4,194,304
|

