![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
2 MOST IMPORTANT
HISTORICAL BIOLOGISTS |
A. Robert Hooke -
1665, Cork Cells B. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek 1673 Living Cells |
|
|
WHICH OF THE
HISTORICAL BIOLOGISTS DISCOVERED CORK CELLS? |
Robert Hooke - 1665
|
|
|
WHICH OF THE HISTORICAL BIOLOGISTS STUDIED LIVING CELLS?
|
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek - 1673
|
|
|
WHAT IS THE
CELL THEORY? |
1. All living things are made of cells.
2. Cells come from other cells. |
|
|
WHAT ARE THE
TWO CELL TYPES? |
A. Prokaryotic
B. Eukargotic |
|
|
WHAT ARE
PROKARYOTIC CELLS? |
1. Non-living cells
2. No Nucleus and Organelles EX: Bacteria |
|
|
WHAT ARE
EUKARYOTIC CELLS? |
1. Living cells
2. Contain a nucleus and organelles 3. Highly Organized 4. Two Types a. Plant b. Animal |
|
|
WHAT IS AN
ORGANELLE? |
(Little organ). The discrete cell structure with a specific function. Many types of organelles.An organelle is to the cell what an organ is to the body.
|
|
|
WHAT IS A
NUCLEUS? |
A) Control center of the cell.
B) Contains DNA which controls all cell functions. |
|
|
WHAT IS NUCLEAR
MEMBRANE? |
A) Membrane surrounding the nucleus
B) Membrane keeps DNA inside, cytoplasm outside |
|
|
WHAT IS A
NUCLEUS? |
FUNCTION: Stores hereditary info in DNA
A. A small, dark body inside the nucleus. B. Synthesizes RNA and ribosomes. |
|
|
WHAT ARE CHROMOSOMES?
|
A) Structures in the nucleus that contain DNA.
B) Different organisms have different number of chromosomes. |
|
|
WHAT IS THE CELL MEMBRANE?
|
A) Boundary of the cell
B) Holds verything inside the cell. C) Regulates passage of chemicals into and out of the cell. |
|
|
WHAT IS THE CYTOPLASM?
|
A) Protein rich semifluid inside of the cell that surrounds the organelles.
|
|
|
WHAT IS GOLGI APPARATUS?
|
FUNCTION: Processes & packages
all substances produced by the cell. A) A system of flattened sacs. B) "Post office" of the cell. |
|
|
LABEL CELL ORGANELLES
|
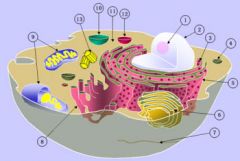
Schematic of typical animal cell, showing subcellular components. Organelles: (1) nucleolus (2) nucleus (3) ribosome (4) vesicle (5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (6) Golgi apparatus (7) Cytoskeleton (8) smooth ER (9) mitochondria (10) vacuole (11) cytoplasm (12) lysosome (13) centrioles
|
|
|
WHAT IS E.R?
|
endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
WHAT IS
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM? |
FUNCTION: Prepares proteins
for export (rough ER); assembles steroids; regulates calcium levels, breaks down toxic substances (Smooth ER). A) Tunnels that transport material from the nucleus. |
|
|
WHAT ARE
RIBOSOMES? |
FUNCTION:
Assemble proteins A) Attached to the E.R. B) Produced in the nucleolis |
|
|
WHAT ARE
LYSOSOMES? |
FUNCTION: Digests molecules, old organelles, and foreign substances.
(Stomach of the cell?) A) Animal cells B) Produced by Golgo Apparatus. C) Contain digestive enzymes which break down foreign material D) Leave the cell to fight bacteria |
|
|
WHAT ARE
MITOCHONDRION? |
FUNCTION:
Transfers energy from organic compounds to ATP. A) Powerhouse of the Cell B) Cell respiration occurs here C) Has it's own DNA 1) Cistern - folded inner membrane |
|
|
Figure 1 : Image of nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.
(1) Nucleus (2) Nuclear pore (3) Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER) (4) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) (5) Ribosome on the rough ER (6) Proteins that are transported (7) Transport vesicle (8) Golgi apparatus (9) Cis face of the Golgi apparatus (10) Trans face of the Golgi apparatus (11) Cisternae of the Golgi apparatus |
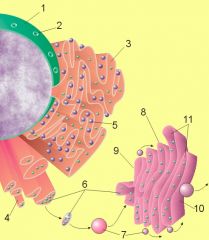
LABEL THE PARTS OF THE GOLGO APPARATUS
|
|
|
WHAT ARE
CENTRIOLES? |
A) Animal cells only
B) Tubular structure that assist in cell reproduction |
|
|
WHAT ARE
VACUOLES? |
FUNCTION: Stores enzymes
and waste products. A) Fluid filled sacs B) They store food, water and waste |
|
|
WHAT ARE
MICROFILAMENTS & MICROTUBULES? |
A) Long filament structrues made of protein
B) Gives the cell structure, support, movement, and division of cells. |
|
|
WHAT IS THE CELL WALL ?
(PLANT CELLS ONLY) |
FUNCTION: Supports and protects the cell
A) Rigid structure surrounding the cell membrane B) Made of cellulose |
|
|
WHAT IS THE MIDDLE LAMELLA ?
(PLANT CELLS ONLY) |
A) Are between cell wall and cell membrane
|
|
|
WHAT ARE PECTINS?
|
(Plant Cells Only)
A) A substance that bonds cells together/ (IN cooking, pectins acts as a thickening agent.) |
|
|
WHAT ARE CHLOROPLASTS?
|
A) small green organelles
B) Contain pigment - chlorofill C) Photosynthesis occurs here. |
|
|
CELL MEMBRANE?
|
A)Provides protestion; regulated passage of materials through the cell.
|
|
|
WHAT IS CELL TRANSPORT?
|
Passive Transport -No energy required by the cell.
1. Diffusion 2. Facilitated Diffusion 3. Osmosis C) |
|
|
CELL TRANSPORT:
WHAT IS DIFFUSION? |
The movement of molecules in a cell from an area high to low concentration.
|
|
|
CELL TRANSPORT:
WHAT IS FACILITATED DIFFUSION |
Diffusion through a cell membrane assisted by carrier proteins.
(This porcess is carried out for molecules that cannot diffuse rapidly into the cell.) |
|
|
CELL TRANSPORT:
WHAT IS OSMOSIS? |
A)Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
B) The direction of osmosis depends on the concentration of soluted on each side of the membrane. C) Osmosis can be described as hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic |
|
|
HYPOTONIC
SOLUTION |
The concentration of salt outside the cell is lower than that inside the cell.
RESULT: Water diffuses into the cell until equilibrium is reached. |
|
|
HYPERTONIC
SOLUTION |
The concentration of the solutes on the outside of the cell is higher than the amount of salt in the cytoplasm. inside the cell.
RESULT: Water diffuses out of the cell until equilibrium is reached. |
|
|
ISOTONIC
SOLUTION |
Equal concentrations of water and solute both inside and outside the cell membrane.
RESULT: Equilibrium. |
|
|
ACTIVE
TRANSPORT |
The movement of materials from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration (Requires energy)
A) Cell Membrane Pump Endocytosis Exocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis |
|
|
ACTIVE TRANSPORT:
PUMP |
Sodium Potassium Pump
Image: |
|
|
ACTIVE TRANSPORT:
Enzyme Protein carrier (A.T.) |
Image:
|
|
|
ACTIVE TRANSPORT:
Endocytosis |
The process where cells ingest external particles.
|
|
|
ACTIVE TRANSPORT:
Exocytosis |
The release of a particle from cytoplasm out of the cell.
|
|
|
PHAGOCYTOSIS
|
Another word for endocytosis
The engulment of large particles. |
|
|
PINOCYTOSIS
|
Engulfment of fluid. The membrane folds around the object, and the object is sealed off.
"cell-drinking" |
|
|
ENDOCYTOSIS
|
Synonym for endocytosis. This process is concerned with the uptake of solutes and single molecules such as proteins.
|
|
|
ENDOCYTOSIS-
DIVIDED INTO TWO PROCESSES: |
A) Phagocytosis
B) Pinocytosis. |
|
|
WHAT SINGLE FACTOR
LIMITS THE SIZE THAT MOST CELLS ARE ABLE TO ATTAIN? |
By the ratio between their outer suface area and their volume.
|
|
|
GIVE 3 EXAMPLES OF HOW CELLS' SHAPES ARE SUITED TO THEIR FUNCTIONS.
|
Nerve cell
Skin cell White Blood cell |
|
|
HOW CAN YOU TELL
IF A UNICELLULAR ORGANISM IS A PROKARARYTOTE OR A EUKARYOTE? |
An organism that lacks a membrane-bound nuceus and other organelles is call a Prokararote. If it contains a nucleus and other organelles is call a Eukaryote.
|
|
|
LIST NINE ORGANELLES
|
1. Mitochondrian
2. Ribosome 3. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 4. Golgi Apparatus 5. Lysosome 6. Microtubules 7. Nucleus 8. Cell Wall (plant cell) 9. Vacuole (plant cell) |
|
|
NAME THE 3
COMPONENTS OF A EUKARYOTIC CELL. |
1) A cell membrane
2) A nucleus 3) Other organelles |
|
|
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE
BETWEEN THE NUCLEAUS AND NUCLEOLUS? |
The Nucleolus in inside the nucelus and makes rybosomes.
|
|
|
WHICH ORGANELLES ARE
SURROUNDED BY TWO MEMBRANES? |
Chlolorplasts like mitochondria and the nucleus.
|

