![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
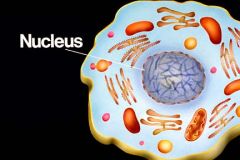
|
Structure: Special Nuclear Membrane, contains Nucleolus, largest organelle, provides information on making proteins. Function: Contains nucleic acids such as DNA and RNAthat code in the human body for certain amino acids |
|
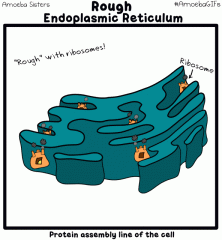
|
Structure: Flattened Membranes - extension of nuclear membrane, transports systems in the cell between nucleus and ribosome. Function: Made of lipids (fat) doesn't dissolve in water |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
Structure: Stacks membranes that carry proteins throughout the cell. Function: Proteins finish their final form in the Golgi apparatus. Some proteins cannot be released from the cell. |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Structure: Several folds inside to increase the efficiency. Known as power plant of cell. Energy is made through cellular respiration. Function: Breaks down Glucose when oxygen is present, which releases carbon dioxide and molecules called ATP. |
|
|
Chloroplast |
Structure: Glucose is made in a process during photosynthesis. Process needs sunlight and chloroplast has a stroma and pigments that capture light energy. |
|
|
Cell Membrane (Plasma) |
Structure: Controls what leaves and is in cell, allows materials to move in and out through openings. Molecules can grab materials and force them out of the cell. Function: Made of 2 layers with lipids. Proteins are embedded in lipids, which control what goes through it |
|
|
Cell Wall |
Structure: protects cell. Helps hold water in cell. Also maintains shape of cells plants, bacteria, and fungus. Function: Inside fungus and bacteria cells, also made with other chemicals. Inside plants. Made of cellulose embedded in matrix of protein |
|
|
Vacuole |
Structure: Bubble bound to membrane. Can contain water and important chemicals. More than 1 type of Vacuole and each vacuole has a specific job. Function: Has some enzymes, mostly H20. Protects cell from harmful chemicals. |
|
|
Lysosome |
Structure: Membrane that can digest things inside membrane bubble. Helpful for disposing dead cells. Function: Digestive enzymes that break protein to amino acids |
|
|
Centriole/Centromere |
Structure: Divides DNA. Works with spindle fibers. Function: Made of proteins called actin and myosin that react to each other, which creates movement. Same proteins that make muscle |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Structure: Helps maintain cell shape and allows cell to move. Made of complex fibers Function: Made of several proteins that make micro tubes. H20 binds with Cytoskeleton and turns inside of cell into gel-like substance. |
|
|
Ribosome |
Structure: Site where proteins are created Function: Made of RNA and proteins. Amino Acids put together in a certain way to create certain protein. Protein are then used for structure and enzyme building. |
|
|
Cytoplasm / Cytosol |
Structure: Semi- Fluid that surrounds all other organelles. Function: Contains enzymes, water is repelled by lipids, and mostly H20 must have this for most reactions to create |

