![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
108 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Information Transfer |
DNA to RNA to Protein to carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids |
|
|
|
What direction do strands of DNA run? |
Anti parallel |
|
|
|
What are base pairs held together by? |
Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
|
What are the classification kingdoms? |
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes |
|
|
|
Hydroxyl |
-OH |
|
|
|
Carbonyl |
-CO |
|
|
|
Carboxyl |
-COOH |
|
|
|
Amino Acid |
NH2 |
|
|
|
Sulfhydral |
-SH |
|
|
|
Phosphate |
O O- P -O O |
|
|
|
Methyl |
H C H H |
|
|
|
Molecular diversity in carbon skeleton variation |
Branching, length, double bond position, ring presence |
|
|
|
Structral isomer |
Different covalent arrangement |
|
|
|
Cis trans isomers |
Different spatial arrangements |
|
|
|
Enantiomers |
Mirror images of each other |
|
|
|
Oparin-Haldane hypothesis |
Organic molecules that formed the building blocks of life could have been formed given conditions that prevailed on primitive earth, like a reducing atmosphere that lacked oxygen |
|
|
|
Miller Urey Experiment |
Demonstrated that abiotic synthesis of biologically important molecules is possible |
|
|
|
Alternative hypothesis to Oparin-Haldane |
Deep sea vents, extraterrestrial |
|
|
|
By what reactions are polymers built? |
Dehydration |
|
|
|
By what reactions are polymers broken down? |
Hydrolysis |
|
|
|
What are the monomers and polymers of carbohydrates? |
Polymer- polysaccharides Monomer- monosaccharides |
|
|
|
What are the monomers and polymers of proteins? |
Polymer- polypeptides Monomer- amino acids |
|
|
|
What are the polymers and monomers of nucleic acids? |
Polymer- DNA and RNA Monomer- nucleotides |
|
|
|
What are the polymers and monomers of lipids? |
Polymer- triacylglycerol Monomer- glycerol, fatty acids Polymer-phospholipids Monomer- glycerol phosphate deritive, fatty acids Polymer- steroids |
There are three polymers |
|
|
By what bond are monosaccharides joined? |
Glycosidic |
|
|
|
What polysaccharides store energy in animal cells and plant cells? |
Starch for plants, glycogen for animals |
|
|
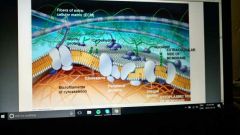
|
Just ******* memorize this |
|
|
|
What are amino acids? |
Monomers of proteins, made of carboxyl and amino groups with a differing side chain called R group |
|
|
|
How do you know if an amino acid is hydrophobic? |
Methyl group |
|
|
|
How do you know if a side chain us hydrophilic? |
Hydroxyl group, sulfhydral group, if they have a charge |
|
|
|
What are amino acids joined by? |
Peptide bonds |
|
|
|
What is the primary structure of a protein? |
Sequence of amino acids, determined by inherited genetic information |
|
|
|
What is the secondary structure of a protein? |
Hydrogen bonds between repeating constituents. Things like coils or sheets |
|
|
|
What are fibrous proteins ? |
Proteins defined primarily by their secondary structure |
|
|
|
What are globular proteins? |
Proteins defined by higher order structure, such as tertiary and quaternary |
|
|
|
What is the tertiary structure of a protein? |
The three dimensional structure of an entire polypeptide chain. Determined by r groups |
|
|
|
What is quaternary structure of a protein? |
When two or more proteins link together |
|
|
|
What are cofactors? |
A nonprotein compound bound to a protein that is essential for that protein's function |
|
|
|
What are folding pathway |
How a protein folds, sometimes by the help of a chaperone |
|
|
|
What are polynucleotides? |
Polymers of nucleotides, such as DNA and RNA |
|
|
|
What are nucleotides linked by? |
Phosphodiester bonds |
|
|
|
What is the function of DNA |
Storing hereditary information. |
|
|
|
What is the function of RNA? |
Many different functions, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, function in gene expression |
|
|
|
Are lipids hydrophilic or hydrophobic? |
Hydrophobic |
|
|
|
What are glycerol and fatty acids joined by? |
Ester linkages |
|
|
|
Do saturated fats have double bonds? |
No. |
|
|
|
Are saturated fats solid at room temperature? |
Yes |
|
|
|
Do unsaturated fats have double bonds? |
Yes |
|
|
|
Are unsaturated fats solid at room temperature? |
No they are liquid |
|
|
|
What are the functions of triacylglycerols? |
Energy, consultation, protection of vital organs |
|
|
|
What is the structure of a phospholipid? |
Two hydrophobic fatty acid tails and a hydrophilic phosphate head |
|
|
|
What are steroids? |
Lipids with a carbon skeleton consisting of four fuses rings |
|
|
|
Where is cholesterol located? |
In the animal cell membrane |
|
|
|
What is the cell theory? |
All organisms are composed of cells, the cell is the basic structral and functional unit of organisms, cells arise from the division of pre existing cells |
|
|
|
What are the basic features of all cells? |
Plasma membrane, cytosol, chromosomes, ribosomes. |
|
|
|
What is the basic structure of a prokaryotic cell? |
No nucleus, DNA in nucleoid, no organelles, cytoplasm in plasma membrane and cell wall |
|
|
|
What is peptidoglycan? |
Network of sugar polymers linked by polypeptides in the cell walls of bacteria |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a nucleus? |
Information centre |
|
|
|
DNA is organized into discrete units called... |
Chromosomss |
|
|
|
DNA and proteins of chromosomes together are called... |
Chromatin |
|
|
|
Where is protein synthesized? |
Ribosomes |
|
|
|
What is the function of the nucleolus? |
Area of nucleus just for the synthesize of rRNA and ribosomal subunits |
|
|
|
What's the difference between free and bound ribosomes? |
Free ribosomes are in the cytosol, bound ribosomes are on the outside of endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
|
What does the endomembrane system consist of? |
Nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, plasma membrane, vacuoles (plants) |
|
|
|
What connects endoplasmic reticulum? |
Either continuous or connected by vesicles |
|
|
|
What are glycoproteins? |
Proteins covalently bonded to carbohydrates formed in the RER |
|
|
|
What is the metabolic function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum ? |
Metabolism of lipids, carbohydrates, drug, and xenobiotic things. Also stores calcium |
|
|
|
What's the difference between the cis and trans face of the golgi apparatus? |
Cis is receiving trans is shipping |
|
|
|
What is the function of lysosomes? |
Digestion of macromolecules |
|
|
|
What is phagocytosis? |
When a lysosome engulfs a smaller cell or organism |
|
|
|
What does the protein COPI dictate? |
Retrieval transport from Golgi to ER |
|
|
|
What does the protein COPI dictate? |
Forward transport from ER to cis Golgi |
|
|
|
What does the protein clathrin dictate? |
Trans golgi to lysosomes and plasma membrane, plasma membrane to endosomes (receptor mediated endocytosis) |
|
|
|
What is the endosymbiotic theory? |
Chloroplasts and mitochondria evolved from bacteria |
|
|
|
What are some proofs for the endosymbiont theory? |
Their morphology, how they reproduce, the genetic information |
|
|
|
What are peroxisomes? |
Specialized metabolic compartments bounded by a single membrane |
|
|
|
What does the enzyme in peroxisomes do? |
Transfers hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen |
|
|
|
What is the cytoskeleton made of ? |
Microtubules, intermediate filaments, microfilaments |
|
|
|
What is microtubules made of? |
Alpha and beta and y tubulin |
|
|
|
What are intermediate filaments made of? |
Keratin |
|
|
|
What are microfilaments made of? |
Actin |
|
|
|
What is the function of microtubules? |
maintenance of cell shape, cell locomotion, chromosomal movement, organelle movement |
|
|
|
What is the function of intermediate filaments? |
Mechanical strength to cells, tissue specific roles, Anchorage of organelles, formation if nuclear lamina |
|
|
|
What is the function of microfilament? |
Maintainance and change of cell shape, muscle contractor, cell division, cytoplasmic streaming, cell motility |
|
|
|
What is the extra cellular matrix? |
Support made of glycoproteins, made for support adhesion movement and regulations. |
|
|
|
What are tight junctions? |
Tight seals that prevent leaks of ions of molecules between cells |
|
|
|
What are desmosomes? |
Anchoring junction, create flexible adherence points are anchired beneath their plasma membrane by the cytoskeleton |
|
|
|
What are gap junctions? |
Allow small molecules and ions to flow between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells |
|
|
|
Advantages of compartmentalization |
Separation of function. Isolation of harmful products. Organelles increase quantity of membrane as a function of volume |
|
|
|
Frye Edidin Experiment |
Fusing a mouse and human cell after colouring the phosplipids and seeing them mix together. Proved the fluid mosaic model of membrane |
|
|
|
What does cholesterol do in the membrane? |
Modulates the fluidity of the membranes, increases fluidity at low temperatures, decreases fluidity at high temperatures |
|
|
|
What are IMPs? |
Integral membrane proteins through hydrophobic interactions between fatty acids and amino acids in the protein. |
|
|
|
What are the functions of membrane proteins? |
Transport, enzymatic activity, signal transduction, cell cell recognition, intercellular joining, attachment |
|
|
|
Can hydrophobic molecules pass through the membrane? |
Yes. Things like o2, co2, and hydrocarbons |
|
|
|
Can polar but uncharged molecules pass through the membrane? |
Small molecules but not larger ones |
|
|
|
Can charged molecules pass through the membrane? |
No |
|
|
|
Explain diffusion |
When populations of molecules move from an area of high concentration to low concentration |
|
|
|
Describe osmosis |
When water diffuses along its concentration gradient |
|
|
|
If the concentrations of the solute are the same... |
Solutions are isotonic, or isoomotic. Water can pass freely but the neg flow in one direction will balance the other |
|
|
|
Solution with the greater concentration of solute will be |
Hyperosomotic, or hypertonic |
|
|
|
The solution with the lesser concentration of solute will be |
hypoosomotic (hypotonic) |
|
|
|
What solution should animal cells he in? |
Isotonic |
|
|
|
What solution should plant cells be in? |
Hypotonic |
|
|
|
What is facilitated diffusion? |
Transport with the help of a protein along the concentration gradient, without the use of energy |
|
|
|
What is active transport? |
Transport using proteins, requiring energy, including pumps and cotransporters |
|
|
|
What is membrane potential? |
Voltage difference across a membrane |
|
|
|
What is cotransport? |
Active transport of a solute indirectly transports other solutes |
|
|
|
What are forms of bulk transport? |
Exocytosis, endocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis |
|

