![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
"what is the purpose of the ovule in plants
|
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells
|
|
|
which generation is found in the seed of gumnosperm and angiosperm plants
|
seed plants
|
|
|
what is gymnosperm
|
a seed plant with the ovules borne on the surface of a sporophyll
|
|
|
what are microspores
|
The smaller type of spore, bearing male gametes
|
|
|
what are megaspores
|
the larger type of spore bearing female gametes
|
|
|
What is the difference between pollination and fertilization?
|
Pollination is the spreading of pollen from the male to the female part of a flower.
Fertilization is the sperm and egg joining to form a zygote. |
|
|
What Is An Example Of Angiosperms?
|
daisy rose any flowering plant
|
|
|
what is an example of gymnosperm plants
|
conifers, cycads, ginkgoes, and gnetophytes
|
|
|
what are monocots
|
flower parts in threes or multiples of three, herbaceous, parallel venation, never woody
|
|
|
what are eudicots
|
flowering parts in fours or fives, woody or herbaceous, net venation, can be woody
|
|
|
what is double fertilization
|
egg & polar body/nucleli are fertilized
|
|
|
what is the endosperm
|
is the tissue inside the seeds of flowering plants at the time of fertilization
|
|
|
what is the embryo sac
|
produces the egg cell for fertilization
|
|
|
what are the three parts of the seed
|
seed coat, embryo & endosperm (3n)
|
|
|
what is chemosynthetic
|
a bacteria able to make organic molecules utilizing in organic molecules
|
|
|
what is the scientific name for the organism that couses black death
|
Yersinia pestis
|
|
|
waht is saprotrophic
|
most bacteria. they send out digestive enzymes in to the environment & take up the resulting nutrient molecules
|
|
|
what is a colony
|
cells that decended from an original cell
|
|
|
what does an endospore contain and what is it incased in
|
contains a copy of the genetic material incased by heavy protective spore coats
|
|
|
what are the tree taxonomic domains
|
bacteria, archaea & eukaryotes
|
|
|
which domain to bacteria belong to
|
bacteria
|
|
|
what are the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
|
prokaryotes have no nucleus or membrane and they have bound organelles
|
|
|
what are three techniques used to identify bacteria
|
staining technique (gram stain), shape, & colony morphology
|
|
|
what is the name used for round bacteria
|
cocci
|
|
|
what is the name used for rod bacteria
|
bacilli
|
|
|
what is the name used for spiral bacteria
|
spirilla
|
|
|
what color do gram positive bacteria stain
|
purple
|
|
|
what color do gram negitive bacteria stain
|
pink
|
|
|
which domain do protists belong to
|
eukaryots
|
|
|
which protist organism may be the ancestor to the first plants
|
green algae
|
|
|
what type of reproduction is used by volvox
|
sezually & asexually
|
|
|
are doughter colonies produced sexually or asexually
|
asexually
|
|
|
what is the cell wall of diatoms impregnated with
|
silica
|
|
|
which organism is responsible for red tides
|
dino flagellates
|
|
|
what three forms of locomotion are used by protozoa
|
psuedopods, cilia, flagella
|
|
|
what is evolution
|
the process by which life has changed through time
|
|
|
what is a species
|
a group of similarly constructed organisms that share common genes
|
|
|
what is a population
|
all members of a species living in a particular area
|
|
|
what is a fossil
|
remains or ecidence of some organism that lived long ago
|
|
|
what are the three types of evidence that suggest various types of organisms are related through common descent
|
fossil record, comparative anatomy & biochemical comparison
|
|
|
how is the age of a fossil measured
|
relative and absolute dating
|
|
|
how does the process of dating work
|
doesnt give exact date just dates that this one died before that one
|
|
|
what is the difference between homologous and analogous structures
|
homologus come from the same embryo tissue analogous does not come from the same embry tissue
|
|
|
what structures are used to indicate an evolutionary relationship
|
homologus
|
|
|
what happens to the paired pharyngeal pouches in aquatic animals
|
become functunal gills
|
|
|
what happens to the paired pharyngeal puches in humans
|
1st pair becomes the cavity of the middle ear & auditory tube. 2nd pair becomes tonsils. 3rd & 4th pairs become the thymus & parathyroid glans
|
|
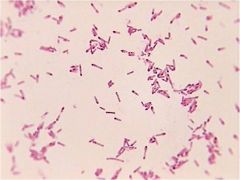
|
gram negitive baccilli
|
|
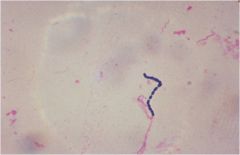
|
gram positive cocci
|
|
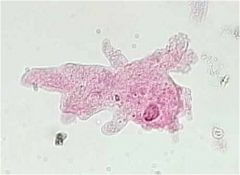
|
amoebozoa amoeba proteus
|
|
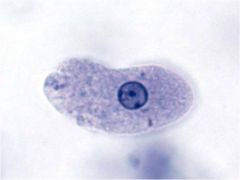
|
amoebozoa entamoeba
|
|
|
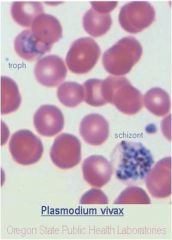
apicomplexans plasmodium
|
|
|
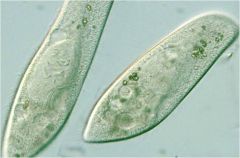
ciliata paramecium
|
|
|
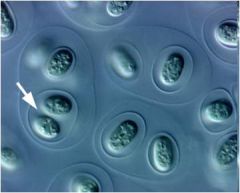
cyanobacteria gloeocapsa
|
|
|
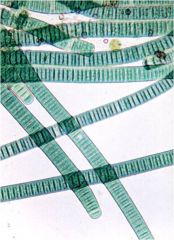
cyanobacteria oscillatoria
|
|
|
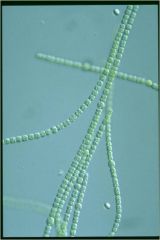
cynobacteria anabaena
|
|
|
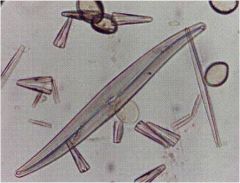
diatoms
|
|
|
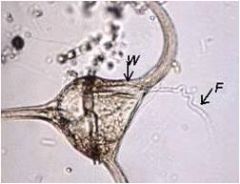
dinoflagellates ceratium
|
|
|
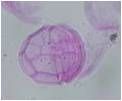
dinoflagellates peridinium
|
|
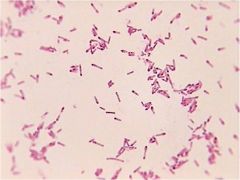
|
gram negitive bacilli.jpegs
|
|
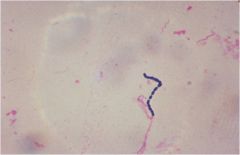
|
Gram positive cocci
|
|
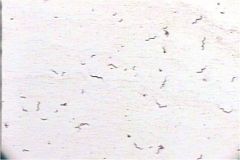
|
spirilla
|
|

|
spirogyra desmids
|
|
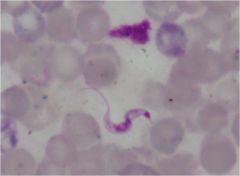
|
typanosoma
|
|
|
volvox
|

