![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
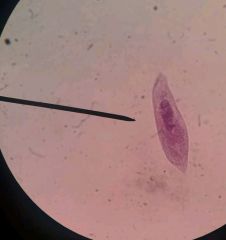
Paramecium Caudatum Alveolata
|
|
|
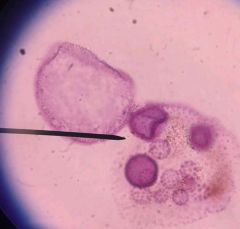
Volvox Green Algae ; Chlorophyta
|
|

|
Fucus Stramenopiles ; Phaeophyta
|
|
|
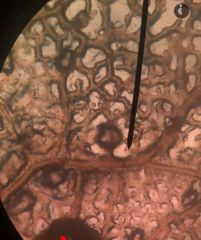
Physarum (Slime mold) Amoebozoa
|
|
|
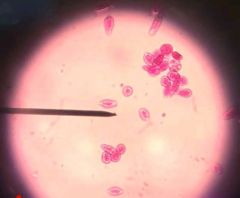
Euglena Euglenozoa
|
|
|
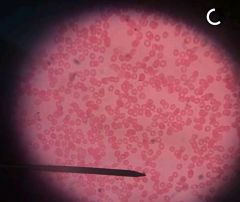
Plasmodium Falciparum Alveolata ; Apicomplexa
|
|
|
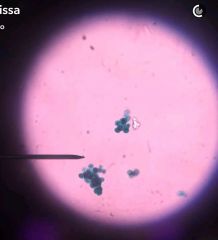
Chlamydmonas Green Algae ; Chorophyta
|
|
|
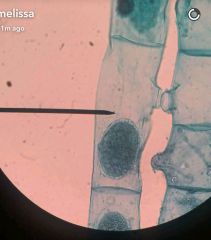
Spirogyra Green Algae ; Charophyta
|
|
|
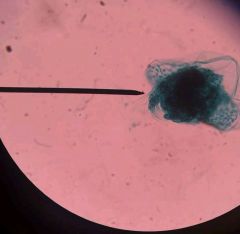
Diatoms Stramenopiles
|
|
|
Ceratium Alveolata ; Dinoflagellates
|
|
|
Trypanosoma Euglenozoa
|
|
|
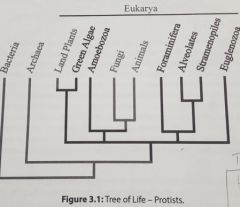
CLADES •Amoebozoa•Alveolates •Euglenozoa •Stramenopiles*- Golden algae, Yellow-green Algae, Diatoms - Phaeophytes*– Brown algae; Fucus •Green Algae-Phylum: Chlorophyta/Charophyta |
|

|
Amoeba Amoebozoa Pseudopodia- "False feet" Locomotion Phagocytosis - capture of prey Nucleus |
|
|
Green Algae Possible structural arrangements:
|
Green Algae Characteristics:
|
|
|
Sexual reproduction in Green Algae |
Gamete - Sex cell Isogamy- indistinguishable difference between male and female, motile gametes Heterogamy- Both gametes motile, but differ in apperence; females possess larger hametes (eggs) Oogamy- Large non-motile egg, smaller motile sperm |
|
|
Protists A diverse paraphyletic grouping or organisms classified by nutritional mode |
Algae: Plant-like autotrophs Protozoa: Animal like heterotrophs Slime Molds: Fungus-like, absorptive, heterotrophs |

