![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Who invented the microscope in 1670?
|
Anton von Leeuenhoek (dutchman)
|
|
|
What is a cell?
|
The smallest biological unit that can be considered to be alive.
|
|
|
What are the three principles of cell theory?
|
1. all living things are composed of one or more cells
2. the cell is the smallest thing capable of life on its own 3. cells come from other cells |
|
|
What is a scientific theory?
|
An accepted idea in science that is taken as "the truth until further notice"
|
|
|
To form new and better theories you do what?
|
set out to disprove or prove the current theory to be false
|
|
|
What type of organisms or cells have no nucleus or membrane bound organelles?
|
prokaryotic
|
|
|
What is the nucleus?
|
control center of the cell, contains the DNA
|
|
|
What type of cell has a nucleus and membrane bound organelles?
|
eukaryotic
|
|
|
What is an organelle?
|
a tiny, membrane-bound structure inside a cell that carries out a specific function for the cell (not always membrane-bound)
|
|
|
What is a plastid?
|
a plant cell organelle that contains pigments and is usually involved in food production or storage
|
|
|
What is a chromoplast?
|
a plastid that may contain pigmented molecules
|
|
|
What is a chloroplast?
|
an green organelle that contains the pigment chlorophyll and is involved in food-processing process of photosynthesis
|
|
|
What is photosynthesis?
|
process in which plants make glucose from carbon dioxide gas using the photonic energy of light
|
|
|
What is a cell membrane or plasma membrane?
|
the outer limit of an animal cell
|
|
|
What is the protein-rich liquid interior content of a cell?
|
Cytoplasm
|
|
|
What are the rod-like strands of supporting proteins that help the cell maintain thir shape and are the internal support system of the cell?
|
cytoskeleton
|
|
|
What is the central vacuole?
|
central water-filled organelle unique to plants (maintains water pressure)
|
|
|
What is it called when the chloroplasts/organelles are seen moving around in the cell circulating around the central vacuole?
|
cytoplasmic streaming
|
|
|
What is the cell wall?
|
The outer limit of a plant cell, rigid, made of cellulose
|
|
|
What is cellulose?
|
roughage or dietary fibre
|
|
|
What does a qualitative test show?
|
it tells whether a substance is present or not
|
|
|
What test do you run if you are trying to determine the amount of a substance present?
|
quantitative test
|
|
|
What is Applied Science?
|
They have a goal, most research is this type i.e. medical and pharmaceutical
|
|
|
What is the research for the sake of research alone (done with grants)?
|
Pure Science
|
|
|
What is theoretical science?
|
Science of ideas - done in your head or on computers
|
|
|
Name four biological molecules common to all living things:
|
1) Carbohydrates
2) Proteins 3) Lipids 4) Nucleic acids |
|
|
What is monomer?
|
General term for a molecule made up of similar small repeating units.
|
|
|
Biomolecule made of repeating sugar units or monomers (Carbohydrates, proteins, & nucleic acids)
|
polymers
|
|
|
What is a saccharide?
|
sugar
|
|
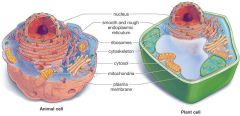
Look at an animal cell and a plant cell side by side...
|
they are similar in many ways.
|
|
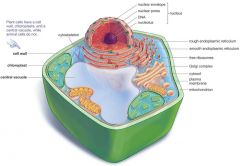
What does a plant cell have that a animal cell do not have?
|
Cell wall, central vacuole, and chloroplasts
|
|
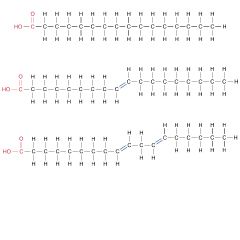
Compare the three types of fatty acids: Saturated, Mono-unsaturated, Poly-unsaturated
|
Saturated acid has no double bonds. Mono-unsaturated fatty acid has one double bond. (cis if h on same side) Poly-unsaturated fatty acid has two or more double bonds. (trans if h on different sides) (cis if h on same side)
|
|
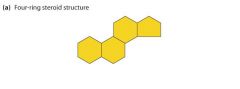
This structure is the basic molecular structure for which class of lipids:
|
Steroid, the basis of a cholesterol molecule
|
|
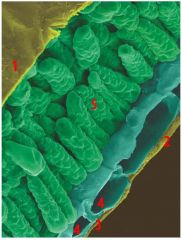
Name items 1-5: Upper Epidermis, Mesophyll cells, Lower Epidermis, Stomata, Guard Cell
|
1) Upper Epidermis
2) Lower Epidermis 3) Stomata 4) Guard Cells 5) Mesophyll Cells |
|
|
A functional protein, it makes or breaks a chemical bond
|
enzyme
|
|
|
Scientific name for hydrophobic molecules
|
Lipid
|
|
|
kind of lipid that biological membranes are made of
|
phospholipid
|
|
|
monomer unit of nucleic acid
|
nucleotide
|
|
|
the sum of all chemical reactions in your body
|
metabolism
|
|
|
term used to describe the shape of DNA
|
double helix
|
|
|
a fat that contains no double bonds
|
saturated fat
|
|
|
biomolecule of repeating amino acid units
|
protein
|
|
|
term that refers to the shape of a molecule
|
conformation
|
|
|
examples of dna and rna
|
nucleic acids
|
|
|
simple carb made of one sugar molecule
|
monosaccharides
|
|
|
simple carb made of two sugar molecules
|
disaccharides
|
|
|
single repeating units of polymer
|
monomer
|
|
|
the monomers that proteins are made of
|
amino acids
|
|
|
a fat that contains multiple double bonds
|
polyunsaturated fat
|
|
|
a molecule with 4 carbon rings like cholesteral
|
steroid
|
|
|
the monomeric form of a carbohydrate
|
sugar
|
|
|
a glycerol molecule with 3 fatty acids chemically bonded to it
|
triglyceride
|
|
|
carbs composed of many sugar subunits (monomers)
|
polymer
|
|
|
describes a fatty acid that has the maximum number of hydrogens attached (all single bonds)
|
saturated fatty acid
|

