![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diagram of a Microscope
|

|
|
|
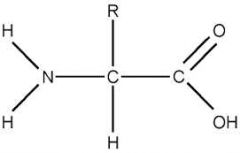
Diagram of An Amino Acid/ Protein
|
|
|
|
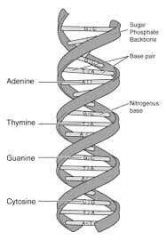
Diagram of DNA
|
|
|
|
Diagram of the Food Web
|

|
|
|
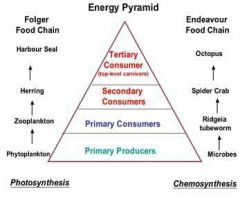
Diagram of Energy Pyramid
|
|
|
|
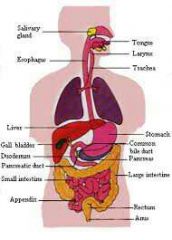
Diagram of Digestive System
|
|
|
|
Human Growth Hormone(HGH)
|
A protein produced by the pituitary gland that regulates growth
|
|
|
Genetically Producing HGH
|
Created by using genetically engineered bacteria to produce the hormone
|
|
|
Bioethics
|
The analysis if right and wrong actions in biological issues
|
|
|
The Control In Experiments
|
The standard to compare changes
|
|
|
Qualitive Experiments
|
Using senses
|
|
|
Quantitive Experiments
|
Using measurements
|
|
|
Micrometers
|
(Measure of Length)➡1mm=um
|
|
|
Microscope Total Magneficiation
|
Eyepiece × Objective Power
|
|
|
Field of Vision(Microscopes)
|
The lower the power the greater the field of vision
|
|
|
How Images Are Viewed
|
Images are inverted and reversed
|
|
|
Why Can Living Organisms Move In and Out of Focus?
|
They are moving through different levels in the fluid
|
|
|
Hypothesis
|
An explanation that can be tested through experiments/observation
|
|
|
Theory
|
An explanation that is supported by many observations
|
|
|
Theory of Natural Selection
|
Organisms change gradually over time
|
|
|
Lamarck's Idea
|
Characteristics acquired in ones lifetime cab be inherited (false)
|
|
|
Darwin's Theory Of Natural Selection
|
Variations among organisms can be inherited; survival favors some organisms over others; only some organisms survive to reproduce
|
|
|
Thomas Malthus Theory
|
Suggested that members of a species compete to survive
|
|
|
Natural Selection
|
Organisms best adapted to their environment are most likely to have offspring
|
|
|
Species
|
A group of closely related organisms that naturally reproduce and produce fertile offspring
|
|
|
Scientific Ideas
|
Constantly tested against new evidence and modified as needed
|
|
|
Characteristics of Science
|
Based on the assumption that the natural world can be investigated and explained; relies on the results of careful observation and controsllrd experimentation; results can be repeatable in order to be accepted
|
|
|
Elements
|
Only made up of 1 kind of atom
|
|
|
Compound
|
Two or more elements that combine chemically
|
|
|
What are chemical reactions in cells used for?
|
Cell growth, maintenance, energy storage, and cell development
|
|
|
Ion
|
An atom that has gained or lost an electron(s)
|
|
|
What do Ionic Bonds involve?
|
The transfer of electrons
|
|
|
Covalent Bond
|
A bond involving the sharing of electrons to help fill electron shells
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bond
|
A bond that involves the hydrogen of water molecule that is attracted to the oxygen of another water molecule
|
|
|
pH
|
Acids have more H+ than OH- (Between 0 and 7); Bases have more OH- than H+ (Between 7 and 14); Neutral is H=OH- and is 7 (Water)
|
|
|
Makeup of Organic Compounds
|
Contain hydrogen and carbon atoms
|
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
Contain C, H, O ; they are a source of energy; have simple sugars (monosaccharides) as their building blocks (such as glucose)
|
|
|
Glucose Molecules Link
|
Glucose molecules are linked together in long chains to produce starch
|
|
|
Cellulose
|
Cellulose is a type of carbohydrate and formed from glucose molecules through dehydration synthesis reactions
|
|
|
How do plants store carbohydrates?
|
Plants store carbohydrates in the form of starch
|
|
|
Lipids
|
Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks; Have long tails and H & C; Phospholipids are components of cell membranes
|
|
|
Proteins
|
Amino acids are the building blocks; When amino acids combine water is released (dehydration synthesis) ; A peptide bond is formed with C and N between two amino acids by taking an H atom from the amino group of one amino acid in the OH from the acid (carboxyl)group of another amino acid
|
|
|
Nucleic Acid Monomer
|
Nucleotides
|
|
|
DNA Nucleotide Composition
|
Composed of a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and nitrogen base (A,T,C,G)
|
|
|
How do nucleotides differ?
|
Based upon their kind of nitrogen base
|
|
|
What are the nitrogen bases of DNA?
|
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
|
|
|
What is the base pair rule?
|
A - T, C - G
|
|
|
When does replication of a double-stranded DNA molecule begin?
|
When the strands separate at the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen base pairs
|
|
|
Who provided the double helix model of DNA?
|
Watson and Crick
|
|
|
Free Energy
|
The energy available for organisms to do work
|
|
|
Autotrophs
|
Producers that obtain their energy from nonliving sources such as the sun, soil, and air
|
|
|
How Do Producers Capture Energy?
|
Producers are able to capture energy from sunlight and combine it to produce chemical energy
|
|
|
Heterotrophs
|
Consumers
|
|
|
Factors In An Ecosystem
|
Biotic factors are living components and abiotoc are nonliving components
|
|
|
What makes up the biosphere?
|
All the ecosystems of the Earth
|
|
|
Food Webs
|
Made up of producers and consumers( though occasionally decomposers) with arrow going to the organsims obtaining energy
|
|
|
Decomposers Energy Source
|
Decomposers rely on dead orgamisms for energy from nutrients
|
|
|
Energy Pyramids
|
Show a one way flow of energy in which energy eventually leaves the ecosystem as heat
|
|
|
Free Energy vs. Entropy
|
As free energy decreases, entropy increases and vice versa
|
|
|
Community In an Ecosystem
|
All interacting populations in a given area represent a community
|
|
|
Entropy Decrease In Universe
|
Heat given off by an ecosystem results in a decrease in the entropy of the universe
|
|
|
Population In An Ecosystem
|
Organisms of the same species represent a population
|
|
|
ATP
|
Energy is released when the bond between the last 2 phosphates is broken
|
|
|
Substrate
|
The substance the enzyme acts on
|
|
|
Active Site
|
The area where the substrate and enzyme meet
|
|
|
What do enzymes have?
|
Optimum temperature and pH
|
|
|
Function Of Enzymes In A Cell
|
To control specific chemical reactions
|
|
|
Where is the enzyme placed in a chemical equation?
|
Above the yield arrow
|
|
|
Digestive Track In Humans
|
Oral Cavity---Epiglottis---Esophagus---Stomach---Small Intestine---Large Intestine---Anus
|
|
|
Peristalsis
|
Muscular activity that keeps food moving through the digestive system
|
|
|
Carbohydrate Digestion
|
Starts in the mouth, and completed in the small intestine
|
|
|
Protein Digestion
|
Starts in the stomach, completed in the small intestine
|
|
|
Lipid Digestion
|
Starts and is completed in the small intestine
|
|
|
Villi's Function
|
To increase the surface are in the small intestine for nutrient absorption
|
|
|
Large Intestine
|
Absorbs water into the bloodstream and is where feces is formed
|
|
|
Gall Bladder
|
Stores bile while the liver produces it
|
|
|
Where is Gastric Juice Produced?
|
In the stomach
|
|
|
Emulsification
|
The breaking down of fat globules into droplets
|
|
|
What Is The Cell Membrane Made Out Of?
|
Layers of phospolipids and proteins
|
|
|
Diffusion
|
A substance moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
|
|
|
Concentration Gradient
|
Formed due to the molecules of a substance moving randomly through the system
|
|
|
Osmosis
|
The diffusion of water
|
|
|
What Will Happen To An Animal Cell When Placed In Pure Water?
|
It will swell and possibly burst
|
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion
|
Works with the concentration gradient
|
|
|
Passive Transport
|
Works with the concentration gradient
|
|
|
Examples Of Passive Transport Molecules
|
Oxygen and Carbon Dioxode
|
|
|
Active Transport
|
Works independently off the concentration gradient
|
|
|
Main Source Of Energy For Active Transport
|
The hydrolysis of ATP
|

