![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is active site in enzyme? |
Area of the surface of an enzyme molecule with a shape that is complementary to the shape of the substrate molecule |
|
|
What does catalyst mean? |
Chemical that speed up the rate of a reactions and remains reusable and unchanged after the reaction |
|
|
What does extracellular mean? |
Outside the cell |
|
|
What does intracellular mean? |
Inside the cell |
|
|
What does metabolism/metabolic? |
Chemical reactions that take place inside living cells or organisms |
|
|
Why are enzymes called biological catalysts? |
Because the speed up metabolic reactions in living organisms |
|
|
The number of reactions that an enzyme molecule can catalyse per second is known as what? |
Turnover number |
|
|
Did you know? |
Enzymes do not produce unwanted by products and rarely make mistakes |
|
|
Some enzymes need what to catalyse some reactions? |
Cofactors |
|
|
The instructions for making enzymes are encoded on genes. Box the fans has a mutation that alters the sequence of amino acids in the protein. How will it affect enzyme? |
May alter the enzymes tertiary structure and prevent it from functioning |
|
|
Catabolic reactions are all catalysed by enzymes. Another type of reactions is also catalyzed by enzymes. What is it? |
Anabolic |
|
|
Anabolic reactions? |
Building up molecules and such |
|
|
Catabolic reactions? |
Breaking down molecules and such |
|
|
Catabolic reaction is catalyzed by what enzyme in stomach? |
Pepsin |
|
|
Catabolic reactions in mouth are catalysed by what enzymes in the saliva? |
Amylase |
|
|
Read!! |

|
|
|
Amylase breaks down what exactly in mouth? |
Starch into simpler sugar |
|
|
Amylase is also located somewhere other than in mouth in saliva. Where? |
Small intestine |
|
|
What three factors may have affect on rate of reaction? |
Pressure Temperature pH Enzyme concentration Substrate concentration |
|
|
What's activation energy? |
The energy that is needed to be supplied for most reactions to start |
|
|
How do enzymes reduce the activation energy required for reactions? |
They help the molecules collide successfully |
|
|
There are two hypotheses for how enzymes are able to reduce activation energy for reactions. One is lock and key hypothesis and the other one is induced fit hypothesis. Summaries the induced fit hypothesis |
It's like lock and key where the substrate has complementary shape to the active site of the enzyme so they "lock" however when the substrate leaves at the end, the enzymes active site shape changes slightly. |
|
|
Study tip |

|
|
|
Enzymes that act within cells are called what? |
Intracellular enzymes |
|
|
All enzymes are what proteins? |
Globular proteins |
|
|
Enzymes are soluble in water. True or false? |
True |
|
|
Enzyme action occurs both intracdullularly and extracellularly. Give example of intracellular |
DNA replication is an intracellular process that involved many enzymes like DNA polymerase and DNA ligase |
|
|
Enzyme action occurs both intracellularly and extracellularly. Give example of extracellular |
Digestion inolvss the extracellular action of enzymes such as pepsin and amylase |
|
|
Digestion of starch Starch polymers are first broken down by chewing which partially breaks it down to what? What enzyme then break it down even further and where else other than in mouth the enzyme is located? |
Starch is partially broken down to maltose by chewing then amylase in saliva breaks it further down. Amylase is also located in small intestine |
|
|
Describe metabolic pathway? |
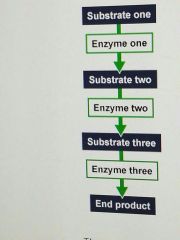
As a series of chemical reactions that start with a substrate and finish with an end product |
|
|
Example of complex metabolic pathways? |
Respiration and photosynthesis |
|
|
Digestion of proteins What enzyme that catalyzes the digestion of protein into smaller what and then what?
|
Protease catalyzes digestion of proteins into smaller peptides then amino acids |
|
|
State the type of biological molecule used to form enzymes |
Protein |
|
|
Name the monomers that form protein biological molecule |
Amino acids |
|
|
Name how the structures of proteins determine enzymes activity |
It will cause the tertiary structure of the enzyme to be specific and so the active site will be able to bind to specific substrate to catalyse reaction |
|
|
Explain how catabolism and anabolism are related to metabolism |
Catabolism is breaking down molecules
Anabolic is building up molecules = cause reaction where metabolism is the total sum of reactions occurring in body |
|

3a. Answer it |
Easy to understand representation |
|

Answer 3b |

|
|
|
Explain the meaning of the term activation energy |
Energy required to start an reaction |
|
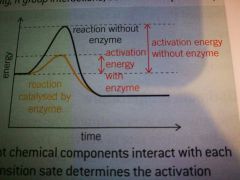
Explain the energy changes occurring resulting in the transition state model (yellow line) |
Enzymes reduce the activation energy via catalyzing the reaction as bonds are broken in the substrate therefore less energy needed later on to break the bonds as they're already broken |
|
|
Discuss why the models of enzyme action have changed over time (4 marks) |

|

