![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the order of early stages of embryonic development
|
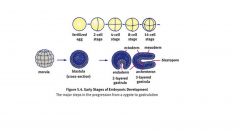
|
|
|
Mnemonic for 3 germ layers:
Ectoderm Mesoderm Endoderm |
Ectoderm = attractoderm
- Hair , nails, lens of eye, nervous system Mesoderm = Means of motion - musculoskeletal system, circulatory system, excretory system, gonads, muscular and connective tissue of digestive and respiratory system Endoderm = Enternal Organs - epithelial linings of digestive and respiratory tract, parts of liver, pancreas, thyroid, bladder, and distal urinary and reproductive tracts |
|
|
Which organ is the site where nutrient, gas and waste exchange occur between a fetus and the mother?
|
Placenta
-glucose, water, amino acids, and inorganic salts and transferred by diffusion |
|
|
Which shunt connects the right and left atria in the fetal heart?
Which shunt reroutes blood the pulmonary artery to the aorta? Which shunt reroutes blood from the liver to the inferior vena cava? |
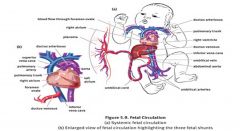
foramen ovale
ductus arteriosus ductus venosus |
|
|
Which direction does the blood flow in the umbilical arteries and veins? Which is oxygenated?
|
Umbilical arteries flow deoxygenated blood away from fetus
Umbilical veins flow oxygenated blood towards the fetus |
|
|
How many chromosomes are in human
Autosomal cells Germ Cells |
Autosomal cells: 46 chromosomes
Germ Cells: 23 Chromosomes |
|
|
Explain what happens in each stage of the cell cycle:
G1 Phase S Phase G2 Phase |
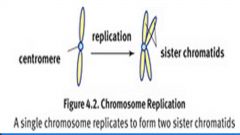
G1: Growth of organelles and size
S Phase: Genetic material replicates. Each chromosome will have 2 identical chromatids which are bound by the centromere. Note the ploidy number does not change. Still 2n, 46 chromosomes and 92 chromatids G2: Growth again to make sure there are enough cytoplasm and organelles |
|
|
Describe the stages of Mitosis
|
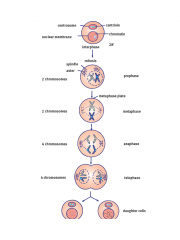
|
|
|
What are 4 types of asexual reproduction?
|
Binary Fission
Budding Regeneration Parthenogenesis |
|
|
How are the results of binary fission different than budding?
|
Binary fission results in cells of equal size.
Budding results in cells of unequal size Both however give rise to genetically identical cells. |
|
|
What is the ploidy number for organisms that reproduce via parthenogenesis?
|
Haploid because only 1 parent contributed the genetic material
|
|
|
Describe meiosis
|
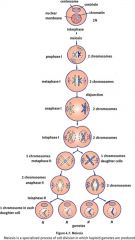
Note that crossing over occurs with homologous chromosomes, not identical sister chromatids.
|
|
|
What will happen if nondisjunction occurs during anaphase I or II?
|
One of the gametes will have extra chromosomes while the other gamete will have none.
|
|
|
What is the pathway of sperm from creation to ejaculation?
|
Seminiferous Tubules
Epididymis Vas Deferens Ejaculatory Duct Urethra Penis Note: Think SEVEN UP |
|
|
List the order of sperm maturity
|

|
|
|
Describe Oogensis
|
Primary oocytes (2n) are frozen at prophase I until menstration then it will complete meiosis I to create a secondary oocyte (n) which will be frozen at metaphase II. The zona pellucida and corona radiata form around the oocytes. Meiosis II is triggered to continue if a sperm penetrates these layers. The secondary oocyte then splits again to form an ovum (n) and polar body. End result will be 1 mature ovum and 3 polar bodies.
|

