![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
123 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Taxonomy |
Classification of organisms |
|
|
|
Plasma b cells are essential because they |
Produce antibodies that clump bacteria so macrophages can ingest them |
|
|
|
Killer t-cells do what? |
Attach directly to the cells |
|
|
|
Engulfing pathogens is the job of |
Macrophages |
|
|
|
Clotting is done by |
Platelets and other protein fibers |
|
|
|
Biome |
Ecosystem defined by climate characteristics |
|
|
|
Ecosystem |
Group of populations found in a given locality |
|
|
|
Population |
# Of species in a ecosystem |
|
|
|
Organism |
Single individual |
|
|
|
Community |
Where populations interact |
|
|
|
Biosphere |

|
|
|
|
Habitat |
Physical place where species live |
|
|
|
Niche |
The role a species play |
|
|
|
Energy cycle |
Food chain |
|
|
|
1st trophic level |
Grass |
|
|
|
2nd trophic level |
Grasshoppers |
|
|
|
Hydrologic cycle |
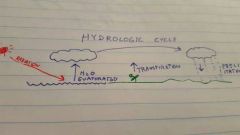
|
|
|
|
Water vapor in the air |
Greenhouse gas |
|
|
|
Nitrogen cycle |

|
|
|
|
Carbon cycle |
Photosynthesis Decomposition Calcium carbonate = limestone dissolved |
|
|
|
Phosphorus cycle |
Only found in solid form Erosion. |
|
|
|
Biome |
Ecosystem defined by climate characteristics |
|
|
|
2 basic biome's |
Terrestrial and aquatic |
|
|
|
Terrestrial biomes |
Biomes that exist on land |
|
|
|
Aquatic biomes |
Biomes in large bodies of water |
|
|
|
Biogeography |
Distribution of organisms in a location |
|
|
|
Introduced species |
Spices moved through human transportation |
|
|
|
Ethology |
How animals act and react in their environment. |
|
|
|
Behavior |
What and how an organism does. |
|
|
|
Innate behaviors |
Instincts. Stereotyped behaviors |
|
|
|
4 stereotyped/innate behaviors |
Taxes Kineses Reflexes Fixed Action Patterns |
|
|
|
Innate behavior: Taxes (taxis) |
Response to a stimulus |
|
|
|
Innate behavior: kineses |
Changes in speed of movement from reaction to a stimuli |
|
|
|
Innate behavior: reflexes |
Automatic movement of a body part |
|
|
|
Innate behavior: fixed action patterns FAP |
Complex behaviors in response to a stimulus |
|
|
|
Fixed action reflex |
Complex reaction. Releaser or sign stimulus. (Courtship,feeding) |
|
|
|
3 Learned behavior's |
Conditioning Habituation Imprinting |
|
|
|
Learned behavior: conditioning |
Applying an old response to a new stimulus. (Dog salivating) |
|
|
|
Learned behavior: Habituation |
Less and less response to a stimulus. (Cat hissing at dog) |
|
|
|
Learned behavior: Imprinting |
Behavior that developed during a critical part of life. (Geese response to mother) |
|
|
|
Altruism |
Traits that serve the society and self. |
|
|
|
Evolution is driven by |
Natural selection |
|
|
|
Darwin's book |
Origin of species (1859) |
|
|
|
Carrying capacity (K) |
Limited # of organisms an ecosystem can support. K |
|
|
|
Modern synthesys |
Evolution is a process of gradual adaptive changes |
|
|
|
Gene pool |
Collection of genes in a population |
|
|
|
Differential reproduction |
Changing of traits over time |
|
|
|
Mutation |
DNA sequence change |
|
|
|
Genetic drift |
Change in frequency of genes |
Causes a reduction in genetic variety |
|
|
Gene migration |
New genes from an immigrant organism |
Dog cross-breeding |
|
|
Hardy-weinberg and Allele Frequencies |
Random mating=same geneotype ratios and gene frequencies |
Mathematic studies of genes |
|
|
Hardy-Weinberg Law equation |
P + q = 1. P and q represent frequencies of genes |
|
|
|
Species |
Interbreeding population |
|
|
|
2 ways to produce species |
Allopatric speciation Sympatric speciation |
Speciation |
|
|
Polymorphism |
Genetic variatio |
|
|
|
Balanced polymorphism |
Keeps any one particular trait from dominating |
|
|
|
Theory: life began |
4 billionz yrz agoz |
|
|
|
Oparin hypothesis |
Earth is 4.6-bllnz yrs old Little oxygen present. More ammonia, hydrogen, methane, steam |
|
|
|
Opportunistic life strategy |
Short lifespan Short maturation High # of offspring Easily wiped out |
Dandelion |
|
|
Equilibrial life strategy |
Long life span Low maturity rate Few offspring Don't disperse |
K-selected Oak tree |
|
|
Altruistic trait |
Needs of the community over their own need |
|
|
|
Kin selection |
Altruism towards a relative |
|
|
|
The altruism trait survives through |
Kin selection |
|
|
|
Taxonomy |
Organising organisms based on genes |
|
|
|
Carolus Linnaeus' book |
Systema Naturae (1735) 1st book on taxonomy |
|
|
|
Systema Naturae |
Based taxonomic keys on morphological differences |
|
|
|
Morphological |
Study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. |
|
|
|
Linnaeus' 2 latin -based categories of organisms |
Genus Species |
Binomial nomenclature |
|
|
Genus |
class of things that have common characteristics |
|
|
|
Species |
A class of individuals having some common characteristics |
|
|
|
Genus' have |
1 or more species |
|
|
|
Humans are |
Homo sapiens Homo is the genus name Sapiens is the species name |
"Man who is wise" |
|
|
7 categories of species |
Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species |
|
|
|
Modern classification is |
Archaea Eubacteria ArchaeaEubacteriaEukaryota Eukaryota |
|
|
|
Archaea |
Prokaryotic Unique RNA |
Able to live in extreme ecosystems |
|
|
Eukaryota |
Organisms that poses eukaryotic cells |
|
|
|
Eucariota kingdoms |
Protisa Fungi ProtisaFungiAnimaliaPlantae Animalia AnimaliaPlantae Plantae |
4 kingdoms |
|
|
9 phyla in the kingdom Animalia |
1. Porifera - sponges 2. Cindaria - jellyfish 3. Plantyhelminthes - flat worms 4. Nematoda - round worms 5. Mollusca - snails,clams, squid 6. Annelida - segmented worms 7. Anthropoda - crabs, spiders 8. Echinodermata - sea stars, sand dollars 9. Chordata - fish, amphibians, reptiles,birds, mammals |
|
|
|
Vertebres |
Urochordata - tails Cephalochordata - head cord Vertebrata - backbone |
Within the phylum Chordata |
|
|
Vertebrata's 2 superclasses |
Aganatha (no jaws) Aganatha (no jaws)Gnathostomata (with jaws) Gnathostomata (with jaws) |
|
|
|
Gnathostomata 6 classes |

|
|
|
|
Antibody |
identify and neutralize pathogens such as bacteria and viruses |
Immunoglobulin |
|
|
Alelle |
Different forms of the same gene |
|
|
|
Calvin cycle |
C reaction that takes place in chloroplasts |
Occurs during photosynthesis |
|
|
Calvin cycle steps |
Grab: grabs cO2, maxes 6-carbon molecuel Split: splits the enzyme with ATP into 2 parts Leave: 3 carbons contain sugar Switch: using ATP +NADPH, the molecule is changed into a 5-carbon molecuel. REPEAT |
Grab Split Leave Switch REPEAT |
|
|
ATP |
Molecular unit of energy transfer |
Often used as a coenzyme Nucleoside triphosphate |
|
|
Enzyme |
Produced by an organism. Acts as a catalyst |
Biological catalyst |
|
|
Phosphate |
Major role in biological processes |
Inorganic Phosphorus + oxygen |
|
|
Triphosphate |
Same thing as ATP |
ATP |
|
|
Enzyme |
Macromolecular Catalyst |
Catalyst |
|
|
Oviduct |
Fertilization of the egg happens here |
Fallopian tube |
|
|
DNA strand |
CGTAGY |
|
|
|
RNA strand |
GCAUCA |
No thyme, only uracil |
|
|
Insulin |
Pulls sugars out of the blood stream |
Diabetics lack this |
|
|
Chlorophyll |
Green pigment found in plant chloroplasts and photosynthetic bacteria |
Allows photosynthesis to occur |
|
|
Chloroplast |
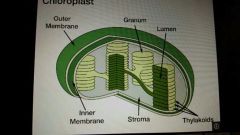
Conduct photosynthesis |
Sun |
|
|
2 phases in photosynthetic process |
Photosynthesis Calvin cycle |
|
|
|
Photosynthesis |
1. Chlorophyll absorbs light 2. Water separates into hydro, O2,and high energy elec. 3. O2 is released into the atmosphere 4. Hydrogen is grabbed until needed 5. Excited chlorophyll is used to produce ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate |
|
|
|
Calvin cycle |
6 cO2 molecules link w/hydrogen, forming glucose. Glucose forms polysaccharides |
Occors in the stroma |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Starch + sugars |
|
|
|
Chromosomes are located in |
Prokaryotes |
|
|
|
Meiosis of a diploid cell results in |
4 haploid cells |
|
|
|
Meiosis |
chromosome is reduced from tdiploid to haploid number. |
|
|
|
Fertilization |
nuclei of two gametes fuse. Chromosome haploid to diploid |
|
|
|
Process by which a zygote is formed |
Fertilization |
|
|
|
Mitosis |
Process by which the nuclei of somatic body cells divide |
|
|
|
Meiosis |
Process by which haploid cells are formed from diploid cells |
|
|
|
Reptiles |
Includes snakes |
|
|
|
Mammals |
Whales, produce milk |
|
|
|
Moist skin for gas exchange |
Bony fidh |
|
|
|
Total energy incorporated into the ecosystem is dependent on |
Total amount of photosynthesis |
|
|
|
Protein synthesis is the main function of |
Ribosome |
|
|
|
A diet deficiency in iodine will lead to |
Decreased metabolic rate |
|
|
|
Nephron's do |
Filtration |
|
|
|
Aerobic respiration of glucose occurs at a |
Lower temp |
|
|
|
What plant cell is dead at maturitt |
Xylem vessel element |
|
|
|
Phenotypic ratio of offspring is |
1 : 1 |
|
|
|
Decomposers are |
Heterotrophic |
|
|
|
Universal nature of genetic code supports the view that |
All living organisms share a common ancestor |
|
|
|
Two haploid gametes form a diploid zygote |
Fertilization |
|
|
|
Mitosis |
The division of a haploid or diploid cell into duplicate daughter cells |
|
|
|
Chromosome number is reduced in half |
Meiosis |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form 2 daughter cells. |
Cytokinesis |
Cell movement |

