![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mitosis
|
nuclear cell division within somatic cells
|
|
|
Somatic Cells
|
body cells
|
|
|
Meosis
|
also nuclear cell division but in germ cells, makes gametes
|
|
|
chromosome
|
molecules of DNA and proteins that contain genes "colored bodies"
|
|
|
gametes
|
sex cells
|
|
|
Rate of Divison for E.Coli
|
every 20 minutes
|
|
|
Rate of division for Stomach Lining
|
6 hours
|
|
|
Rate of Division for nerve and muscle cells
|
rarely to never
|
|
|
Rate of Division for liver cells
|
don't divide as adults, but if a piece gets remnoved it fixes itself
|
|
|
Rate of Divison for Skin Cells
|
2 weeks
|
|
|
Homologous Chromosomes
|
in pairs, same size, same genes, but from different parents
|
|
|
Diploid number
|
2n-body cells
pairs of chromosomes |
|
|
Haploid number
|
1n-sex cells
1 set of chromosomes |
|
|
Sister Chromatids
|
two chromatids that make up a Chromosomes
|
|
|
Chromatids
|
identical to eachother
|
|
|
Chromatin
|
uncondensed form
10,000x longer the chromosomes |
|
|
Nucleosome
|
DNA wrapped around histone protien
|
|
|
Cell cycle
|
period of time from start of one mitosis to the next
|
|
|
Phases of Cell Cycle
|
Interphase,Mitosis, Cytokinesis
|
|
|
Interphase
|
period between cell divisions, this is when most of the work is done.
(80% of cell cycle) |
|
|
Prophase
|
-Chromatin condenses into
chromosomes -nuclear membrane and nucleaus break down -centrioles move to opposite poles |
|
|
Metaphase
|
-sister chromatids attach to spindle
fibers -Chromosomes line up at the middle |
|
|
Anaphase
|
centromeres split
sisters seperate |
|
|
Telophase
|
Chromosome reach opposite ends
Chromosomes uncoil nuclear membrane & necleous reappear |
|
|
Cytokinesis
|
division of cytoplasm
|
|
|
Cytokinesis of Animal Cell
|
cleavage furrow forms-cytoplasm pinches fowards
|
|
|
Cytokinesis of Plant Cell
|
cell plate forms which later becomes the cell wall
|
|
|
Checkpoints of cell cycle
|
Checkpoint control-moniters DNA
Cell-cycle arrest- cell cycle stops untill problem repaired |
|
|
Proto-oncogenes
|
genes that promote cell division and regulate cell cycle
|
|
|
Tumour Supressors
|
genes that inhibit cell division
|
|
|
Cancer
|
cells lose abillity to control rate of division
|
|
|
Tumor
|
abnormal mass of cells that has lost control over their growth and division
|
|
|
Benigh
|
non cancerous
|
|
|
Malignant
|
cancer
|
|
|
Metasis
|
when cancer spreads to different areas of the body through the blood stream
|
|
|
Characteristics of Cancer cells
|
1)grow and divide abnormally
2)Cytoplasm/cell membrane become altered 3) cells have a weakened capacity for adhesion 4)usually have lethal effects if left untreated |
|
|
Onco-
|
greek for cancer
|
|
|
how many deaths are caused by cancers
|
20%
|
|
|
4 main types of cancer
|
Carcniomas, Sarcomas, Leukemias, lymphomas
|
|
|
most common cancer
|
protrate cancer---breast cancer
|
|
|
what happens if cancer cells are in culture
|
don't stop dividing.
|
|
|
Treatments for cancer
|
surgery, chemotherapy, raditation
|
|
|
df
|
w
|
|
|
Whatever
|
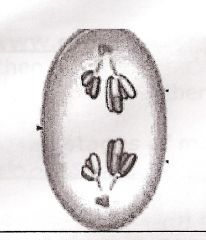
Identify drawing as to type of cell division
|
|
|
Whatever
|
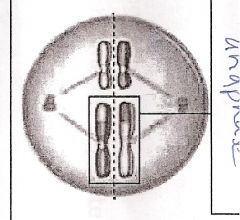
Identify drawing.
|

